5G Welding Position
Introduction
In the world of welding, precision and technique are paramount. Among the various welding positions, the 5G welding position stands out for its unique requirements and applications. But what exactly is the 5G welding position, and why is it so important? Let’s dive into the world of 5G welding and explore its intricacies.
Understanding Welding Positions
Before we get into the specifics of the 5G welding position, it’s important to have a basic understanding of welding positions in general.
Definition and Classification of Welding Positions
Welding positions refer to the orientation of the weld joint and the welder’s position while performing the weld. The American Welding Society (AWS) classifies welding positions into several types: 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and 6G. These classifications help standardize welding practices and ensure consistency across different projects.
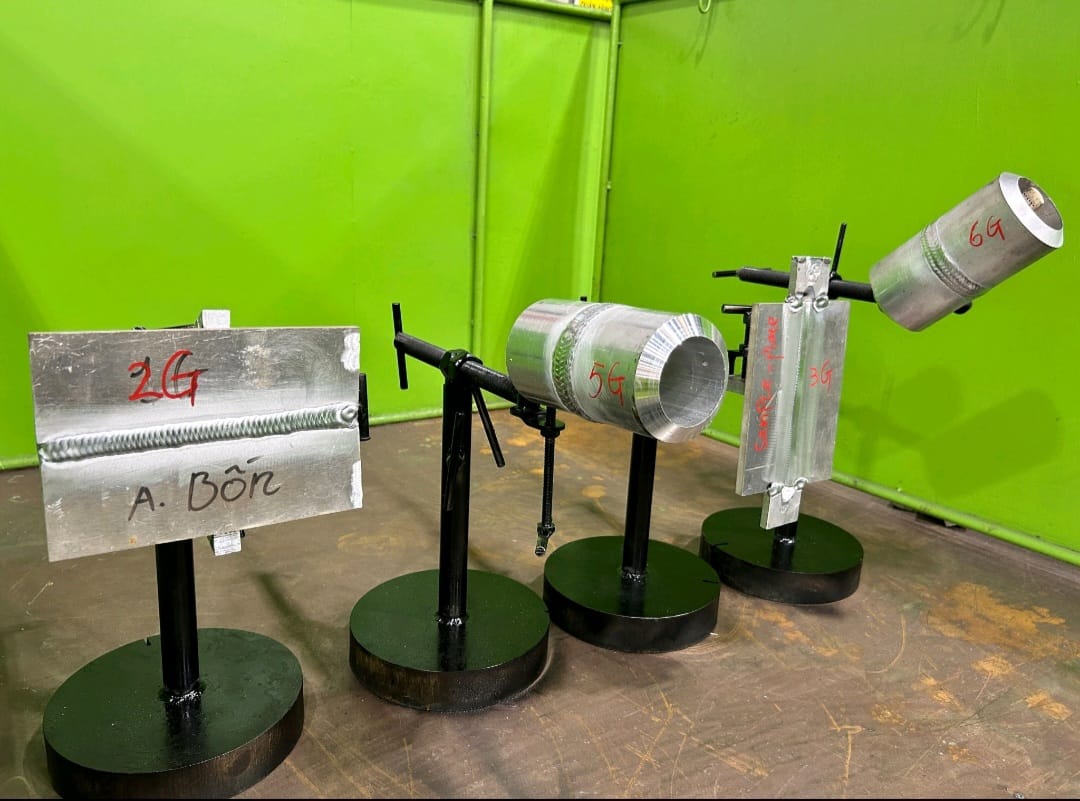

Common Welding Positions: 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and 6G
- 1G (Flat Position): The weld joint is horizontal, and the welding is performed from above the joint.
- 2G (Horizontal Position): The weld joint is vertical, and the welding is performed horizontally.
- 3G (Vertical Position): The weld joint is vertical, and the welding is performed vertically.
- 4G (Overhead Position): The weld joint is horizontal, and the welding is performed from below the joint.
- 5G (Inclined Position): The pipe is positioned horizontally, but the welding is performed around the pipe’s circumference.
- 6G (Inclined Position at 45 degrees): The pipe is positioned at a 45-degree angle, and the welding is performed around the pipe’s circumference.
Detailed Explanation of 5G Position
The 5G welding position is specifically used for welding pipes. Unlike other welding positions where the pipe may be rotated during welding, the pipe in the 5G position remains stationary. The welder must move around the pipe to perform the weld. This position is also known as the “fixed horizontal position.”
What Makes 5G Position Unique?
Unlike flat or vertical welding, the 5G position requires welders to adapt to changing orientations as they work around the pipe. This dynamic environment makes it a challenging yet rewarding position to master.
Applications of 5G Welding Position
The 5G welding position is commonly used in industries where pipe welding is crucial, such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing. The ability to weld pipes in a fixed position is essential for maintaining the integrity of pipelines and ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Advantages of 5G Position
The 5G welding position offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in many industrial applications.
Improved Welding Quality
The 5G position allows for better control over the welding process, resulting in higher quality welds. The stationary pipe provides a stable welding environment, reducing the risk of defects.
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
Welding in the 5G position can be more efficient than other positions, as it eliminates the need to rotate the pipe. This can save time and increase productivity, especially in large-scale projects.
Versatility in Various Welding Tasks
The 5G welding position is versatile and can be used for a variety of welding tasks. Whether it’s welding pipelines, structural components, or pressure vessels, the 5G position is adaptable to different welding requirements.
Challenges in 5G Position
Despite its advantages, the 5G welding position comes with its own set of challenges.
Difficulty in Maintaining Consistency
Maintaining a consistent weld around the entire circumference of the pipe can be challenging, especially for less experienced welders.
Requirement of Skilled Welders
The 5G position demands a high level of skill and experience, making it less accessible for beginners.
Equipment and Setup Challenges
Setting up the equipment for 5G welding can be more complex compared to other positions, requiring careful planning and execution.
Techniques for Mastering 5G Position
Mastering the 5G welding position takes practice and dedication. Here are some techniques to help welders improve their skills.
Training and Certification Programs
Participating in training and certification programs is essential for mastering the 5G welding position. These programs provide hands-on experience and instruction from experienced professionals.
Tips and Tricks for Welders
- Consistent Speed: Maintain a consistent welding speed to ensure even welds.
- Proper Positioning: Position yourself comfortably to reduce fatigue and improve control.
- Use of Supports: Utilize supports to stabilize yourself while welding around the pipe.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Inconsistent Speed: Avoid varying your speed, as this can lead to uneven welds.
- Poor Preparation: Ensure the pipe is properly cleaned and prepared before welding.
- Ignoring Safety Protocols: Always follow safety protocols to prevent accidents and injuries.
Tools and Equipment for 5G Welding
Having the right tools and equipment is crucial for successful 5G welding.
Essential Tools for 5G Welding
Basic tools include welding machines, electrodes, and protective gear. A good understanding of these tools is essential for any welder.
Advanced Equipment for Enhanced Efficiency
Advanced equipment like automated welding systems and precision clamps can significantly improve the efficiency and quality of 5G welds.
Safety Precautions in 5G Welding
Safety should always be a top priority in welding, and the 5G position is no exception.
Importance of Safety Gear
Welders should always wear appropriate safety gear, including helmets, gloves, and protective clothing.
Common Safety Hazards and How to Avoid Them
Common hazards include exposure to harmful fumes, electrical shocks, and burns. Proper ventilation, grounding of equipment, and careful handling can mitigate these risks.
Comparing 5G with Other Positions
Understanding how the 5G welding position compares to other positions can help welders choose the right approach for their projects.
5G vs. 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, and 6G
- 5G vs. 1G: 5G is used for fixed pipes, while 1G is for flat welding.
- 5G vs. 2G: 2G involves horizontal welding on vertical joints, whereas 5G involves welding around a stationary pipe.
- 5G vs. 3G: 3G is for vertical joints, while 5G is for horizontal pipes.
- 5G vs. 4G: 4G is overhead welding, whereas 5G is horizontal.
- 5G vs. 6G: 6G involves welding at a 45-degree angle, making it more challenging than 5G.
Suitability for Different Welding Projects
The 5G welding position is ideal for projects involving large pipelines or fixed pipes. It provides stability and control, which are crucial for high-quality welds.
Equipment and Tools for 5G Position
Having the right equipment and tools is essential for successful 5G welding.
Essential Welding Equipment
- Welding Machine: A reliable welding machine with adjustable settings.
- Protective Gear: Welding helmet, gloves, and protective clothing.
- Clamps and Fixtures: To secure the pipe in place.
Recommended Tools and Accessories
- Welding Rods: Choose the right type of welding rods for the material being welded.
- Grinder: For preparing and finishing the weld.
- Measuring Tools: To ensure precise alignment and positioning.
Maintenance and Care of Welding Tools
Regular maintenance and care of welding tools are crucial for ensuring their longevity and performance. Clean and inspect tools regularly, and replace any worn or damaged parts.
FAQs
What is a 5G welding position?
The 5G welding position involves welding a pipe that is fixed horizontally, requiring the welder to move around the pipe and adapt to different orientations.
How does 5G welding compare to 6G welding?
5G welding is similar to 6G welding but does not involve a 45-degree angle. Both positions require high skill levels and offer unique challenges and benefits.
What are the key skills required for 5G welding?
Key skills include precision, consistency, and the ability to adapt to different angles. Experience and proper training are also crucial.
Can beginners start with 5G welding?
While beginners can learn 5G welding, it is recommended to gain experience in simpler positions first before tackling the complexities of 5G.
What industries primarily use 5G welding?
Industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing commonly use 5G welding due to its ability to produce strong, reliable welds in fixed pipes.
Conclusion
The 5G welding position is a crucial aspect of modern welding practices, offering numerous advantages in terms of quality, efficiency, and versatility. While it presents certain challenges, mastering this position can open up a world of opportunities for welders. By understanding the intricacies of the 5G welding position and staying updated with industry advancements, welders can ensure they remain at the forefront of their field.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders