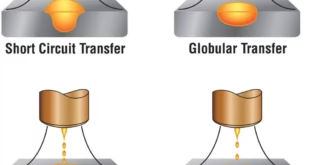
Spray vs Short-Circuit vs Pulsed MIG What Are MIG Transfer Modes? MIG transfer modes describe how molten filler metal moves from the wire electrode into the weld pool during MIG (GMAW) welding. The selected transfer mode directly affects: Heat input Penetration Spatter Bead appearance Welding position capability The three main …
Read More »BackStep Technique for Tig Welding
BackStep Technique for Tig Welding Thin Metal TIG welding thin metal demands a surgeon’s touch: tight control of heat input, steady hand movements, and a welding sequence that prevents the plate from becoming a warped pancake. The backstep technique is a proven method to limit longitudinal distortion in thin-sheet TIG …
Read More »Welding Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Welding Super Duplex Stainless Steel Super duplex stainless steels (SDSS) sit at the high-performance end of stainless metallurgy: they pair very high strength with excellent resistance to localized corrosion (pitting and crevice) in chloride-bearing environments. Because of that combination they’re widely used in aggressive process environments — think oil & …
Read More »Globular Transfer
Globular Transfer in MIG Welding Globular transfer is one of the classic metal-transfer modes encountered in Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), commonly called MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding when inert gases are used. It sits between short-circuiting transfer and spray transfer in both behavior and effects: the molten wire forms …
Read More »Carbon Steel Welding Electrodes
Carbon Steel Welding Electrodes – A Complete Guide When it comes to welding carbon steel, the choice of electrode can make the difference between a flawless weld and one riddled with defects. Carbon steel is the most widely used steel type in manufacturing, construction, and repair because of its strength, …
Read More »Wind Tower Welding
Wind Tower Welding and Fabrication Process Role of Wind Towers in Renewable Energy Wind towers are the backbone of wind turbines, enabling the conversion of wind energy into clean electrical power. These tall, cylindrical structures elevate the turbine blades to heights where wind speeds are higher and more consistent, ensuring …
Read More »Arc Stability and Proper Fusion in GMAW
Arc Stability and Proper Fusion in GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding) What Is GMAW and Why Is Arc Stability Important? Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), commonly known as MIG welding, is one of the most widely used arc welding processes today. Its appeal lies in its speed, versatility, and ease …
Read More »Hydrostatic Testing
Hydrostatic Testing of Fabricated Piping What Is Hydrostatic Testing? Hydrostatic testing is a non-destructive pressure test used to verify the strength and leak-tightness of fabricated piping systems. The procedure involves filling the piping with a liquid—most commonly water—pressurizing it to a value above the design pressure, and observing it for …
Read More »Piping Fabrication Tolerances
Piping Fabrication Tolerances: Standards, Practices, and Control In any industrial piping system—whether in oil refineries, chemical plants, or power stations—the term “tolerance” holds critical importance. It’s not just about precision; it’s about ensuring that every pipe, flange, and fitting lines up perfectly to form a leak-proof, structurally sound system. What …
Read More »Brazing Copper
Brazing Copper: Techniques, Alloys, and Best Practices Brazing copper is a vital joining method used across multiple industries, including HVAC, plumbing, automotive, and electrical systems. It offers a reliable way to bond copper components using a filler metal without melting the base metal. This process allows manufacturers and fabricators to …
Read More » Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders