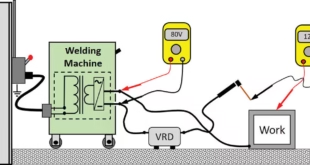
Introduction
Welding is a critical process in various industries, from construction to manufacturing. However, alongside the benefits of welding, there are inherent risks, particularly when it comes to electrical safety. Welding involves the use of high electrical currents, which can pose serious hazards if not properly managed. In this article, we’ll delve deep into the realm of electrical safety in welding, providing valuable insights, tips, and guidelines to ensure a secure working environment.
Electrical Safety in Welding: A Vital Concern
Welding operations often require high currents to generate the heat necessary for fusing metal components. This demand for electrical power can lead to potential safety hazards, including electric shock, fires, and damage to equipment. By implementing stringent safety measures and adhering to best practices, workers can carry out welding tasks with confidence and minimize the associated risks.

Electrical Safety Measures
Electrical safety is paramount in welding, and several measures must be implemented to protect welders and maintain a secure work environment. Here are key electrical safety measures in welding:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Insulated Gloves
- Purpose: Insulated gloves protect welders from electrical shock by providing a barrier between their hands and live electrical parts or equipment.
- Selection: Welders should choose gloves specifically designed for electrical work, ensuring they are properly insulated and in good condition.
- Flame-Resistant Clothing
- Purpose: Flame-resistant clothing shields welders from sparks, splatter, and flames generated during welding. It also protects against burns from contact with hot surfaces.
- Materials: Flame-resistant clothing is typically made from materials like treated cotton, Nomex, or Kevlar, which resist ignition and provide thermal insulation.
- Full Coverage: Welders should wear flame-resistant jackets, pants, and aprons, with long sleeves and legs to ensure complete protection.
Safe Work Practices
- Proper Training and Certification
- Training: Welders should undergo comprehensive training programs to understand the equipment, safety procedures, and welding techniques. Certification ensures that they are qualified to perform welding tasks safely.
- Continuous Learning: Welders should stay updated with industry standards and safety practices through ongoing education and training.
- Keeping Work Areas Dry and Clean
- Importance: Water and moisture can increase the risk of electric shock. Therefore, it’s crucial to keep welding work areas dry and free from puddles.
- Cleaning: Regularly cleaning work areas helps prevent slips, trips, and falls, and ensures that equipment and cables are free from debris that could compromise electrical safety.
- Maintaining Equipment
- Inspections: Regular inspections of welding equipment, cables, and connectors are necessary to identify and address any wear, damage, or defects that could compromise electrical safety.
- Repair and Replacement: Faulty equipment or components should be repaired or replaced promptly to prevent accidents or equipment failure during welding.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
- Purpose: Lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures are essential for de-energizing and securing equipment before maintenance or repair work. This prevents unexpected electrical starts or discharges.
- Training: Welders and maintenance personnel should be trained in LOTO procedures and use locks and tags to isolate equipment from power sources.
Emergency Response Planning
- First Aid and CPR Training
- Skills: Welders and personnel should undergo first aid and CPR training to provide immediate assistance in case of injuries, electrical shocks, or other emergencies.
- First Aid Kits: First aid kits equipped with essential supplies should be readily available in the welding area.
- Fire Extinguishers and Firefighting Equipment
- Fire Prevention: Welding areas should be equipped with appropriate fire extinguishers and firefighting equipment to combat fires caused by sparks, hot metal, or flammable materials.
- Emergency Response Plan: Establishing an emergency response plan that includes evacuation procedures and designated assembly points is crucial for swift and organized responses to emergencies.
Grounding and Bonding
Grounding and bonding are fundamental electrical safety practices in welding that help mitigate electrical hazards and ensure safe working conditions. Here’s an overview of these critical aspects:
Importance of Grounding
- Safety: Grounding is essential to prevent electric shock and reduce the risk of electrical accidents, including arc flash incidents.
- Stability: Grounding provides a stable reference point for electrical circuits, ensuring consistent and safe current flow.
- Equipment Protection: Proper grounding helps protect equipment and welding machines from electrical faults and voltage surges.
Grounding Techniques
- Grounding Electrode Systems
- Components: Grounding electrode systems include grounding electrodes, such as rods or plates, that are securely connected to the earth.
- Function: These systems provide a low-resistance path for electrical currents to dissipate harmlessly into the ground, preventing the buildup of electric charge.
- Proper Installation: Grounding electrodes must be installed according to industry standards and kept in good condition. Periodic inspections ensure their effectiveness.
- Equipment Grounding
- Equipment Connection: Welding equipment, electrode holders, and other conductive components must be properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks and arc flash hazards.
- Grounding Conductors: Welding cables often include an equipment grounding conductor, ensuring a reliable path for fault currents to flow safely to ground.
- Resistance Testing: Regularly testing the resistance of equipment grounding conductors helps ensure they remain effective.
Bonding of Conductive Materials
- Purpose: Bonding involves connecting conductive materials and equipment to prevent differences in electrical potential. This prevents electrical sparks, shocks, and potential fires.
- Examples: Bonding can include connecting metal workpieces to welding tables or bonding metallic containers to prevent static electricity buildup.
- Static Discharge: Proper bonding can prevent dangerous static discharge in areas where flammable gases or materials are present.
Testing and Maintenance of Grounding and Bonding Systems
- Regular Inspection: Periodic inspections of grounding and bonding systems are crucial to identify wear, corrosion, or damage that could compromise their effectiveness.
- Resistance Testing: Testing the resistance of grounding conductors ensures that they provide a low-resistance path to ground.
- Repairs and Upkeep: Any damaged or corroded grounding or bonding components should be repaired or replaced promptly to maintain electrical safety.
- Documentation: Keep records of inspections, tests, and maintenance activities to ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations.
Electrical Codes and Regulations
Compliance with electrical codes and regulations is a critical aspect of ensuring electrical safety in welding operations. Here’s an exploration of the relevant standards and guidelines:
Overview of Relevant Standards and Regulations
- Purpose: Standards and regulations in welding are established to protect workers, the public, and property from electrical hazards, ensuring that welding operations are conducted safely and in compliance with recognized industry practices.
- Consistency: These standards and regulations provide a consistent framework for welding safety across industries, facilitating safe practices and equipment use.
- Global Perspective: While some standards are specific to certain regions, organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American Welding Society (AWS) have developed international guidelines to promote safety and quality in welding.
National Electrical Code (NEC) and Welding
- NEC Overview: The National Electrical Code (NEC), also known as NFPA 70, is a widely adopted electrical safety code in the United States. It sets the standard for safe electrical installation and operation across various industries.
- Relevance to Welding: The NEC contains specific sections and articles that pertain to welding safety. Welding equipment, electrical supply, and grounding requirements are covered in these sections.
- Equipment Design: The NEC provides guidelines for the design and installation of welding equipment to prevent electrical hazards, such as electric shock and arc flash.
- Workplace Wiring: It addresses the wiring and electrical supply infrastructure in welding workplaces, emphasizing proper grounding and bonding techniques.
- Regular Updates: The NEC is regularly updated to incorporate the latest safety practices and technological advancements, ensuring that welding operations remain safe and up-to-date.
OSHA Guidelines for Welding Electrical Safety
- OSHA’s Role: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States sets and enforces workplace safety regulations, including those related to welding electrical safety.
- Welding Safety Standard: OSHA has specific regulations related to welding, including 29 CFR 1910.252, which covers welding, cutting, and brazing. It addresses various aspects of welding safety, including electrical safety.
- Key Provisions: OSHA regulations require employers to provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), ensure safe working conditions, conduct hazard assessments, and implement training programs for welders and other personnel involved in welding operations.
- Compliance and Inspections: OSHA conducts inspections to ensure compliance with safety regulations. Non-compliance can result in penalties and fines.
- Continuous Improvement: OSHA regulations are designed to encourage continuous improvement in workplace safety, including electrical safety in welding operations.
Future Trends and Technologies
The field of welding continues to evolve, with a focus on enhancing electrical safety. Here are some anticipated future trends and technologies in welding safety:
Advancements in Electrical Safety Equipment
- Smart Helmets: Helmets equipped with augmented reality (AR) displays and sensors will provide welders with real-time information, including potential electrical hazards and equipment status.
- Wireless Monitoring: Wireless sensors and connectivity will allow for remote monitoring of equipment, enabling early detection of electrical issues and potential hazards.
- Advanced Insulation Materials: Ongoing research into advanced materials will result in better-insulated gloves, clothing, and equipment, further reducing the risk of electric shock and arc flash incidents.
- Enhanced PPE: Personal protective equipment will become more technologically advanced, with features such as built-in communication systems and integrated safety sensors.
Integration of Automation and Safety Systems
- Robotic Welding: Increased integration of robots in welding operations will improve precision and reduce the need for human intervention, minimizing exposure to electrical hazards.
- Machine Learning and AI: Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms will be used to analyze data from welding processes and identify potential safety issues in real-time.
- Safety Interlocks: Automation systems will include safety interlocks that prevent welding equipment from operating if safety conditions, such as proper grounding, are not met.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance systems will become more sophisticated, using data analytics to anticipate equipment failures and prevent electrical hazards.
Industry Initiatives and Research in Welding Safety
- Research Collaborations: Industry stakeholders, academic institutions, and government agencies will collaborate on research projects to develop innovative safety solutions for welding.
- Safety Standards Enhancement: Organizations like the AWS and OSHA will continue to update and improve safety standards to reflect advancements in technology and knowledge.
- Workplace Safety Culture: Companies will place a stronger emphasis on fostering a culture of safety, with regular safety training and open communication about potential hazards.
- Green Welding Technologies: Research into environmentally friendly welding processes will focus on reducing hazardous emissions and waste, contributing to overall workplace safety.
Case Studies and Examples
Examining real-life incidents, learning from accidents, and highlighting successful implementations of safety measures can provide valuable insights into the importance of electrical safety in welding operations.
Real-life incidents Related to Electrical Safety in Welding
- Electric Shock Incident: In a manufacturing facility, a welder suffered an electric shock while using a poorly maintained welding machine. The incident highlighted the critical need for regular equipment inspections and maintenance to prevent electrical hazards.
- Arc Flash Incident: During a welding operation in a confined space, an uncontrolled arc flash occurred, resulting in severe burns to a welder. The incident emphasized the importance of proper safety protocols, including confined space entry procedures and adequate protective gear.
- Fire in Welding Workshop: In a welding workshop, a fire erupted due to sparks igniting nearby flammable materials. The incident underscored the necessity of effective fire prevention measures, such as keeping the work area clear of combustibles and having firefighting equipment readily available.
Lessons Learned from Accidents
- Preventative Maintenance: Regular maintenance and inspections of welding equipment and electrical systems are crucial to identifying and addressing potential hazards before accidents occur.
- Training and Education: Adequate training and certification of welders are essential to ensure they understand the risks associated with welding operations and can respond effectively to emergencies.
- Proper Risk Assessment: Comprehensive hazard assessments should be conducted to identify and mitigate electrical hazards specific to each welding task or environment.
- Continuous Improvement: Accidents should be thoroughly investigated, and lessons learned should be integrated into safety programs to continuously improve electrical safety measures.
Successful Implementations of Safety Measures
- Improved Equipment Design: A manufacturing company invested in modern welding machines with advanced safety features, including built-in arc fault protection and ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), reducing the risk of electrical incidents.
- Training and Certification Program: A welding school implemented a rigorous training and certification program for its students, focusing on electrical safety. As a result, graduates were well-prepared to work safely in various welding environments.
- Emergency Response Plan: A fabrication shop developed a comprehensive emergency response plan that included regular drills and training for employees. When an arc flash incident occurred, the well-prepared response minimized injuries and equipment damage.
- Continuous Monitoring: A construction company introduced a system for continuous monitoring of welding equipment and electrical systems. This proactive approach allowed them to identify and address potential issues before they could escalate into hazards.
FAQ’s
Is welding without proper ventilation dangerous?
Yes, welding without proper ventilation can be hazardous. Welding produces fumes and gases that contain harmful substances, including metal oxides and shielding gases. Inhaling these fumes can lead to respiratory issues and long-term health problems. Adequate ventilation helps minimize the concentration of these fumes, ensuring a safer work environment.
How does electrical shock occur during welding?
Electrical shock in welding can occur when a welder comes into contact with live electrical parts or conducts electricity through their body. This can happen if the welding machine is not properly grounded, if there are faulty cables, or if the workpiece is not adequately insulated. Proper grounding, isolation, and the use of appropriate PPE can prevent electrical shock.
Why is it important to inspect welding equipment before starting work?
Inspecting welding equipment before starting work is crucial to identify any potential hazards or defects. Damaged cables, worn-out connectors, or faulty machinery can lead to accidents, fires, and injuries. Regular equipment inspections and maintenance ensure that welding operations are carried out safely and efficiently.
What is the role of personal protective equipment (PPE) in welding safety?
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in welding safety by providing a physical barrier between the welder and potential hazards. PPE such as flame-resistant clothing, welding helmets, gloves, and safety glasses protect welders from sparks, intense light, and heat. Properly selected and worn PPE enhances worker safety and reduces the risk of injuries.
How can I prevent fires during welding?
To prevent fires during welding, several measures should be taken. Clear the work area of flammable materials, use fire-resistant barriers, and keep fire extinguishers readily available. Additionally, maintain proper ventilation to dissipate heat and gases. Adhering to fire safety protocols and practicing fire prevention techniques significantly reduces the risk of fires.
Why is training essential for welding safety?
Training is essential for welding safety because it equips workers with the knowledge and skills to identify and mitigate potential hazards. Properly trained welders understand how to operate equipment safely, recognize dangerous situations, and respond effectively in emergencies. Training enhances overall workplace safety and reduces the likelihood of accidents.
Conclusion
Prioritizing electrical safety in welding is a responsibility that cannot be understated. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure a secure working environment, protect personnel from harm, and preserve valuable equipment. Remember that electrical safety is a collective effort that requires continuous education, adherence to protocols, and a commitment to best practices.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders