What is Forge Welding
Definition of forge welding
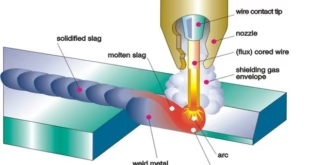
Forge welding is a metalworking technique that uses heat and pressure to join two pieces of metal together. It is one of the oldest and most traditional methods of welding and is commonly used to create strong and durable joints in metal fabrication. In forge welding, the metal pieces are heated in a forge or furnace until they reach the proper temperature for welding. The metal is then placed together and external pressure is applied, typically with a hammer, to fuse the metal pieces together. The pressure and heat work together to create a strong bond between the metal pieces. The final step is to cool and hammer the weld to create a strong bond. It’s important to note that flux is usually applied to protect the metal from oxidation and impurities that can weaken the weld.

Importance of forge welding in metalworking
Forge welding is an important method of welding in metalworking for a few reasons:
High strength
Forge welding produces a strong and durable weld that can withstand high temperatures and heavy loads. This makes it ideal for applications such as construction, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery.
Versatility
Forge welding can be used to weld a variety of metals, including steel and iron. This makes it a versatile option for a wide range of metalworking projects.
Traditional method
Forge welding is a traditional method of welding that has been used for centuries. It is still used today in many fields, especially blacksmithing and other artisanal works.
Manual skills
Forge welding requires a high level of manual skill and precision. This makes it a valuable skill for metalworkers to learn, as it allows them to create high-quality, custom-made products.
Joint design
Forge welding allows for a wide range of joint designs, including lap joints, T-joints, and corner joints. This allows for greater design flexibility and can help to improve the strength and durability of the finished product.
Low-Cost
Forge welding is a low-cost method of welding as it does not require any special equipment or power source other than a forge or heat source, an anvil, hammer, tongs and filler material.
Materials and Equipment
Materials:
Steel or iron for the pieces to be welded
The pieces to be welded should be made of steel or iron, as these materials are able to withstand the high temperatures required for forge welding. The pieces should be clean and free of rust, oil, or other contaminants.
Steel or iron for the welding rod or filler material
The welding rod or filler material should be made of steel or iron as well, and should be of the same or similar composition as the pieces to be welded. This will ensure a strong and durable weld. The welding rod or filler material can be in the form of a rod, wire, or powder.
Flux (such as borax or silica)
Flux is a material that is applied to the pieces before welding to help remove impurities and protect the metal from oxidation. Borax and silica are common types of flux used in forge welding.
Equipment:
- Forge or heat source
A forge is a furnace that is used to heat metal for shaping, forging or welding. A gas or coal forge is the two most common types of forge used for forge welding. The forge should be able to reach temperatures of at least 2,500°F (1,371°C) for steel and 1,800°F (982°C) for iron, so that the metal can be heated to the appropriate temperature for welding.
- Anvil
An anvil is a large, heavy metal block that is used as a surface for hammering and shaping metal. An anvil is necessary for forge welding as it provides a sturdy surface to work on and it allows the welder to hammer and shape the metal as it is being heated.
- Hammer
A hammer is used to shape and forge the metal as it is being heated. A hammer with a rounded face is ideal for forge welding as it allows the welder to shape the metal without causing cracks or warping.
- Tongs
Tongs are used to hold the metal as it is being heated in the forge, and to remove it from the forge once it has reached the appropriate temperature for welding.
- Protective gear
Forge welding requires the use of protective gear such as gloves and safety glasses to protect the welder from the intense heat and flying sparks.
Optional equipment:
- Welding clamp or vise
A welding clamp or vise can be used to hold the pieces in place while they are being welded, ensuring a proper alignment and a strong weld.
- Chipping hammer or wire brush
A chipping hammer or wire brush can be used to clean the pieces before welding, removing any rust, oil, or other contaminants that could weaken the weld.
- Quenching container
A quenching container is used to cool the welded pieces after welding. This can be in the form of a water bucket or oil bath. This is important to harden the metal and also to prevent cracking.
Preparation
Preparing a welding forge for forge welding involves several steps to ensure that the metal is heated to the appropriate temperature and that the work area is safe and ready for welding.
- Clear the work area of any debris or materials that could be a fire hazard. Make sure that the forge and anvil are clean and free of rust, oil, or other contaminants.
- Mix the flux (such as borax or silica) with water to create a paste. This paste will be applied to the metal before welding to help remove impurities and protect the metal from oxidation.
- Turn on the forge and allow it to heat up to the appropriate temperature for the type of metal being welded. For steel, the forge should reach temperatures of at least 2,500°F (1,371°C) and for iron, it should reach at least 1,800°F (982°C).
- Clean the metal pieces to be welded using a chipping hammer or wire brush to remove any rust, oil, or other contaminants that could weaken the weld. Apply the flux paste to the metal using a brush or your hand.
- If using a welding clamp or vise, align the metal pieces in the clamp or vise to ensure that they are properly aligned for welding. If not using a clamp or vise, align the metal pieces on the anvil to ensure proper alignment.
- Using tongs, carefully insert the metal into the forge and allow it to heat up to the appropriate temperature. The metal should be heated until it is a dull red color, indicating that it is at the proper temperature for welding.
- Before starting the welding process, put on protective gear such as gloves and safety glasses to protect yourself from the intense heat and flying sparks.
- Using tongs, carefully remove the metal from the forge and place it on the anvil.
By following these steps, the welding forge will be properly prepared for forge welding, ensuring a strong and durable weld.
Welding Process
Forge welding is a process in which two or more pieces of steel or iron are heated and then hammered together to create a weld. The process involves several steps, including preparing the materials, heating the metal, and welding the pieces together.
1-Preparation
Before starting the forge welding process, the materials should be cleaned and prepared. This includes removing any rust, oil, or other contaminants from the pieces to be welded, as well as ensuring that the pieces are of the same or similar composition. The welder should also prepare the flux, which will be applied to the pieces before welding.
2-Heating
The pieces to be welded are placed in a forge or heat source and heated to the appropriate temperature for the type of metal being used. For steel, the temperature should be at least 2,500°F (1,371°C), while for iron the temperature should be at least 1,800°F (982°C). The metal is heated until it reaches a bright orange or yellow color, indicating that it is at the correct temperature for welding.
3-Applying flux
Once the metal is heated, the welder applies flux to the pieces. The flux helps remove impurities and protect the metal from oxidation, which can weaken the weld.
4-Welding
The welder uses tongs to remove the heated metal from the forge and places it on the anvil. The welder then hammers the pieces together, shaping and forging the metal as it cools. The welder should use a hammer with a rounded face to avoid causing cracks or warping in the metal.
5-Cooling
After the metal has been welded, it needs to be cooled. This can be done by placing the welded pieces in a quenching container, such as a water bucket or oil bath, which will rapidly cool the metal and harden it. This also helps to prevent cracking.
6-Cleaning and Finishing
After the metal has cooled, the welder should remove any excess flux and clean the welded pieces. The welder can use a chipping hammer or wire brush to remove any slag and smooth out the weld. The welder can also use a file or grinder to remove any imperfections.
Forge welding is a skilled and demanding process, and it takes a lot of practice and experience to master. Safety is also very important, as the high temperatures, flying sparks, and hammering can be dangerous. It is important to wear protective gear such as gloves and safety glasses and to follow proper safety guidelines.
Post-Welding
Post-welding steps are an important part of the forge welding process, as they help to ensure the quality and strength of the weld. These steps include:
1-After the welding is complete, the pieces must be cooled down slowly to prevent cracking or warping. This can be done by placing the pieces in a quenching container, such as a water bucket or oil bath. The cooling rate should be slow enough to avoid thermal shock, which can cause cracking.
2-Once the pieces have cooled, the weld should be cleaned of any flux or slag that may have accumulated during the welding process. This can be done using a chipping hammer or wire brush. It is important to remove any impurities as they can weaken the weld.
3-The weld should be inspected for any defects such as cracks, porosity, or lack of fusion. These defects can weaken the weld and reduce its overall strength. If any defects are found, the weld may need to be redone.
4-After the cleaning and inspection, the welded pieces may need to be reshaped to achieve the desired final shape. This can be done using a hammer and anvil.
5- To relieve the internal stress caused by the welding process that can lead to cracking, the welded pieces should be heated up to a lower temperature than the critical temperature, then cooled down.
6-To increase the strength and hardness of the weld, the welded pieces may be heat treated. This can be done by heating the pieces to a high temperature and then quenching them in a liquid or gas, depending on the desired properties.
It is important to note that post-welding steps will vary depending on the type of steel and the application of the welded piece. It is always best to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or industry standards for the specific post-welding steps required for a particular project.
FAQs
Are forge welds strong?
Forge welding is a method of welding in which the metal is heated until it becomes malleable, and then pressure is applied to fuse the two pieces together. When done properly, forge welds can be very strong. They can be stronger than base metals and can be used to join dissimilar metals. However, the strength of a forge weld depends on many factors, including the quality of the metal, the skill of the welder, and the conditions under which the welding is done.
What steel is best for forge?
The best steel for forging depends on the intended use and desired properties of the finished product.
1045 steel is a popular choice for forging as it has good machinability and can be heat treated to increase its strength.
4340 steel is also often used for forging as it has excellent strength and toughness properties and can be heat treated to increase its hardness.
Other options include 5160, 6150, and O1.
Ultimately, the best steel for forging will depend on the specific application and desired properties of the finished product. It’s best to consult with a professional or conduct further research to determine the best steel for your specific project.
What is the raw material for forging?
The raw material for forging is typically a piece of steel in the form of a billet, bar, or bloom. Billets and bars are usually rectangular or round in shape and are usually smaller than blooms. Blooms are generally larger and more massive and are often used for more significant or complex forgings.
Other materials can also be used for forging such as aluminum, titanium, and even copper and brass. Each material has its own properties and characteristics that need to be taken into account when choosing the best material for a specific forging project.
The choice of raw material will depend on the specific application and desired properties of the finished product.
Which metal Cannot be forged?
Can all metals be forged?
Most metals can be forged, but some are more difficult to work with than others. Forging is a process that involves shaping metal using compressive forces, typically with hammering or pressing. Metals that are relatively soft and ductile, such as gold, silver, copper, and aluminum, can be easily forged. Harder metals, such as steel and titanium, can also be forged, but they require more specialized equipment and greater skill. Some metals, such as mercury, cannot be forged because they are in a liquid state at room temperature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, forge welding is a traditional method of welding that is still widely used in metalworking today. It is known for its high strength and durability, making it ideal for applications such as construction, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery. The method is versatile as it can be used to weld a variety of metals, including steel and iron. It is also cost-effective and requires only a minimal set of equipment. Forge welding requires a high level of manual skill and precision, making it a valuable skill for metalworkers to learn. It offers a wide range of joint designs and can help to improve the strength and durability of the finished product. With its many benefits and traditional use, forge welding is a valuable method of welding in the metalworking industry.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders