Atomic Hydrogen Welding
Introduction
Atomic Hydrogen Welding (AHW) is a highly specialized welding method that uses an atomic hydrogen torch to produce a high-temperature flame for welding. This process was first introduced in the early 20th century and has since been used in a variety of industries for welding materials that are challenging to work with using traditional welding methods. Compared to other welding processes, AHW is known for its high precision and speed, making it an attractive option for a range of applications. Despite its benefits, the process also has limitations, including a limited range of materials that can be welded and the need for specialized equipment. Nevertheless, Atomic Hydrogen Welding remains an important welding method for those who require precise and efficient welding of certain materials.

The Welding Process
Description of the Process
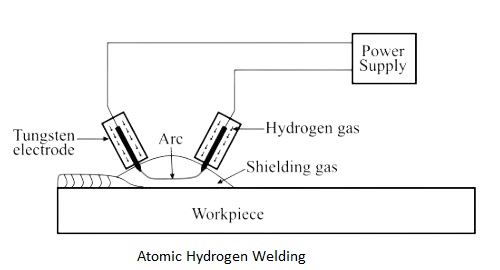
Atomic Hydrogen Welding involves the use of a hydrogen torch that produces a high-temperature flame for welding. The process works by dissociating molecular hydrogen into atomic hydrogen, which then reacts with the metal being welded to create a highly concentrated heat source. This intense heat source is what allows for precise and efficient welding of certain materials.
Advantages of Using Atomic Hydrogen Welding
One of the biggest advantages of using Atomic Hydrogen Welding is its high precision and speed, making it an attractive option for a range of applications. The process is also known for producing high-quality welds with minimal distortion, making it ideal for use on sensitive or intricate materials.
Limitations of the Process
Despite its many benefits, Atomic Hydrogen Welding has a number of limitations that should be considered. One of the main limitations is that the process is only suitable for a limited range of materials, including certain metals and alloys. Additionally, the specialized equipment required for AHW can be expensive and difficult to maintain, making it less accessible for some users. Furthermore, the process can be dangerous due to the high temperatures involved, and proper safety measures must always be taken.
Equipment for Atomic hydrogen welding
Atomic hydrogen welding equipment typically consists of the following:
Hydrogen torch: to generate and control the flow of hydrogen gas.
Power source: to generate the electrical energy needed for the welding process.
Regulators: to control the pressure and flow of hydrogen gas.
Cooling system: to cool the welding torch and prevent overheating.
Shielding gas: to protect the welding area from oxidation and other contaminants.
Welding wire: to provide filler material for the weld.
Welding helmet: to protect the welder’s face and eyes from the bright light produced during the welding process.
These are the basic components of an AHW system. However, the specific equipment used may vary depending on the type of welding being performed and the materials being joined.
Working of Atomic hydrogen welding
Atomic hydrogen welding (AHW) is a welding process that uses hydrogen gas as the shielding and cooling medium to produce high-quality, high-strength welds. It works by passing an electric current through two electrodes that form the ends of the material to be welded. The hydrogen atoms produced by the process combine to form molecular hydrogen, which acts as a shield against atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen, reducing oxidation and nitrogen absorption. The process is typically used for welding high-alloy and dissimilar metals, as well as for welding metals with low melting points, such as aluminum and magnesium.
Applications
- Atomic Hydrogen Welding is used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. The process is particularly useful for welding materials that are challenging to work with using traditional welding methods, such as those with high melting points or those that are brittle or prone to cracking.
- AHW is suitable for a limited range of materials, including certain metals and alloys. Some of the most common materials that can be welded using this process include tungsten, molybdenum, and tantalum.
- Atomic Hydrogen Welding has been used in a number of successful applications, including the welding of titanium alloys for aerospace components and the welding of medical implant materials such as stainless steel and cobalt-chrome. The process has also been used in the electronics industry for welding components such as transistors and diodes. These are just a few examples of the many applications of Atomic Hydrogen Welding and demonstrate its versatility as a welding method.
Advantages of Atomic Hydrogen Welding
- High welding speed: Atomic hydrogen welding can be performed at a high speed, reducing the overall welding time and increasing efficiency.
- High precision: The narrow and concentrated arc of atomic hydrogen welding results in a high level of precision and control over the welding process.
- Minimal heat affected zone: The welding process creates a minimal heat-affected zone, reducing the risk of warping or other heat-related deformations in the metal.
- No filler material needed: Unlike other welding processes, atomic hydrogen welding does not require the use of filler materials, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Versatile: Atomic hydrogen welding can be used to weld a wide range of metals, including those that are difficult to weld with traditional methods.
- Minimal fumes and smoke: The welding process generates minimal fumes and smoke, making it a safer and more environmentally friendly process.
Disadvantages of Atomic Hydrogen Welding
- High temperature: Atomic hydrogen welding requires high temperatures, which can result in warping or distortion of the metal being welded.
- Equipment cost: The equipment required for atomic hydrogen welding is expensive and can be difficult to obtain.
- Limited use: The process is limited to welding certain types of metals, such as steel and iron, and is not suitable for welding other materials like aluminum or copper.
- Hazardous gases: The process generates hazardous gases, such as hydrogen and carbon monoxide, that must be carefully controlled and ventilated.
- Complexity: Atomic hydrogen welding is a complex process that requires skilled operators and specialized training.
- Time-consuming: The process is time-consuming and requires a longer welding time compared to other welding methods.
Safety Concerns
Hazards associated with the welding process
The high temperatures involved in Atomic Hydrogen Welding can present a number of safety hazards, including the risk of fire and explosion. Additionally, the use of hydrogen gas as a fuel source presents a risk of asphyxiation, and the intense heat produced by the welding process can cause burns or other injuries.
Measures taken to ensure safety
To minimize the risks associated with Atomic Hydrogen Welding, it is important to follow strict safety protocols. This may include the use of personal protective equipment, such as protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection. In addition, proper ventilation should be provided to ensure that dangerous gases are not inhaled.
Personal Protective Equipment
The use of personal protective equipment is critical for ensuring the safety of the welder during the Atomic Hydrogen Welding process. This may include protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection, as well as respiratory protection if necessary. In addition, it is important to follow all safety guidelines provided by the equipment manufacturer and to undergo proper training before using the equipment. By taking these precautions, the risk of injury or harm can be greatly reduced.
FAQs
What is the importance of atomic hydrogen in welding process?
Importance of atomic hydrogen in welding process: Atomic hydrogen is important in the welding process because it provides a highly concentrated heat source that is capable of welding certain materials that are challenging to work with using traditional welding methods. By dissociating molecular hydrogen into atomic hydrogen, a high-temperature flame is produced that is able to reach extremely high temperatures and efficiently weld the materials.
What is the power source for atomic hydrogen welding?
Power source for atomic hydrogen welding: The power source for Atomic Hydrogen Welding is typically a direct current power supply, which is used to provide the energy needed to dissociate molecular hydrogen into atomic hydrogen.
What is the benefit of hydrogen welding?
Benefit of hydrogen welding: One of the benefits of hydrogen welding is its high precision and speed, making it an attractive option for a range of applications. The process is also known for producing high-quality welds with minimal distortion, making it ideal for use on sensitive or intricate materials.
What is atomic hydrogen welding electrodes have long life?
Long life of atomic hydrogen welding electrodes: The electrodes used in Atomic Hydrogen Welding can have a long life due to the high temperatures involved in the welding process, which can help to reduce the amount of electrode wear.
Why is hydrogen a problem in welds?
Hydrogen as a problem in welds: Hydrogen can be a problem in welds because it can cause porosity or cracking in the weld. This can occur if the hydrogen is absorbed into the metal being welded or if it is present in the atmosphere during the welding process.
What equipment is used in atomic hydrogen welding?
Equipment used in atomic hydrogen welding: The main piece of equipment used in Atomic Hydrogen Welding is the hydrogen torch, which is a specialized device that can dissociate molecular hydrogen into atomic hydrogen. Other equipment may include a power source, hoses, and gas tanks.
What is heat affected zone in atomic hydrogen welding?
Heat affected zone in atomic hydrogen welding: The heat affected zone (HAZ) in Atomic Hydrogen Welding refers to the portion of the material that is affected by the heat of the welding process, but not melted. The size of the HAZ can have a significant impact on the quality and integrity of the weld.
What are the applications of atomic hydrogen?
Applications of atomic hydrogen: Atomic hydrogen has a number of applications, including use as a fuel source, in spectroscopy, and in the production of semiconductors. In welding, atomic hydrogen is used as a heat source in the Atomic Hydrogen Welding process.
What is the temperature of atomic hydrogen torch?
Temperature of atomic hydrogen torch: The temperature of an atomic hydrogen torch can reach extremely high temperatures, typically in the range of 6,000 to 8,000 Kelvin (10,340 to 13,340°F). The exact temperature will depend on the materials being welded, the type of hydrogen torch being used, and the power source being used.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Atomic Hydrogen Welding is a highly specialized welding method that has a number of benefits, including high precision and speed, and the ability to produce high-quality welds with minimal distortion. Despite its limitations, including a limited range of materials that can be welded and the need for specialized equipment, the process remains an important welding method for those who require precise and efficient welding of certain materials. Safety is also a critical consideration when using Atomic Hydrogen Welding, and strict safety protocols should be followed to minimize the risk of injury or harm. Overall, Atomic Hydrogen Welding is a versatile and useful welding method that has a wide range of applications in industries such as aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders