Automated Welding Systems
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced industrial world, automation has become a game-changer, revolutionizing the way we approach various tasks, and welding is no exception. Automated welding systems have rapidly gained popularity in the welding industry, offering enhanced precision, speed, and consistency. But what exactly are automated welding systems, and why are they so crucial in modern manufacturing? This article will delve deep into the world of automated welding, exploring its various types, advantages, challenges, and future trends.
What are Automated Welding Systems?
Automated welding systems are advanced setups that use machinery, software, and robotics to perform welding tasks with minimal human intervention. These systems are designed to execute welding processes with a high degree of accuracy and consistency, making them ideal for large-scale production environments where uniformity and speed are critical. The key components of an automated welding system typically include a welding power source, a welding robot or manipulator, a controller, and various sensors to monitor the welding process.
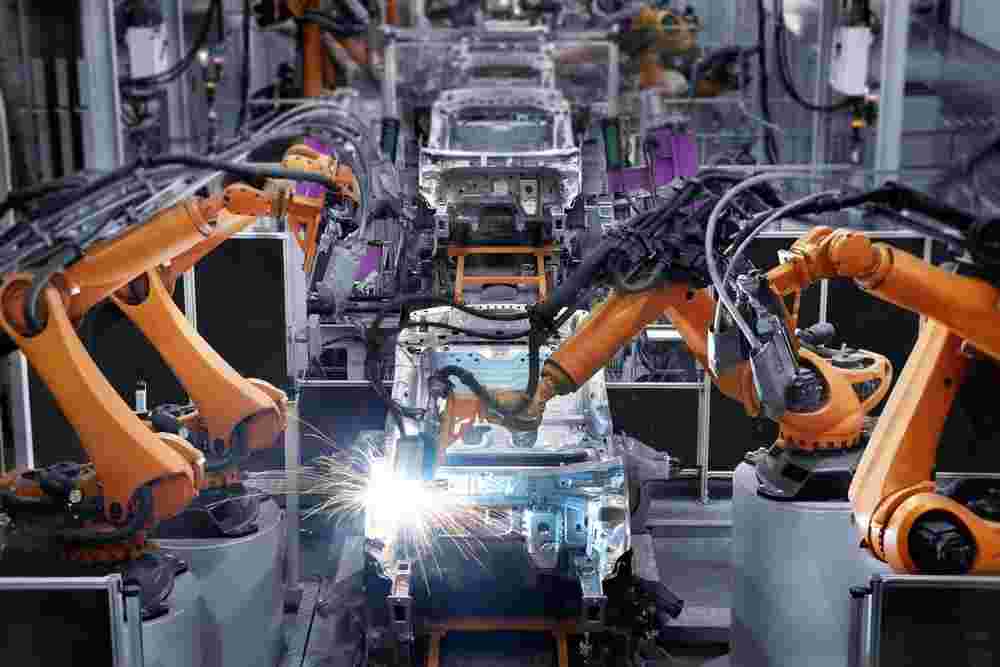
The Evolution of Welding: From Manual to Automated
Welding has come a long way from its early days of manual operation. Initially, welding was a labor-intensive process, requiring skilled workers to perform precise tasks by hand. As technology advanced, the industry saw the introduction of semi-automated systems, which still required significant human oversight. The real breakthrough came with the development of fully automated welding systems, which allowed for the complete automation of the welding process. This transition not only increased efficiency but also opened up new possibilities for complex and large-scale welding projects.
Types of Automated Welding Systems
Automated welding systems come in various forms, each suited to different applications and industries.
Fixed Automation Systems
Fixed automation systems, also known as hard automation, are designed for high-volume production runs. These systems are typically customized for specific welding tasks and are best suited for repetitive welding operations. The primary advantage of fixed automation systems is their ability to produce consistent, high-quality welds at a rapid pace. However, their lack of flexibility can be a drawback when different welding tasks are required.
Flexible Automation Systems
Flexible automation systems offer greater versatility compared to fixed automation. These systems can be easily reprogrammed to handle different welding tasks, making them ideal for industries that require a high degree of customization. Flexible automation systems are particularly useful in low to medium-volume production runs where the welding requirements frequently change.
Robotic Welding Systems
Robotic welding systems represent the pinnacle of welding automation. These systems use robotic arms equipped with welding tools to perform highly precise and complex welding tasks. Robotic welding is commonly used in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision and consistency are paramount. The robots can be programmed to perform a wide range of welding techniques, including MIG, TIG, and spot welding, making them extremely versatile.
How Automated Welding Systems Work
Automated welding systems rely heavily on advanced software and programming to control the welding process. The system’s controller is programmed with specific welding parameters, such as speed, voltage, and amperage, which the robot or manipulator follows precisely. Sensors are integrated into the system to monitor the welding process in real-time, providing feedback to ensure that the welds meet the required quality standards. This level of automation minimizes the risk of human error and ensures that each weld is performed with consistent accuracy.
Advantages of Automated Welding Systems
The benefits of automated welding systems are numerous, making them an attractive option for many industries.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Automated welding systems can perform tasks much faster than human welders, significantly boosting production rates. They can operate 24/7 without fatigue, leading to higher output.
- Improved Weld Quality and Consistency: Automation ensures that each weld is performed to the same high standard, reducing the likelihood of defects and rework.
- Cost Savings and Reduced Labor Requirements: While the initial investment in automated welding systems can be high, the long-term savings in labor costs and increased productivity often justify the expense.
- Enhanced Safety for Welders: By automating the welding process, workers are exposed to fewer hazards, such as harmful fumes, sparks, and the risk of burns.
Challenges of Automated Welding Systems
Despite their advantages, automated welding systems are not without their challenges.
- High Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs: The upfront cost of purchasing and installing automated welding systems can be prohibitive for some businesses. Additionally, ongoing maintenance is required to keep the systems running smoothly.
- Complexity in Setup and Operation: Setting up an automated welding system requires specialized knowledge and expertise, which can be a barrier for some companies.
- Limited Flexibility for Certain Welding Tasks: While automated systems excel in high-volume production, they may not be as effective for smaller, customized projects where flexibility is essential.
- Dependence on Skilled Technicians: Automated systems require skilled technicians to program and maintain them, which can add to operational costs.
Applications of Automated Welding Systems
Automated welding systems are widely used across various industries due to their versatility and efficiency.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, automated welding systems are essential for assembling vehicle frames and components. The high precision and speed of robotic welding systems make them ideal for producing the millions of welds required in car manufacturing.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies on automated welding systems to produce critical components with high precision. The consistency and quality of robotic welding are crucial in ensuring the safety and reliability of aerospace parts.
Construction and Infrastructure
Automated welding systems are used in the construction of large structures, such as bridges and buildings, where consistent weld quality is vital. These systems can handle the heavy-duty welding tasks required in construction projects.
Shipbuilding and Marine Industry
In the shipbuilding industry, automated welding systems are used to weld large sections of ships, ensuring strong and durable joints. The ability to perform complex welding tasks with high precision is essential in this industry.
Future Trends in Automated Welding Systems
As technology continues to evolve, so too will automated welding systems. Several trends are shaping the future of this field.
- Advancements in Robotic Welding Technology: Continued improvements in robotic technology will make automated welding systems even more efficient and capable of handling more complex tasks.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Welding: AI and machine learning will play a significant role in optimizing welding processes, making them more adaptable and efficient.
- The Role of Industry 4.0 and IoT in Automated Welding: The integration of automated welding systems with Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable real-time monitoring and data analysis, further enhancing the efficiency of welding operations.
- The Future of Automated Welding in Various Industries: As industries continue to embrace automation, the demand for automated welding systems is expected to grow, with new applications emerging in areas such as renewable energy and advanced manufacturing.
FAQs
What are the main types of automated welding systems?
The main types of automated welding systems include fixed automation systems, flexible automation systems, and robotic welding systems. Fixed systems are designed for high-volume, repetitive tasks, flexible systems offer versatility for various tasks, and robotic systems are highly precise, suitable for complex welding operations.
How does automated welding improve safety in the workplace?
Automated welding improves safety by reducing human exposure to hazardous conditions like intense heat, harmful fumes, and ultraviolet radiation. Since robots or machines handle the actual welding process, the risk of injuries such as burns or inhalation of toxic substances is significantly reduced.
Can automated welding systems be used for all types of welding?
While automated welding systems are versatile and can handle many types of welding, they are most commonly used for processes like MIG, TIG, and spot welding. However, some highly specialized or intricate welding tasks may still require manual intervention or advanced programming to automate effectively.
What industries benefit the most from automated welding systems?
Industries that benefit the most from automated welding systems include automotive, aerospace, construction, shipbuilding, and heavy manufacturing. These sectors often require high-volume production, precise welds, and consistent quality, all of which automated welding systems excel at providing.
How is AI influencing the future of automated welding?
AI is revolutionizing automated welding by enabling systems to learn and adapt to different welding conditions in real-time. With machine learning algorithms, welding robots can optimize their operations, improve accuracy, and even predict potential issues before they occur. This integration of AI enhances efficiency and opens up new possibilities for automated welding in more complex applications.
Conclusion
Automated welding systems are transforming the welding industry, offering unparalleled efficiency, precision, and safety. As technology continues to advance, these systems will become even more integral to manufacturing processes across various industries. While there are challenges associated with implementing automated welding systems, the benefits they offer make them a worthwhile investment for many companies. The future of welding is undoubtedly automated, and those who embrace this technology will be well-positioned to lead in their respective fields.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders



