Pipe Welding Positions
Introduction
Understanding pipe welding positions is crucial for any welder aiming for proficiency and excellence. These positions dictate the approach, technique, and ultimately the quality of the weld. In this article, we will explore the various pipe welding positions, their applications, and tips for mastering them.
What are Pipe Welding Positions?
Pipe welding positions refer to the various orientations in which a welder might work on a pipe. These positions are standardized to ensure consistency and quality across different projects and industries. Understanding these positions is essential as they affect the welding technique and the final outcome.
Types of Pipe Welding Positions
Pipe welding positions are categorized based on the orientation of the pipe and the direction of the weld. Understanding these positions helps welders choose the right techniques and equipment to ensure high-quality welds. Here’s a detailed explanation of the main types of pipe welding positions:
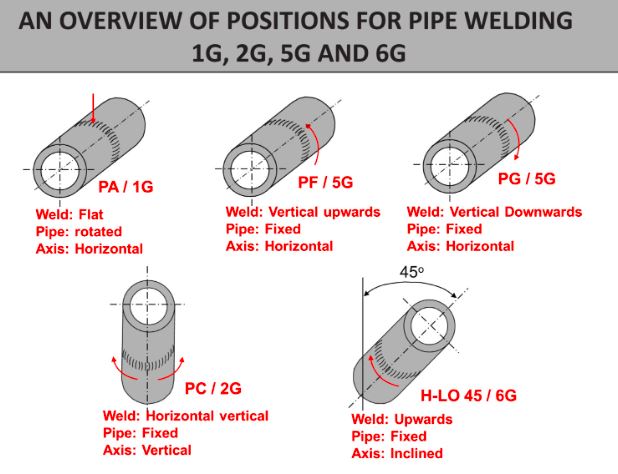
PA/1G Position
The PA/1G position, or flat position, is the simplest pipe welding position. The pipe is placed horizontally, and the welder performs the weld on the top side of the pipe.
Description:
- The pipe is fixed horizontally.
- The welder works from above the pipe.
- The weld is performed on the top side of the pipe.
Applications and Benefits:
- Commonly used for straightforward projects.
- Easier to control the weld pool, making it ideal for beginners.
- Provides a stable working environment.
PC/2G Position
The PC/2G position is a horizontal position where the pipe is placed vertically, and the welder works on the side of the pipe.
Description:
- The pipe is fixed vertically.
- The weld is performed horizontally around the pipe’s circumference.
- The welder must manage gravity’s effect on the molten weld pool.
Applications and Benefits:
- Frequently used in structural and piping systems.
- Offers good penetration and fusion.
- Requires more skill than the 1G position due to the horizontal welding direction.
PF/5G Position
In the PF/5G position, the pipe is placed horizontally, and the welder works around the circumference of the pipe. This position requires welding in multiple orientations, including overhead, vertical, and horizontal.
Description:
- The pipe is fixed horizontally.
- Welding occurs around the entire circumference of the pipe.
- Welders must adapt to changing positions as they move around the pipe.
Applications and Benefits:
- Widely used in pipeline construction.
- Ensures consistent weld quality around the entire pipe.
- Challenges the welder to maintain uniform welds in different orientations.
PG/5G Position
The PG/5G position is similar to the PF/5G position but focuses on vertical welding. The pipe is positioned horizontally, and the welding is performed vertically.
Description:
- The pipe is fixed horizontally.
- Welding is done vertically, often in an upward direction.
- Gravity affects the weld pool, adding complexity to the process.
Applications and Benefits:
- Essential for specific vertical welding applications.
- Requires precision and control to manage the molten weld pool.
- Often used in situations where vertical joints are required.
H-LO 45/6G Position
The H-LO 45/6G position is one of the most challenging and advanced pipe welding positions. The pipe is fixed at a 45-degree angle, and the welder must perform the weld in various orientations.
Description:
- The pipe is set at a 45-degree angle.
- The weld is performed around the entire circumference of the pipe.
- The welder must manage multiple orientations, including overhead, vertical, and horizontal positions.
Applications and Benefits:
- Critical for high-pressure systems and complex projects.
- Demonstrates a high level of welding skill and proficiency.
- Often used for certification and testing purposes due to its difficulty.
Special Position: 6GR Position
The 6GR position is a variant of the 6G position but includes a restriction ring, adding another layer of difficulty. This position is primarily used for testing and certifying welders.
Description:
- Similar to the 6G position with a 45-degree angled pipe.
- A restriction ring is added near the weld joint.
- Requires welders to demonstrate advanced welding skills under restricted conditions.
Applications and Benefits:
- Used for certification and testing of welders.
- Ensures welders can perform high-quality welds under difficult conditions.
- Demonstrates proficiency in handling restricted access to the weld area.
How to Choose the Right Welding Position
Choosing the right welding position depends on several factors, including the project’s requirements, the welder’s skill level, and the specific application. It’s essential to match the position with the job to ensure quality and efficiency.
Techniques for Mastering Pipe Welding Positions
Tips for Beginners
- Start with the 1G position to build foundational skills.
- Practice regularly to improve hand-eye coordination.
- Learn to adjust settings based on the welding position.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Maintaining a steady hand in awkward positions.
- Ensuring consistent weld quality.
- Overcoming visibility issues.
Tools and Equipment for Pipe Welding
Must-Have Tools
- Welding helmet with auto-darkening feature.
- High-quality welding machine.
- Clamps and fixtures to hold pipes in place.
Advanced Equipment for Professionals
- Pipe stands and rollers.
- Orbital welding machines for precision.
- Inspection tools for quality control.
FAQs
What is the most challenging pipe welding position?
The 6G position is often considered the most challenging due to the need to weld around a pipe set at a 45-degree angle.
How long does it take to master pipe welding positions?
The time required varies, but with consistent practice and proper training, it can take several months to a few years.
Are there any shortcuts to learning pipe welding positions?
There are no shortcuts; mastering pipe welding positions requires practice, patience, and dedication.
What are the common mistakes in pipe welding?
Common mistakes include poor alignment, inadequate penetration, and inconsistent weld quality.
How can I improve my pipe welding skills quickly?
Regular practice, taking advanced training courses, and learning from experienced welders can help improve your skills quickly.
How does pipe size affect welding position?
Larger pipes may require different welding positions to ensure proper weld penetration and ease of handling during the welding process.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering different pipe welding positions is essential for any welder. These positions not only affect the technique but also the quality and integrity of the weld. Continuous practice, proper training, and adherence to safety measures are key to becoming proficient in pipe welding.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders