Weld Overlay: Enhancing Performance and Durability
Weld overlay is a versatile process widely used in various industries to enhance the performance and durability of engineering components. This article provides an in-depth exploration of weld overlay, its applications, techniques, advantages, challenges, and future trends.
Introduction to Weld Overlay
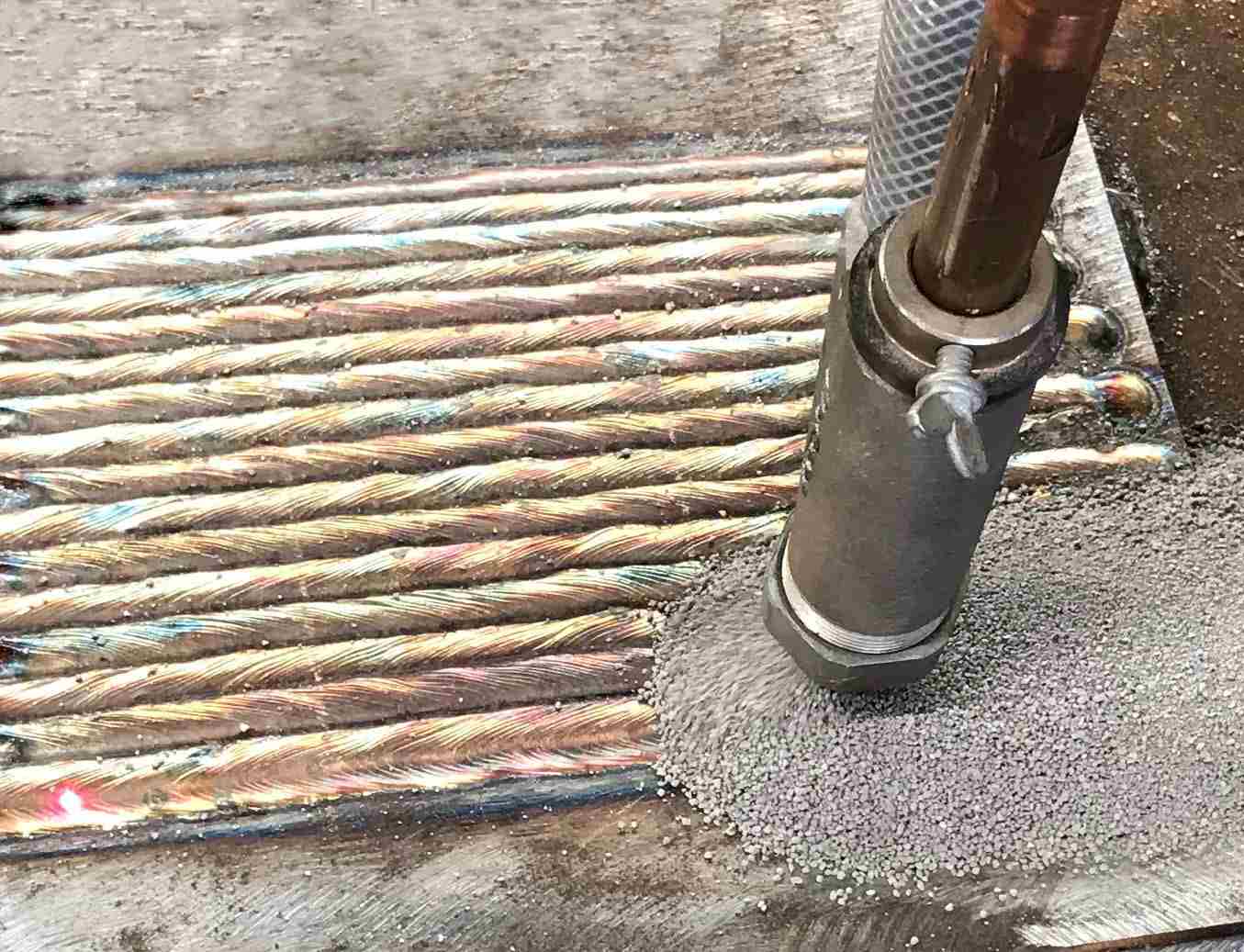
Weld overlay, also known as cladding or hardfacing, involves depositing a layer of material onto the surface of a substrate to improve its properties. This process is commonly employed to enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and mechanical properties of components subjected to harsh operating conditions.
Understanding the Process
What is Weld Overlay?
Weld overlay is a welding technique used to apply a protective or functional layer onto the surface of a substrate. The overlay material can be chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, such as resistance to corrosion, erosion, or abrasion.
How Does Weld Overlay Work?
In weld overlay, a heat source, typically an electric arc, is used to melt the overlay material, which is then deposited onto the substrate surface. The molten overlay material solidifies to form a bonded layer, providing the desired properties to the substrate.
Applications of Weld Overlay
Weld overlay finds extensive applications across various industries, including:
Corrosion Resistance
In corrosive environments, weld overlay can protect metal components from chemical degradation, extending their service life.
Wear Resistance
Components subjected to abrasive wear, such as mining equipment and industrial machinery, can benefit from weld overlay to increase their wear resistance and durability.
Repair and Restoration
Weld overlay is also used for repairing and restoring worn or damaged components, offering a cost-effective alternative to replacement.
Materials Used in Weld Overlay
Base Materials
The substrate material onto which the overlay is deposited plays a crucial role in determining the performance of the final component.
Overlay Materials
A wide range of overlay materials are available, including stainless steel, nickel-based alloys, and hardfacing alloys, each chosen for its specific properties and application requirements.
Types of Weld Overlay Techniques
Several welding processes can be utilized for weld overlay, including:
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
SAW involves feeding a continuous wire electrode and flux onto the workpiece, creating a submerged arc that melts the base metal and overlay material.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
GTAW, also known as TIG welding, utilizes a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce a high-quality weld with precise control over heat input.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
FCAW uses a continuously fed consumable electrode with a flux core, providing higher deposition rates compared to GTAW.
Advantages of Weld Overlay
Cost-Effectiveness
Weld overlay offers a cost-effective solution for improving the performance of components without the need for complete replacement.
Versatility
The versatility of weld overlay allows for customization of material composition and thickness to meet specific application requirements.
Enhanced Performance
By imparting superior properties to the substrate, weld overlay enhances component performance and extends service life.
Challenges and Considerations
Thermal Stresses
The difference in thermal expansion coefficients between the base metal and overlay material can lead to residual stresses, affecting the integrity of the weld.
Material Compatibility
Selecting compatible base and overlay materials is essential to prevent issues such as intergranular corrosion and cracking.
Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation, including cleaning and preheating, is critical to ensure good adhesion and quality of the overlay.
Quality Control and Inspection
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
NDT techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiography are used to detect defects and ensure the integrity of weld overlay.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is performed to assess weld quality, including surface finish, penetration, and alignment.
Dimensional Checks
Dimensional checks verify the thickness and uniformity of the overlay layer to meet design specifications.
FAQs
What industries commonly use weld overlay?
Weld overlay is prevalent in industries like oil and gas, power generation, mining, and aerospace due to its ability to enhance durability in harsh environments.
How does weld overlay compare to other surface protection methods?
Weld overlay forms a metallurgical bond with the base metal, offering superior adhesion and durability compared to thermal spray coatings or mechanical cladding.
What factors influence the selection of overlay materials?
Factors such as operating environment, mechanical properties needed, corrosion and wear resistance, cost, and compatibility with the base metal influence material selection.
Are there any limitations to the thickness of the overlay layer?
Excessive thickness can lead to issues like increased residual stresses, distortion, and higher production costs, so it’s essential to balance thickness for optimal performance.
What advancements can we expect in weld overlay technology in the coming years?
Advancements may include improved overlay materials, welding processes, automation, and eco-friendly techniques to enhance efficiency, quality, and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
Weld overlay is a highly effective technique for enhancing the performance and durability of engineering components in various industries. By understanding the process, materials, techniques, and challenges associated with weld overlay, engineers and manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize component performance and prolong service life.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders