Weld Slope and Rotation
Introduction
Welding is an art, a craft, and a science all rolled into one. Among the many factors that contribute to a successful weld, the concepts of weld slope and rotation often go unnoticed, yet they play a pivotal role in determining the quality and strength of the weld. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting, understanding how weld slope and rotation influence your work can make all the difference between a flawless weld and one that needs a redo. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what weld slope and rotation are, why they matter, and how you can master them to achieve the best possible results.
Understanding Weld Slope
What is Weld Slope?
Weld slope refers to the gradual increase or decrease in welding current as you progress through the weld. Imagine it as the “ramp” that controls the power flow to the arc as you start and finish a weld. This control is crucial, especially in processes like TIG and MIG welding, where precision is key.
The Role of Weld Slope in Welding
The weld slope affects everything from the arc stability to the amount of spatter you produce. A well-controlled slope ensures that the arc starts smoothly without a sudden burst of energy that can blow through your material. It also helps in tapering off the current at the end of the weld, preventing crater cracks and other end-of-weld defects.
Types of Weld Slopes
There are two main types of weld slopes: positive and negative. Each type has its own set of applications and benefits.
Positive Slope
In a positive slope, the current gradually increases as you progress through the weld. This is useful in applications where you need to start with a lower current to prevent burn-through and then increase it as the material heats up.
Negative Slope
Conversely, a negative slope means the current decreases over the course of the weld. This can be beneficial in situations where you want to start with a higher current to establish a strong arc and then taper it down to avoid overheating the material.
How to Adjust Weld Slope in Different Welding Processes
Adjusting the weld slope is usually done via the settings on your welding machine. Modern machines often allow for precise control over the slope, with options to set the starting and ending current levels and the duration over which the change occurs. Whether you’re using MIG, TIG, or stick welding, understanding how to tweak these settings can greatly enhance your weld quality.
Understanding Weld Rotation
What is Weld Rotation?
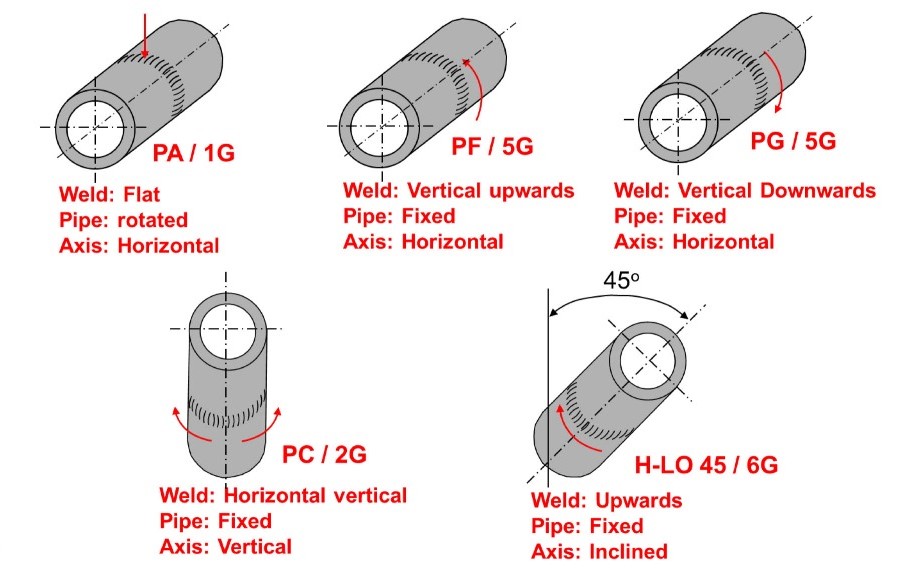
Weld rotation refers to the movement or rotation of the workpiece or the welding head around the axis during the welding process. This is particularly relevant in automated and robotic welding systems, where the rotation can be precisely controlled to achieve consistent welds.
The Role of Weld Rotation in Welding
Weld rotation plays a critical role in ensuring even heat distribution and penetration. When welding cylindrical objects or complex shapes, rotating the workpiece allows the weld to be applied evenly, avoiding areas of excessive heat buildup that could lead to warping or other defects.
Types of Weld Rotation
There are two primary types of weld rotation: fixed and variable.
Fixed Rotation
Fixed rotation means the workpiece rotates at a constant speed throughout the welding process. This is ideal for simpler jobs where consistent heat application is required.
Variable Rotation
Variable rotation allows the speed of rotation to change during the weld. This is useful in more complex welds, where different sections of the workpiece may require different levels of heat input.
How to Control Weld Rotation for Optimal Results
Controlling weld rotation involves both mechanical and software adjustments. In automated systems, you can program the rotation speed and pattern to match the specific requirements of your weld. For manual systems, careful setup and consistent monitoring are key to ensuring the rotation is aiding, rather than hindering, your weld quality.
Interplay Between Weld Slope and Rotation
How Weld Slope and Rotation Work Together
Weld slope and rotation are not isolated factors; they work together to influence the overall quality of the weld. The slope controls the arc energy, while the rotation manages the distribution of that energy across the workpiece. When both are properly synchronized, they produce a weld that is not only strong but also visually appealing.
Impact on Weld Quality
The combined effect of slope and rotation can significantly impact the penetration, bead profile, and overall integrity of the weld. For instance, an incorrect slope setting with improper rotation can lead to uneven welds, incomplete fusion, or excessive spatter. On the other hand, a well-tuned slope and rotation can minimize defects and improve the overall aesthetic of the weld.
Common Issues and Solutions
One common issue is the misalignment between the slope and rotation, leading to problems like undercutting or excessive reinforcement. To solve this, ensure that your machine settings are calibrated correctly and consider running test welds to fine-tune the parameters before starting the actual job.
Practical Applications of Weld Slope and Rotation
Applications in Different Welding Techniques
MIG Welding
In MIG welding, weld slope and rotation can help in controlling spatter and ensuring a smooth, even weld bead. The slope helps in adjusting the arc length and stability, while rotation aids in uniform bead formation.
TIG Welding
TIG welding benefits from precise control over both slope and rotation. The slope ensures a clean start and finish, while rotation can help in achieving consistent penetration, especially in circumferential welds.
Stick Welding
Although less commonly discussed in stick welding, controlling the slope can help in managing heat input, while rotation can be critical when welding pipes or round structures.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Consider a scenario in pipeline welding where weld rotation is critical. A controlled slope and rotation can ensure the weld penetrates uniformly, preventing weak points in the pipeline that could lead to failures under pressure. Another example could be in automotive manufacturing, where precision welds are needed on rotating parts to ensure both strength and aesthetic quality.
Adjusting Weld Slope and Rotation for Different Materials
Material-Specific Considerations
Different materials react differently to heat and weld energy, making it essential to adjust the slope and rotation accordingly.
Welding Steel
When welding steel, a positive slope can help in penetrating thicker sections, while a steady rotation ensures even heat distribution.
Welding Aluminum
Aluminum, being more sensitive to heat, benefits from a negative slope to reduce the risk of burn-through, and careful rotation to prevent warping.
Welding Exotic Alloys
Exotic alloys often require precise control over both slope and rotation to prevent cracking and ensure the weld meets stringent specifications.
Advanced Techniques in Weld Slope and Rotation
Automation in Weld Slope and Rotation
Automation allows for precise control over both slope and rotation, reducing the margin of error and improving repeatability in production environments.
CNC Machines and Robotic Welding
CNC machines and robotic systems can be programmed to adjust slope and rotation dynamically, based on real-time feedback, ensuring optimal welds even in complex scenarios.
Innovations and Future Trends
As technology advances, we’re likely to see even more sophisticated control systems that allow welders to fine-tune slope and rotation with greater precision, leading to higher-quality welds and reduced waste.
Best Practices for Weld Slope and Rotation
Tips for Achieving Optimal Welds
Consistency is key. Ensure that your slope and rotation settings are well-calibrated and test them on scrap material before starting on the actual workpiece.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid setting too steep of a slope, which can cause excessive spatter, or too slow of a rotation, which can lead to overheating in certain areas. Always monitor the weld and make adjustments as necessary.
Maintaining Consistency in Welding
Regular maintenance of your equipment, combined with continuous training, will help you maintain consistency in your welds, ensuring that both slope and rotation are working in harmony.
FAQs
What is the difference between positive and negative weld slope?
Positive weld slope increases the current as you progress through the weld, while negative slope decreases it. Each has its own applications depending on the material and desired outcome.
How does weld rotation affect weld penetration?
Weld rotation ensures even heat distribution, which in turn affects penetration. Proper rotation prevents uneven welds and helps achieve consistent penetration across the workpiece.
Can weld slope and rotation be automated?
Yes, modern welding machines and robotic systems allow for the automation of both weld slope and rotation, ensuring precision and consistency.
What adjustments should I make for welding different materials?
Adjustments depend on the material’s heat sensitivity. For example, use a positive slope for steel to enhance penetration, and a negative slope for aluminum to prevent burn-through. Rotation speed should also be adjusted based on the material thickness.
How can I prevent common weld defects related to slope and rotation?
To prevent defects, ensure your machine settings are calibrated correctly, and run test welds to fine-tune your slope and rotation parameters. Monitoring and adjusting in real-time can also help mitigate issues as they arise.
Conclusion
Mastering weld slope and rotation is essential for any welder looking to produce high-quality, reliable welds. These factors, often overlooked, can be the difference between a good weld and a great one. By understanding and controlling slope and rotation, you can improve your welding skills and produce work that stands up to scrutiny in any industry.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders