Considerations for Welding in Extreme Cold Weather
Welding in extreme cold weather presents a unique set of challenges that require specialized knowledge, preparation, and techniques. The colder the environment, the more complicated the welding process becomes, as low temperatures affect materials, equipment, and even the safety of the welder. In this article, we will delve into the various considerations welders need to keep in mind when working in extreme cold conditions to ensure safety, quality, and efficiency in their projects.
Why Extreme Cold Weather Affects Welding
Welding involves high heat, which can transform materials, specifically metals, into molten liquid that solidifies to form strong bonds. However, when these processes occur in extremely cold environments, everything changes. Cold weather can significantly alter the metal’s properties and how it behaves during welding, affecting the final result.
In low temperatures, metals become more brittle and lose some of their flexibility, making them susceptible to cracks and fractures. Cold temperatures also hinder the welding process by cooling the molten metal faster than in warmer conditions. This rapid cooling can lead to weak joints and poor-quality welds. Moreover, the impact on welding equipment, such as difficulty in maintaining proper gas flow or inconsistent temperatures, can further complicate the process.

Understanding Material Behavior in Cold Weather
It is essential to understand how materials behave when exposed to cold temperatures. Metal, in particular, undergoes changes in its mechanical properties. In extreme cold, the ductility of metals decreases, and their strength increases. However, this increased strength comes at a cost: materials are more likely to crack or fracture when they experience sudden stress.
For welders, this means that metals need to be treated with extra care before, during, and after welding. If the metal is too cold, it will not allow the weld to properly fuse, and instead, it could lead to weak or brittle welds that may fail under stress.
Challenges Faced by Welders in Cold Weather
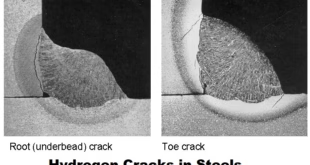
Welding in cold weather comes with various hurdles, starting with reduced flexibility in the welding techniques that are effective in warmer environments. The colder temperatures can slow down the cooling rate of the welded materials, and in some cases, it can even alter the properties of the materials, leading to the formation of weak welds. For example, when welding metals like steel in extremely cold weather, the chances of cracking increase due to the decreased ductility of the material.
Besides material challenges, the cold can also affect the welding equipment. Machines can become harder to operate in freezing temperatures, and this can impact everything from the consistency of the weld to the overall safety of the operation. From frozen hoses to low battery power in welding machines, these problems can severely disrupt the welding process.
Potential Risks of Welding in Cold Weather
Welding in cold weather presents specific risks that must be taken into account. One major risk is the increased likelihood of weld defects. Cracks, porosity, and undercutting are more likely to occur when welding in cold weather, as the lower temperatures affect the cooling process of the weld and the base metal.
Furthermore, working in cold weather increases the danger to the welder’s safety. For instance, cold-induced fatigue can lead to poor decision-making, while icy surfaces can cause slipping hazards. The hands can also become numb, reducing dexterity and leading to mistakes. It is crucial to address both the safety of the welder and the integrity of the weld in extreme cold.
Pre-Welding Preparation for Cold Weather
Proper preparation is crucial when welding in extreme cold. Before starting, it is recommended to preheat the metal to a certain temperature to prevent cracking. Preheating allows the base material to expand and absorb the heat from the weld, making the fusion stronger and more reliable.
Choosing the right welding rods and filler materials is also important. Some welding rods are specifically designed to perform better under colder conditions, providing better fusion and flexibility when exposed to low temperatures.
Moreover, protective gear and clothing should not be overlooked. Welders should wear insulated gloves, thermal socks, and heavy-duty coats to protect themselves from both the welding heat and the cold environment. Ensuring that the welding environment is safe from the elements—such as wind and snow—will help maintain the integrity of the welding process.
Selecting the Right Welding Equipment for Cold Weather
Welding machines and equipment must be chosen carefully when working in extreme cold. It is important to ensure that all machinery and accessories are rated for cold weather conditions. For example, some welding machines may require special coatings or insulation to function properly at low temperatures.
It’s also essential to maintain proper gas flow and shielding in cold conditions. Gas cylinders and regulators can freeze, so they must be carefully stored and handled. The temperature of the gas needs to be maintained to avoid any interruptions in the welding process.
Techniques to Overcome Cold Weather Challenges
Welders must employ specific techniques to combat the challenges posed by extreme cold. One of the most effective strategies is preheating the workpiece. Preheating helps maintain consistent heat throughout the welding process, allowing the material to absorb heat more evenly and reducing the risk of cracks.
Post-heating is just as important. After the weld is completed, allowing the joint to cool gradually (instead of rapidly) reduces the chances of cracks and brittleness. Additionally, controlling the heat input during welding is crucial. Maintaining an even temperature is key to ensuring that the weld penetrates the material adequately without causing defects.
Maintaining Consistency in Cold Weather Welds
In extreme cold, maintaining consistent weld quality is a challenge, but it’s not impossible. The key to achieving consistency is careful monitoring of temperature. This includes controlling the heat before, during, and after the welding process.
Additionally, ensuring uniform heat distribution can prevent stress points and enhance the quality of the weld. It’s critical to ensure that the metal remains in a workable state long enough for the welding process to be effective.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Cold Weather Welding
There are several mistakes welders often make when working in cold conditions. One common mistake is neglecting to control the temperature of the material, which can result in a poor-quality weld. Another error is using inappropriate materials or welding rods that aren’t designed for cold-weather conditions, leading to weak joints.
Inadequate safety measures are another common pitfall. Welders must ensure they are properly insulated and that their workspace is secure from the cold elements. Failure to take these precautions can lead to both poor-quality welds and safety hazards.
Post-Welding Care in Cold Weather
Once the welding process is complete, it is essential to inspect the weld for defects. Cold weather welding often requires extra care during the inspection process to ensure that the weld is strong and durable.
One important post-welding care step is to allow the welded area to cool slowly. Rapid cooling, especially in cold weather, can lead to cracks and distortions. Additionally, ensuring that the weld is adequately stress-tested will help prevent any issues from arising during future use.
FAQs
What is the best welding method for extreme cold weather?
The best welding method for cold weather is typically Stick welding (SMAW) as it works well in low temperatures and uses rods that can withstand freezing conditions.
Can welding rods freeze in cold weather?
Yes, welding rods can absorb moisture and freeze, which can affect the quality of the weld. Always store rods properly and preheat them if necessary.
How can I prevent cracks in my welds during cold weather?
Preheating the material, selecting the appropriate filler material, and controlling the welding speed can help reduce the risk of cracking in cold weather.
What are some common safety issues when welding in the cold?
Slippery surfaces, numb hands, and cold-induced fatigue are common safety issues. Always wear insulated clothing and ensure the work area is secure.
How do I choose the right filler material for cold weather welding?
Choose filler material specifically rated for cold weather, such as low-hydrogen electrodes, which are better suited to handle the stresses of cold temperatures.
Conclusion
Welding in extreme cold weather requires careful preparation, specialized techniques, and the right equipment to ensure success. Understanding how cold temperatures affect metals, adopting proper safety measures, and using the right materials can go a long way in overcoming the challenges associated with cold-weather welding. By taking these considerations into account, welders can ensure that their projects remain strong, safe, and high-quality, even in the harshest conditions.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders