WeldLogic Based Automatic Welding
Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology
Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology is an advanced welding automation solution developed by Inrotech, a leading provider of robotic welding systems. Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology integrates cutting-edge software and hardware components to enhance the efficiency and precision of multipass welding processes. The technology combines intelligent welding process control, automated torch positioning, and accurate wire feeding to optimize weld quality and productivity.
Basics of Multipass Welding
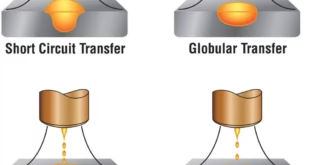
Multipass welding refers to a welding technique that involves the deposition of multiple layers of weld metal to create a strong and durable weld joint. It is typically used when the thickness of the base metal or the required strength of the joint exceeds the capabilities of a single pass weld. Each pass in the multipass welding process involves melting and solidifying a portion of the joint, with subsequent passes building upon the previous ones until the desired weld depth is achieved.
Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology
Introduction to Inrotech and its expertise in welding automation
Inrotech is a renowned company specializing in the development and implementation of advanced welding automation solutions. With years of experience and expertise, Inrotech has established itself as a leader in the field of robotic welding systems, catering to diverse industries. The company’s focus on innovation and cutting-edge technology has enabled them to deliver high-quality solutions for optimizing welding processes.

WeldLogic Technology and its features
WeldLogic Technology is a state-of-the-art welding automation technology developed by Inrotech. It encompasses a comprehensive range of software and hardware components designed to enhance the efficiency, precision, and control of multipass welding processes.
The key features of WeldLogic Technology include:
- Intelligent welding process control: It employs advanced algorithms to dynamically adjust welding parameters, such as current, voltage, and wire speed, in real-time, ensuring optimal weld quality and consistency.
- Automated torch positioning and movement: The technology enables precise and automated positioning of the welding torch, ensuring accurate and repeatable weld placement.
- Real-time monitoring and feedback: WeldLogic Technology provides real-time monitoring of the welding process, allowing for immediate detection and correction of any deviations or defects.
- Seamless integration with wire feeding systems: It seamlessly integrates with wire feeding systems, ensuring accurate and controlled wire delivery during the welding process.
- User-friendly interface: WeldLogic Technology offers an intuitive and user-friendly interface that simplifies programming, setup, and operation, enhancing overall ease of use.
Key Components of Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology
Welding Power Source
High-quality power supply for consistent welding performance:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology incorporates a robust and reliable welding power source that delivers stable and consistent electrical power for efficient welding operations.
- The high-quality power supply ensures consistent arc stability and weld quality, minimizing the risk of defects and ensuring optimal weld penetration.
Adaptive current control for different welding conditions:
- The welding power source in Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology features adaptive current control capabilities.
- It adjusts the welding current in real-time based on the specific welding conditions, such as joint thickness, material properties, and desired penetration depth, to optimize the weld quality and control heat input.
Welding Process Control
Advanced welding process control algorithms:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic incorporates advanced welding process control algorithms that govern various aspects of the welding operation.
- These algorithms optimize welding parameters, such as voltage, current, and wire speed, based on the specific requirements of multipass welding, ensuring consistent and high-quality welds.
Real-time monitoring and adjustments for optimal weld quality:
- The welding process control component of Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology continuously monitors the welding parameters and weld quality in real-time.
- It provides feedback and makes necessary adjustments to maintain optimal welding conditions, such as voltage, current, and travel speed, to achieve the desired weld quality and integrity.
Welding Torch System
Automatic torch positioning and movement:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology includes an automated welding torch positioning and movement system.
- It utilizes precise robotic control to position the torch accurately in the desired welding positions, eliminating human errors and ensuring consistent weld placement.
Precise and repeatable torch motion for consistent welds:
- The welding torch system in Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology offers precise and repeatable motion capabilities.
- It ensures consistent torch movement along the weld joint, maintaining the desired arc length, travel speed, and torch angle for each pass, resulting in consistent and high-quality welds.
Wire Feeding System
Accurate and controlled wire feeding:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic incorporates an accurate and controlled wire feeding system.
- The wire feeding system ensures a consistent and controlled supply of filler wire, maintaining the desired wire feed speed and arc length for optimal weld deposition.
Integration with welding process control for seamless operation:
- The wire feeding system seamlessly integrates with the welding process control component of Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology.
- It allows for synchronized control and adjustment of wire feed speed and welding parameters to maintain optimal welding conditions throughout the multipass welding process.
Applications of Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology
Heavy Fabrication Industries
Shipbuilding and offshore structures:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology finds extensive use in the shipbuilding industry, where multipass welding is crucial for constructing large vessels and offshore structures.
- The technology ensures precise weld placement, optimal welding parameters, and consistent weld quality, meeting the stringent requirements of shipbuilding standards.
- Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology is employed in the construction of oil and gas pipelines, which often involve multipass welding for joining large-diameter pipes.
- The technology enables efficient and precise welding, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the welded joints in pipelines, which are essential for the transportation of oil and gas.
Automotive Manufacturing
Frame and chassis welding:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology is utilized in automotive manufacturing for multipass welding of frames and chassis components.
- It enables consistent and high-quality welds, contributing to the structural integrity and safety of vehicles.
Body-in-white assembly:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology is applied in the body-in-white assembly process in automotive manufacturing.
- The technology facilitates multipass welding of body panels, ensuring accurate weld placement, minimal distortion, and superior joint strength.
Aerospace Industry
Aircraft structural components:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology plays a significant role in the aerospace industry, specifically in the multipass welding of aircraft structural components.
- It enables precise and repeatable welds, ensuring the integrity and strength of critical aircraft structures.
Engine assembly and maintenance:
- Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology is utilized in the assembly and maintenance of aircraft engines, which often involve multipass welding for joining various engine components.
- The technology ensures precise weld placement, optimal welding parameters, and consistent weld quality, contributing to the reliable performance of aircraft engines.
FAQs
What are the types of robots in welding?
The types of robots commonly used in welding are:
- Articulated robots: These robots have multiple joints that provide them with a wide range of motion, making them suitable for complex welding tasks.
- Cartesian robots: Also known as gantry robots, they operate on a three-axis system and are often used for welding in fixed positions.
- SCARA robots: These robots have a vertical arm and can rotate around a fixed base. They are suitable for applications that require high-speed and precise welding.
- Collaborative robots: Designed to work alongside humans, these robots can assist in welding tasks while ensuring safety and flexibility.
What are the applications of robot welding?
The applications of robot welding are diverse and include:
- Automotive manufacturing: Robot welding is extensively used in the automotive industry for welding vehicle frames, chassis, and body-in-white assembly.
- Heavy fabrication: Robot welding is applied in the construction of large structures, such as bridges, ships, and offshore platforms.
- Aerospace industry: Robot welding plays a vital role in the fabrication of aircraft components, ensuring precision and quality in welding operations.
- Pipe and tube manufacturing: Robot welding is employed for welding pipes and tubes used in various industries, including oil and gas, plumbing, and HVAC.
What are the advantages of robotic welding?
The advantages of robotic welding include:
- Improved productivity and efficiency due to the ability to work continuously without breaks or fatigue.
- Consistent and high-quality welds, reducing the chances of defects and rework.
- Enhanced safety for human operators, as robots can perform welding tasks in hazardous environments.
- Increased flexibility and adaptability to different welding applications and materials.
- Cost savings in the long run, as robotic welding can lead to reduced labor costs and increased throughput.
Which of the following robot configuration is extensively used for welding purpose?
The articulated robot configuration is extensively used for welding purposes due to its ability to provide flexibility and reach in complex welding tasks.
What is the most common use of welding robots?
The most common use of welding robots is in automotive manufacturing, where they are employed for welding vehicle frames, chassis, and body-in-white assembly.
What type of robot is used for arc welding?
Industrial robots, such as articulated robots, are commonly used for arc welding processes. They can handle various welding techniques, including gas metal arc welding (GMAW) and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW).
Do welding robots have sensors?
Yes, welding robots can have sensors. These sensors can be used for tasks such as seam tracking, weld quality monitoring, and ensuring proper positioning of the welding torch.
What is the principle of robot welding?
The principle of robot welding involves programming a robot to manipulate a welding torch to perform welding operations with precision and consistency. The robot follows a predetermined path while adjusting welding parameters, such as current, voltage, and wire feed speed, to achieve the desired weld quality.
What is the difference between robotic welding and manual welding?
The main difference between robotic welding and manual welding is the level of automation. Robotic welding involves the use of programmable robots to perform welding tasks, while manual welding relies on human operators who manually control the welding process. Robotic welding offers advantages such as increased productivity, consistent weld quality, and reduced labor costs, while manual welding allows for more flexibility and adaptability to unique or complex welding situations.
Conclusion
Inrotech-WeldLogic Technology has emerged as a groundbreaking solution in the realm of multipass welding. Through its advanced features and capabilities, it has revolutionized welding processes in various industries, including heavy fabrication, automotive manufacturing, and aerospace.
Automation and robotics will play a vital role in the future of multipass welding, alleviating labor-intensive tasks, boosting productivity, and maintaining consistent weld performance. Additionally, sustainability and energy efficiency will take center stage, aligning multipass welding processes with environmental standards and minimizing waste and energy consumption.
Reference: https://www.inrotech.com/
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders