What is Back Weld and Backing Weld?
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
When it comes to welding, understanding the different types of welds is crucial for ensuring the strength and integrity of the joint. If you’re diving into the world of welding, you’ve probably come across terms like “back weld” and “backing weld.” These might sound similar, but they serve distinct purposes and have unique characteristics. So, let’s break them down and see what they’re all about!
Definition of Back Weld
What is a Back Weld?
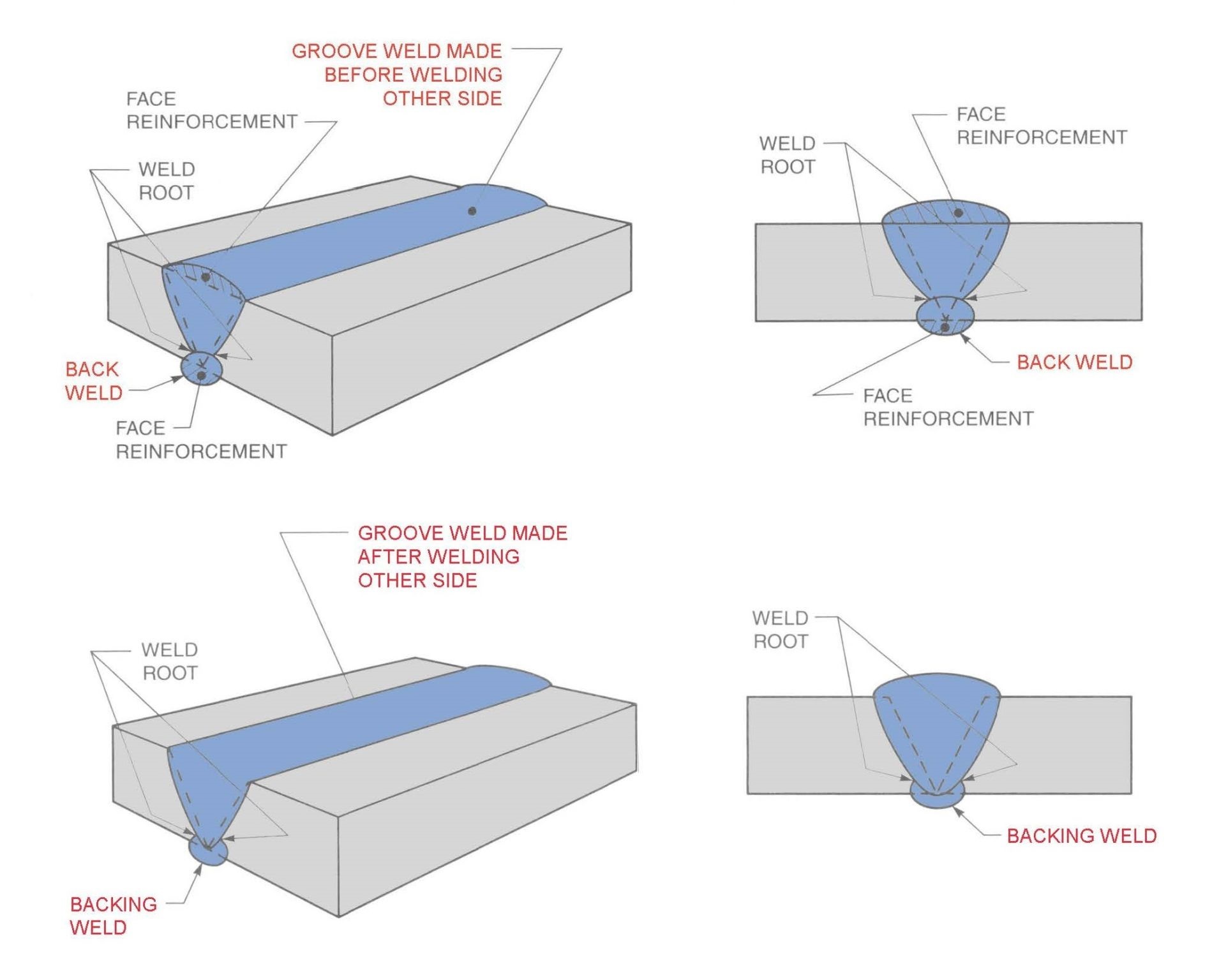
A back weld is a type of weld applied to the reverse side of a joint after the root pass welding is completed. It’s essentially a follow-up weld to reinforce the initial weld and ensure it has penetrated thoroughly. Think of it as the finishing touch to solidify the structure.
Purpose of a Back Weld
The primary purpose of a back weld is to provide additional strength and ensure the integrity of the weld joint. By welding the reverse side, it helps in achieving full penetration and filling any potential gaps or voids left during the root pass. This process enhances the durability and reliability of the weld, making it suitable for applications where joint strength is paramount.
Definition of Backing Weld
What is a Backing Weld?
A backing weld involves the use of a backing material to support the root pass weld. This material can be a weld itself (often called a backing weld) or a non-weldable material like a ceramic or metal strip. The backing material provides a surface against which the root pass can be welded, ensuring a smooth and strong base for subsequent weld layers.
Purpose of a Backing Weld
The main purpose of a backing weld is to support and stabilize the initial root pass, preventing burn-through and ensuring a cleaner, more controlled weld. It acts as a foundation, allowing the welder to focus on creating a high-quality root weld without worrying about gaps or incomplete penetration.
Differences Between Back Weld and Backing Weld
Structural Differences
The back weld is a secondary weld applied on the reverse side of the joint after the root pass, whereas the backing weld involves using a material to support the root pass from the beginning. Back welds are directly part of the welding process, while backing welds can sometimes involve separate materials.
Functional Differences
Functionally, a back weld aims to reinforce and complete the weld joint, ensuring it’s strong and durable. In contrast, a backing weld primarily serves to support and stabilize the initial weld, preventing defects and ensuring a cleaner welding process from the outset.
Applications of Back Welds
Common Uses in Various Industries
Back welds are widely used in industries where the structural integrity of the weld joint is critical. This includes the construction of bridges, buildings, and large metal structures. They’re also common in pipeline welding, where ensuring a leak-proof joint is essential.
Examples of Projects Using Back Welds
Projects that often utilize back welds include the construction of oil and gas pipelines, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery manufacturing. In these scenarios, the additional strength provided by back welds is crucial for safety and durability.
Applications of Backing Welds
Common Uses in Various Industries
Backing welds are commonly used in industries that require precise and defect-free welds from the start. This includes aerospace, automotive, and high-pressure vessel manufacturing. The backing material helps ensure that the initial welds are of the highest quality.
Examples of Projects Using Backing Welds
Examples of projects using backing welds include the fabrication of aircraft components, high-performance automotive parts, and pressure vessels for chemical processing. In these applications, the backing welds help achieve the necessary precision and quality.
Advantages of Using Back Welds
Strength and Durability
One of the key advantages of using back welds is the significant increase in joint strength and durability. By welding the reverse side, any potential weak points or voids are filled, resulting in a more robust and reliable joint.
Cost-effectiveness
While back welds require additional work, they can be cost-effective in the long run by preventing potential failures and reducing the need for costly repairs or replacements. The increased durability means less maintenance and longer service life for the welded structure.
Estimating Weld Cost.
Advantages of Using Backing Welds
Enhanced Quality and Precision
Backing welds allow for a more controlled and precise welding process, reducing the risk of defects like burn-through or incomplete penetration. The backing material provides a stable base, making it easier to create high-quality root passes.
Reduced Risk of Defects
By supporting the root pass, backing welds help minimize the occurrence of welding defects. This results in a cleaner, more reliable weld that meets stringent quality standards, which is particularly important in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a back weld and a backing weld?
The main difference lies in their application: a back weld is applied to the reverse side of a joint after the root pass, while a backing weld involves using a backing material to support the root pass from the start.
Can back welds and backing welds be used together?
Yes, in some complex welding projects, both back welds and backing welds can be used together to ensure maximum joint integrity and strength.
Are there any special tools required for back welds and backing welds?
Generally, standard welding tools are sufficient, but the specific requirements may vary based on the project. Backing welds may require additional materials like ceramic or metal strips.
How do I choose between a back weld and a backing weld for my project?
The choice depends on the specific requirements of your project. If you need to ensure initial root pass quality, a backing weld is beneficial. For added strength and reinforcement, a back weld is ideal.
What are the common challenges associated with back and backing welds?
Common challenges include ensuring full penetration for back welds and selecting the appropriate backing material for backing welds. Proper technique and material selection are crucial for success.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between back welds and backing welds is essential for any welding professional. Both types of welds play crucial roles in different applications, ensuring the strength, quality, and durability of the welded joints. Whether you’re working on constructing a bridge, fabricating an aircraft, or building a pipeline, knowing when and how to use these welds can make all the difference in the success of your project.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders