Welding Problems And Solutions
Introduction
Welding is a crucial process in various industries such as construction, manufacturing, and repair works. It involves joining two or more metal pieces by using heat and pressure to create a permanent bond. While welding has its benefits, it is not without its problems. These problems can range from minor issues like cracks in the weld to more severe ones like weld failures. The good news is that most welding problems have solutions. In this article, we will explore some of the common welding defects and discuss their solutions. From the proper preparation of metal surfaces to the selection of welding techniques and equipment, this article will provide practical tips for avoiding and resolving welding issues.
Common welding problems
- Porosity: This is the presence of small voids or pockets of trapped gas in the weld, causing weak spots in the weld. Solutions include proper joint preparation, cleaning and removing rust and oil, controlling the welding environment and using a suitable shielding gas.
- Warping and Distortion: Heat from welding can cause metal to warp or become distorted, leading to misalignment or even cracking. Solutions include using proper welding techniques, controlling the welding speed, using jigs to hold the workpiece in place, and preheating the workpiece.
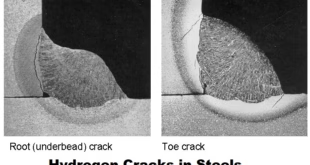
- Crack Formation: Cracks in the weld can be caused by improper welding techniques, incorrect welding parameters, high residual stress, and poor joint design. Solutions include proper joint preparation, controlling the welding speed, reducing the amount of stress on the weld, and using the correct filler metal.
- Incomplete Fusion: This occurs when the welding heat does not reach the base metal, leading to poor weld strength. Solutions include proper joint preparation, using a suitable welding technique, increasing the welding heat, and using a filler metal that matches the base metal.
- Spatter: Spatter is the excess molten metal that is expelled from the weld during the welding process. It can cause surface defects and make cleaning and finishing the weld more difficult. Solutions include using a shielding gas, controlling the welding speed, using a welding wire with a low-spatter formulation, and keeping the tip of the welding gun clean.
- Improper Welding Technique: Poor welding techniques can lead to a range of problems, including improper weld penetration, lack of fusion, and cracking. Solutions include proper training and practice, using the right welding technique for the job, and following proper welding procedures.
- Welding Hazard: Welding can be hazardous, with risks including burns, eye damage, and exposure to fumes and gases. Solutions include using proper protective equipment, following safety procedures, and ensuring good ventilation in the welding area.

Causes of welding problems
Welding is an important process for manufacturing and repair, but it can also be plagued by a number of problems that can compromise the quality of the weld and even render it useless. Some of the most common causes of welding problems are as follows:
- Poor Joint Design: Poor joint design is one of the most common causes of welding problems. The joint design must be appropriate for the type of welding process being used and must allow for proper fit-up and access to the weld joint.
- Contamination: Contamination of the base metal or filler material can lead to porosity and other defects in the weld. This can be caused by oil, grease, rust, or other contaminants that come into contact with the metal prior to welding.
- Improper Welding Techniques: Welding techniques that are not optimized for the specific welding process or material can result in problems such as incomplete fusion, lack of penetration, and excessive spatter.
- Inadequate Weld Preparation: Weld preparation is critical for ensuring a quality weld. Proper preparation includes removing all surface contaminants, ensuring that the joint is clean and dry, and ensuring that the joint surfaces are properly aligned.
- Improper Welding Equipment: Welding equipment that is not properly maintained or is not appropriate for the job can result in problems such as inconsistent welds, excessive heat input, and excessive spatter.
- Improper Filler Material Selection: The type of filler material used in welding must be appropriate for the base metal and the welding process being used. Improper selection can result in weak welds, cracking, and other defects.
- Improper Shielding: Shielding is an important part of the welding process, as it helps to protect the weld from contamination and prevents oxidation. Improper shielding can result in defects such as porosity and poor weld quality.
Solutions to welding problems
While welding problems can be frustrating, there are solutions that can help mitigate or eliminate them. Here are some common solutions to welding problems:
- Proper Joint Design: To avoid problems with poor joint design, manufacturers and repair technicians should consult welding standards and guidelines to ensure that the joint design is appropriate for the type of welding process being used.
- Contamination Control: To avoid problems with contamination, it is important to clean and prepare the metal prior to welding. This may include using solvents or other cleaning agents to remove surface contaminants, or using abrasive blasting to prepare the metal for welding.
- Proper Welding Techniques: To avoid problems with improper welding techniques, it is important to be trained in the correct techniques for the specific welding process and material being used. Welding operators should also follow recommended welding parameters, such as travel speed and welding current, to ensure consistent and quality results.
- Proper Weld Preparation: To avoid problems with inadequate weld preparation, manufacturers and repair technicians should follow recommended cleaning and preparation procedures to ensure that the joint surfaces are clean, dry, and properly aligned prior to welding.
- Proper Welding Equipment Maintenance: To avoid problems with improper welding equipment, it is important to regularly inspect, clean, and maintain welding equipment, including the welding power source, welding torch, and welding cable.
- Proper Filler Material Selection: To avoid problems with improper filler material selection, manufacturers and repair technicians should consult welding standards and guidelines to ensure that the filler material is appropriate for the base metal and the welding process being used.
- Proper Shielding: To avoid problems with improper shielding, manufacturers and repair technicians should use the appropriate shielding gases or fluxes for the specific welding process and material being used.
FAQs
What is the common problem in welding?
Common problems in welding can include inadequate penetration, poor quality welds, distortion, and other issues that can result in structural weakness or failure.
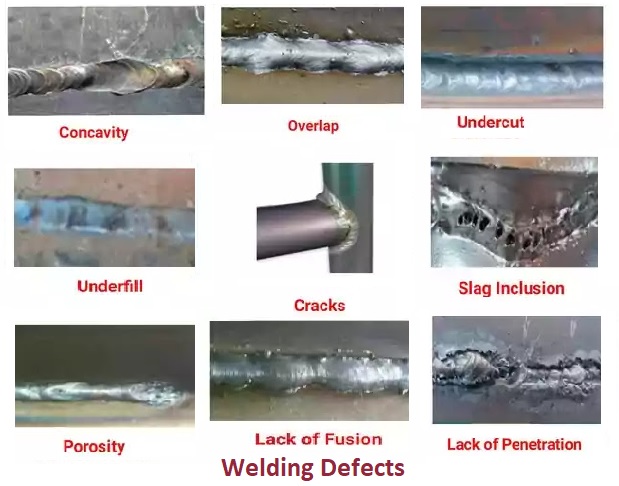
What are the 3 most common defects in welding?
The three most common defects in welding are porosity, lack of fusion, and cracking.
What are 10 most common welding defect?
The 10 most common welding defects are:
- Porosity
- Lack of fusion
- Cracking
- Incomplete penetration
- Undercutting
- Inclusions
- Distortion
- Overlapping
- Spatter
- Inconsistent weld bead size
What are 5 common mistakes to avoid when welding?
Five common mistakes to avoid when welding are:
- Poor preparation of the joint
- Incorrect welding technique
- Using the wrong welding process for the material being welded
- Not properly controlling the heat input
- Failing to properly inspect the finished weld for defects.
What are the 7 common welding defects?
The seven common welding defects are:
- Porosity
- Lack of fusion
- Cracking
- Incomplete penetration
- Undercutting
- Inclusions
- Distortion
What are the 5 causes of weld crack?
The five causes of weld crack are:
- Inadequate joint preparation
- Excessive heat input
- Incompatible base and filler metals
- Residual stress
- Improper welding technique
What are the 5 basic of welding?
The five basics of welding are:
- Understanding the properties of the metals being welded
- Properly preparing the joint
- Selecting the correct welding process
- Maintaining proper heat control
- Ensuring proper weld bead formation
What are the 5 parameters of welding?
The five parameters of welding are:
- Welding current
- Welding voltage
- Welding speed
- Shielding gas flow rate
- Electrode extension
What are the top 5 welding hazards?
The top five welding hazards are:
- Exposure to fumes and gases
- Electrical shock
- Fire and explosion
- UV radiation
- Physical hazards such as burns and eye damage
What are the 4 basic welds?
The four basic welds joints are:
- Butt joint
- Lap joint
- T-joint
- Corner joint
What are 3 safety rules for welding?
Three safety rules for welding are:
- Use proper personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Keep the work area clean and free of flammable materials
- Ensure proper ventilation and air flow in the work area.
What is F4 in welding?
In welding, the term “F4” refers to a specific classification for low hydrogen electrodes, specifically for the E7018 welding electrode.
The F4 classification indicates that the electrode coating has a low moisture content and is designed to be used in environments with low humidity. The low hydrogen content in the electrode helps prevent hydrogen cracking in the welded joint, which can occur when hydrogen gas becomes trapped in the weld and causes cracking over time.
In general, low hydrogen electrodes such as the E7018 F4 are commonly used for welding high-strength steels and critical applications where the welded joint must have high strength and be free from defects.
Conclusion
welding is an important process used in many industries, but it is not without its challenges. Addressing welding problems is crucial to ensure the safety and integrity of the welded component. Welding problems can lead to weakened or defective welds that can result in accidents, injuries, or even fatalities. In addition, poorly welded components can result in costly repairs, downtime, and lost productivity. Addressing welding problems early on can help prevent these issues and ensure that the welding process produces high-quality, reliable results. To address welding problems, it’s important to first identify the root cause of the issue. Welding is a critical process that requires skill, knowledge, and attention to detail. Addressing welding problems early on can help prevent accidents, injuries, and costly repairs. It’s important to work with experienced and knowledgeable welders who can help identify and address welding problems. Additionally, ongoing training and education can help ensure that welders have the skills and knowledge necessary to produce high-quality welds that meet industry standards and requirements.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders