Challenges in Welding Copper Pipes and Tubes
Copper is one of the most widely used metals, valued for its excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and flexibility. Copper pipes and tubes are integral to many industries, especially plumbing, HVAC, electrical, and automotive sectors. However, welding copper is challenging due to its unique properties. This article will dive into the challenges faced when welding copper pipes and tubes, discuss different welding methods, and provide practical solutions to make the process smoother.
Properties of Copper That Affect Welding
Copper’s properties, which make it so valuable in industrial applications, also present specific challenges for welding:
- High Thermal Conductivity: Copper dissipates heat rapidly, which can make maintaining a consistent weld puddle difficult.
- Oxidation Tendency: When exposed to air, copper quickly forms an oxide layer, which interferes with weld quality.
- Softness and Ductility: Copper’s softness can make it susceptible to deformation under high temperatures, causing alignment issues during welding.

Why Welding Copper is Challenging
The inherent properties of copper require specific attention to detail during welding. Here’s why:
- Heat Management Issues: Due to copper’s high thermal conductivity, it’s challenging to maintain heat consistently across the weld. This often leads to overheating and, in extreme cases, may damage the material.
- Oxidation and Contamination: Copper oxidizes rapidly, which can lead to contamination and weak welds. Contaminants can also affect the weld’s strength and appearance.
- Joint Alignment and Fusion Challenges: Copper’s ductility can lead to misalignments and inconsistent welds, especially in thin-walled pipes and tubes.
Common Applications of Copper Welding
Copper welding is essential across several sectors:
- Plumbing and HVAC Systems: Copper pipes are widely used due to their corrosion resistance and conductivity.
- Industrial Machinery and Electrical Systems: Copper is crucial in industrial systems, especially in electrical applications where high conductivity is required.
- Automotive and Aerospace: In these industries, copper is used for electrical wiring, tubing, and certain structural components.
Different Methods for Welding Copper
Each welding method brings its own set of advantages and limitations when working with copper.
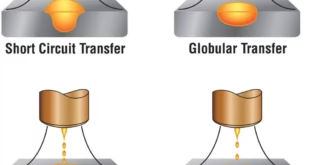
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding
TIG welding is often preferred for copper due to its precision and control over the heat input. However, it requires a skilled operator to avoid overheating and ensure proper fusion.
- Advantages: Precise control and clean welds, suitable for thin copper sections.
- Disadvantages: Slow process and requires skilled operators.
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding
MIG welding can also be used for copper, particularly for thicker sections where higher deposition rates are beneficial. MIG is generally faster but less precise than TIG.
- Advantages: Faster than TIG, works well on thicker copper pipes.
- Disadvantages: Less control, which can make it challenging to avoid heat damage.
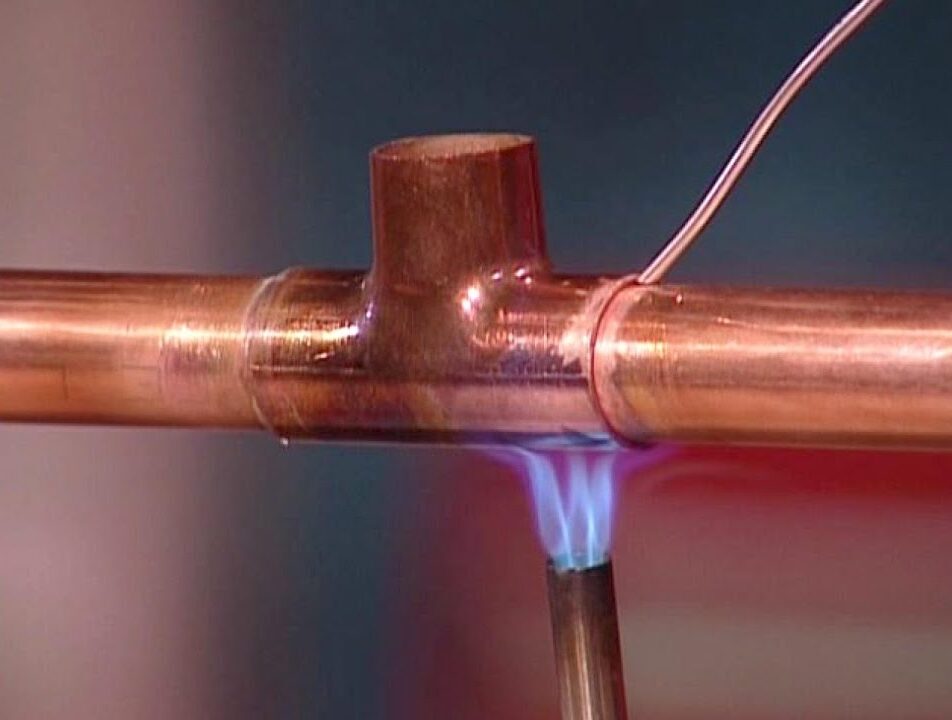
Brazing and Soldering
Brazing and soldering, while technically not welding processes, are commonly used with copper. Brazing is particularly useful for joining copper pipes, providing strong bonds at lower temperatures than welding.
- Differences: Brazing and soldering work at lower temperatures, so they don’t melt the copper.
- Benefits: Lower heat requirements reduce the risk of deformation and oxidation.
Challenges in Each Welding Technique
Each technique has its own set of challenges when applied to copper welding:
- TIG Welding Challenges: Heat control can be difficult, especially in thicker sections, due to copper’s high thermal conductivity.
- MIG Welding Issues: Maintaining a stable arc is challenging, as copper’s surface can be inconsistent.
- Brazing and Soldering: Preparing surfaces properly is essential, as oxidation can interfere with the bonding process.
Material Preparation for Welding Copper
Proper material preparation is essential for successful copper welding:
- Surface Cleaning: Copper surfaces need to be cleaned thoroughly to remove any oxidation or contaminants. This can be done using solvents or mechanical cleaning.
- Oxidation Removal: Removing oxidation ensures a stronger bond and prevents contaminants from weakening the weld.
- Preheating and Heat Control: Preheating can help manage heat flow, especially for thicker sections, allowing for a more consistent weld.
Welding Copper to Other Metals
Joining copper with metals like steel or aluminum requires special attention:
- Challenges in Dissimilar Metal Welding: Copper’s high thermal conductivity and different melting point compared to other metals make this challenging.
- Equipment and Fillers Needed: Special fillers and welding techniques, like using nickel-based fillers or brazing alloys, can improve the bond quality between copper and other metals.
Safety Precautions in Copper Welding
Safety is paramount, especially with copper welding due to potential health and safety hazards:
- Health Risks from Copper Fumes: Inhaling copper fumes can be harmful. It’s essential to work in a well-ventilated area or use fume extractors.
- Protective Gear and Ventilation: Welders should wear appropriate protective gear, including respirators if needed, and ensure adequate ventilation.
- Fire Hazards and Electrical Safety: Due to the high heat involved, there’s a fire risk. It’s crucial to have fire suppression equipment nearby and take necessary precautions.
FAQs
How do I control heat during copper welding?
Proper heat management can be achieved by preheating the material and controlling the welding speed to prevent overheating and damage.
Why does copper oxidize so quickly when welding?
Copper’s high reactivity causes it to form an oxide layer almost immediately upon exposure to air, especially at high temperatures.
What’s the difference between brazing and welding for copper pipes?
Brazing occurs at lower temperatures and doesn’t melt the copper, while welding melts both the filler and base metal for a more robust bond.
Is preheating necessary when welding copper?
Preheating is helpful, especially for thicker sections, to control the rapid heat dissipation and maintain a stable weld puddle.
Can I weld copper to stainless steel?
Yes, but it’s challenging. Using a nickel-based filler and careful heat management can improve the weld quality when joining copper to stainless steel.
Conclusion
Welding copper pipes and tubes is a complex but rewarding process that requires careful heat management, surface preparation, and technique selection. Copper’s unique properties, such as its high thermal conductivity and rapid oxidation, present challenges that can be addressed through specific welding techniques, preheating, and careful material preparation. Despite these challenges, advancements in welding technology continue to make copper welding more efficient and accessible for various industries.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders