Electrical Safety for Welders
Introduction
In the world of welding, precision, skill, and safety go hand in hand. Among the numerous safety considerations, electrical safety holds paramount importance. Welding involves handling electrical equipment and high temperatures, making it crucial for welders to be well-informed about electrical safety measures. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of electrical safety for welders, including essential guidelines, risk management, protective gear, and potential hazards. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting, this article aims to provide valuable insights to ensure a safe and productive welding environment.
Understanding the Basics
Welding equipment operates on electricity, and understanding the fundamentals of electrical safety is fundamental to avoiding accidents and injuries. Let’s delve into the core concepts of electrical safety for welders.
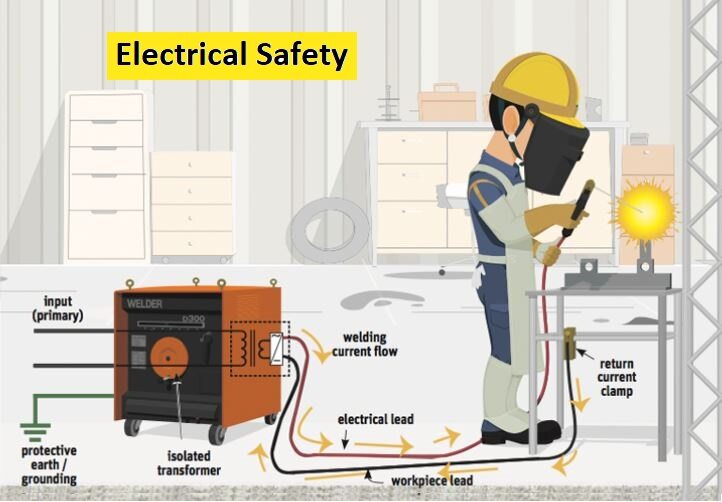
Electrical Circuits and Grounding
Welding machines are powered by electrical circuits, and grounding plays a crucial role in ensuring safety. Proper grounding prevents the buildup of electrical charge on equipment and helps direct the current to the ground in case of a fault. Always check for damaged or missing grounding prongs and ensure a secure ground connection before initiating welding operations.
Identifying Electrical Hazards
Welders work in a dynamic environment where electrical hazards may not always be apparent. Identifying potential electrical risks, such as exposed wires, damaged cables, or faulty equipment, is essential. Regular inspections and maintenance of welding machines can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents.
3. Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Before performing any maintenance or repair on welding equipment, ensure proper lockout/tagout procedures are followed. Lockout/tagout involves disconnecting the power supply and placing locks or tags on the equipment to prevent accidental energization. Following these procedures strictly can prevent severe electrical injuries.
Importance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a vital aspect of ensuring the safety of welders. Proper gear shields welders from various hazards, including electrical shocks, burns, and eye injuries. Let’s explore essential PPE for welders.
4. Welding Helmets and Face Shields
Welding generates intense light and heat, which can be harmful to the eyes and face. Welding helmets and face shields offer essential eye protection and protect the face from sparks and debris. Always wear a quality welding helmet or face shield with the appropriate shade for the welding process.
5. Welding Gloves
Welding gloves are designed to withstand high temperatures and protect the hands from burns and cuts. Choose gloves made from flame-resistant materials with reinforced stitching to ensure maximum protection while handling hot metals.
6. Fire-Resistant Clothing
Welders must wear fire-resistant clothing, such as welding jackets and aprons, to protect their bodies from sparks and splatter. These specially designed garments are crucial in preventing burn injuries during welding operations.
7. Welding Boots
Welding boots with sturdy construction and non-slip soles protect the feet from falling objects and electrical hazards. Comfortable and durable welding boots are essential for maintaining stability and reducing the risk of accidents.
Electrical Safety Measures in Welding Workshops
Welding workshops are dynamic environments where safety protocols must be diligently followed. Implementing the right safety measures can significantly minimize risks and ensure a secure working space for welders.
8. Proper Workshop Layout
Organizing the welding workshop with a focus on safety is crucial. Create designated welding zones with adequate ventilation, keeping flammable materials away from welding areas. Ensure accessible electrical outlets for welding machines, eliminating the need for extension cords.
9. Electrical Inspections and Maintenance
Regular inspections and preventive maintenance of electrical equipment are vital for identifying potential hazards and ensuring safe operation. Work with certified electricians to conduct electrical safety checks and promptly address any issues.
10. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs)
Install Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in electrical circuits to protect against electrical shocks and overcurrent situations. GFCIs immediately cut off the power when detecting abnormal electrical flow, preventing severe accidents.
Potential Electrical Hazards in Welding
Despite taking all necessary precautions, welders must be aware of potential electrical hazards and their consequences. Understanding these hazards empowers welders to respond effectively in critical situations.
11. Electric Shock Risks
Electric shocks can occur when a person comes into contact with live electrical parts or equipment. It is essential to follow safety protocols, such as de-energizing equipment before maintenance, to mitigate electric shock risks.
12. Arc Flashes and Burns
Arc flashes are intense bursts of light and heat generated during welding, posing burn risks to nearby individuals. Welders must maintain a safe distance and wear appropriate PPE to safeguard against arc flash injuries.
13. Electrical Fires
Electrical fires can be disastrous, endangering lives and property. Install fire extinguishers in the welding workshop and train employees on using them correctly. Understanding fire safety measures is essential in handling electrical fires effectively.
FAQs
What Are the Primary Electrical Hazards in Welding?
The primary electrical hazards in welding include electric shocks, arc flashes, and electrical fires. Proper grounding, electrical inspections, and the use of PPE can minimize these risks.
How Can I Protect Myself from Electric Shocks During Welding?
To protect yourself from electric shocks, always inspect equipment for damage, wear appropriate PPE, and follow lockout/tagout procedures when performing maintenance.
Are Welding Helmets with Auto-Darkening Filters Safer?
Yes, welding helmets with auto-darkening filters are safer as they offer constant eye protection, automatically adjusting to the required shade during welding.
Can I Use Extension Cords for Welding Machines?
It is not recommended to use extension cords for welding machines, as they can cause voltage drops and pose safety hazards. Instead, position the welding machine closer to the power source.
How Often Should I Inspect Welding Equipment?
Welding equipment should undergo regular inspections, ideally performed by a certified electrician, to ensure proper functionality and identify potential electrical hazards.
What Should I Do in Case of an Electrical Fire?
In case of an electrical fire, immediately activate the nearest fire extinguisher, turn off power sources if safe to do so, and evacuate the area. Do not attempt to extinguish electrical fires with water.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrical safety is of utmost importance in the welding industry. By following the recommended safety measures, wearing proper PPE, and being aware of potential hazards, welders can ensure a safer working environment for themselves and their colleagues. Regular inspections, preventive maintenance, and adherence to safety protocols are key in preventing electrical accidents. Remember, promoting electrical safety not only protects lives but also paves the way for a brighter and more prosperous future in the world of welding.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders