How to achieve Full Penetration Weld?
When it comes to welding, achieving a strong, durable, and reliable bond between two materials is the ultimate goal. One of the most critical techniques to ensure this is through a full penetration weld. But what exactly does it mean, and why is it so crucial in welding applications?
Definition of Full Penetration Weld
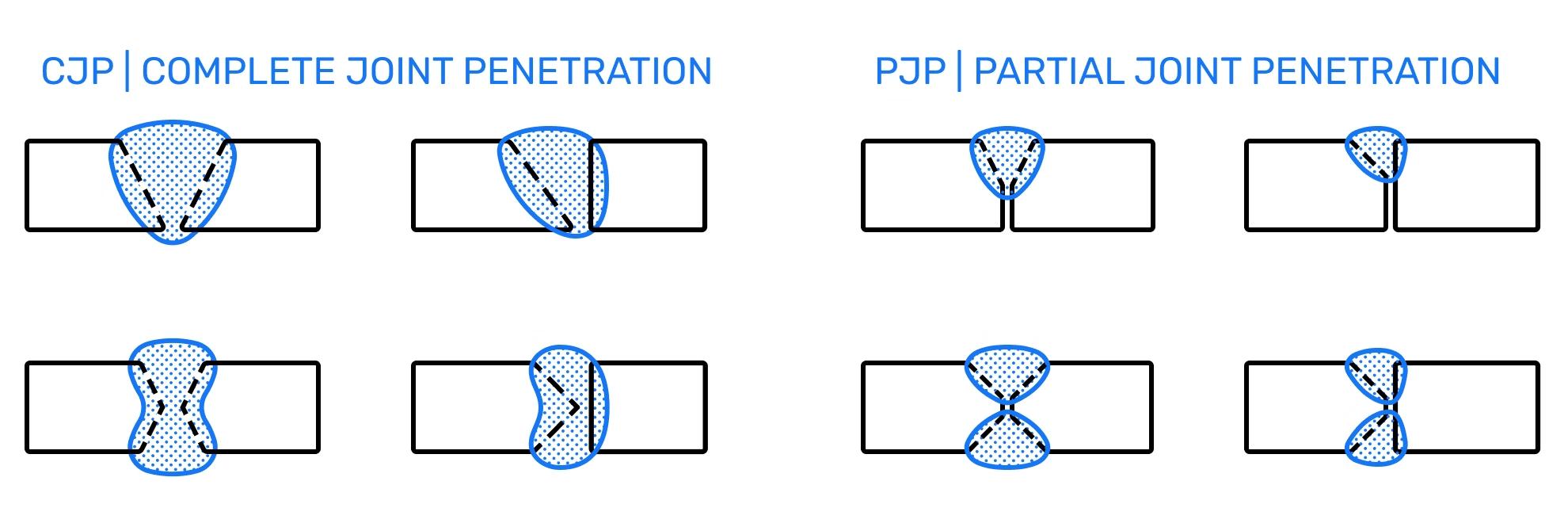
A full penetration weld occurs when the weld metal completely fills the joint, penetrating through the entire thickness of the base materials being joined. This ensures there are no gaps or voids within the welded joint, creating a uniform and seamless connection.
Why Full Penetration Welds Are Important
Full penetration welds are integral to structures that require maximum strength and reliability. Think of bridges, skyscrapers, or pressure vessels. These are structures where failure is not an option. By achieving full penetration, welders ensure the joint can withstand extreme forces, loads, and environmental conditions.
Types of Weld Penetration
Full Penetration vs. Partial Penetration
Not all welds are created equal. Full penetration welds differ significantly from partial penetration welds. While full penetration welds extend through the entire material thickness, partial penetration welds only penetrate partially, making them suitable for applications where lower stress levels are expected.
Common Applications of Full Penetration Welds
Full penetration welds are used in:
- Structural steel fabrication (e.g., bridges, high-rise buildings).
- Pipe welding for oil, gas, and water transportation.
- Aerospace and automotive industries for critical load-bearing components.
- Pressure vessels and boilers.
Key Factors Influencing Full Penetration Welds
Material Type and Thickness
The base material’s type and thickness directly affect how a full penetration weld is achieved. Thicker materials require more heat and proper joint preparation, while certain materials like stainless steel or aluminum may need specialized techniques.
Welding Process Used
Different welding processes impact penetration depth. For instance, TIG welding offers precision and control, making it suitable for thin materials, while MIG and stick welding are preferred for thicker sections.
Joint Design and Preparation
The joint’s design plays a pivotal role in ensuring full penetration. Common designs include butt joints with beveled edges to facilitate better fusion.
How to Achieve a Full Penetration Weld
Proper Joint Preparation
Getting the joint ready is the first step toward a successful weld.
Cleaning and Edge Beveling
Cleanliness is non-negotiable. Any contamination like rust, oil, or paint can prevent proper fusion. Beveling the edges of the joint allows the weld to penetrate deeper into the material.
Selection of the Right Welding Technique
Different techniques offer unique advantages depending on the application.
TIG, MIG, and Stick Welding
- TIG Welding: Best for thin materials and intricate work due to its precision.
- MIG Welding: Offers speed and efficiency, ideal for larger projects.
- Stick Welding: Versatile and effective for outdoor or less controlled environments.
Controlling Heat Input and Travel Speed
Heat input and travel speed must be balanced. Excessive heat can cause burn-through, while insufficient heat may lead to incomplete fusion. A steady hand and practice are essential.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Issues
Some typical problems include:
- Incomplete fusion due to improper heat.
- Burn-through when the heat is too intense.
- Porosity caused by trapped gases.
Tips to Overcome These Challenges
- Use proper joint preparation and cleaning techniques.
- Select the appropriate welding process for the job.
- Practice controlling heat and speed to avoid common pitfalls.
FAQs
What is the difference between full and partial penetration welds?
Full penetration welds penetrate the entire thickness of the material, while partial penetration welds only extend partway through.
Can all materials be used for full penetration welds?
Not all materials are ideal; metals like stainless steel, carbon steel, and aluminum are commonly used.
How do I identify a full penetration weld?
It’s usually verified through inspection methods like ultrasonic or radiographic testing.
What are the most common testing methods for full penetration welds?
Non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic and radiographic testing are widely used.
What are the primary challenges in achieving full penetration welds?
Common challenges include incomplete fusion, burn-through, and porosity, which can be mitigated with proper preparation and technique.
Conclusion
Achieving a full penetration weld requires skill, precision, and the right techniques. While it may seem challenging at first, mastering this critical welding process is essential for ensuring the strength and reliability of welded structures. By understanding the factors involved and practicing diligently, you can achieve consistently high-quality welds.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders