How to Weld Plastic?
Introduction
Plastic welding plays a crucial role in various industries and applications. The ability to join plastic parts together effectively opens up a world of possibilities in fields such as manufacturing, automotive, construction, and even DIY projects. By understanding and mastering plastic welding techniques, individuals can harness its numerous benefits.
One of the key reasons why plastic welding is important is its ability to create strong and durable bonds between plastic components. Unlike traditional adhesives or mechanical fasteners, plastic welding creates a molecular bond between the materials, resulting in a joint that is often stronger than the surrounding plastic itself. This is especially critical when working with load-bearing structures or applications that require high strength and reliability.
Moreover, plastic welding offers the advantage of versatility. Different types of plastics can be welded together, allowing for the repair or modification of various plastic products. This flexibility extends to working with different shapes, sizes, and thicknesses of plastic components. By having the skills to weld plastic, individuals gain the ability to tackle a wide range of projects and solve problems in a cost-effective manner.
Learning plastic welding techniques also provides economic benefits. In many cases, repairing plastic items through welding is more cost-effective than replacing them entirely. Whether it’s fixing a cracked automotive bumper, repairing a damaged plastic container, or even creating custom plastic parts, the ability to weld plastic empowers individuals to save money and extend the lifespan of their plastic items.
Plastic welding contributes to environmental sustainability. By repairing and reusing plastic items, the need for manufacturing new products can be reduced, resulting in a decreased demand for raw materials and energy. Plastic welding promotes a circular economy by minimizing waste and the environmental impact associated with plastic disposal.
Understanding Plastic Welding
Plastic welding is a specialized process that involves joining two or more plastic components together to create a strong and durable bond. It is a versatile method used in various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, construction, and even in DIY projects. Understanding the basics of plastic welding is essential for successful implementation.
Plastics suitable for welding can be categorized into thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. Thermoplastics are the most common type used in plastic welding. These plastics can be melted and reshaped multiple times without undergoing significant chemical change. Some examples of thermoplastics suitable for welding include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS).
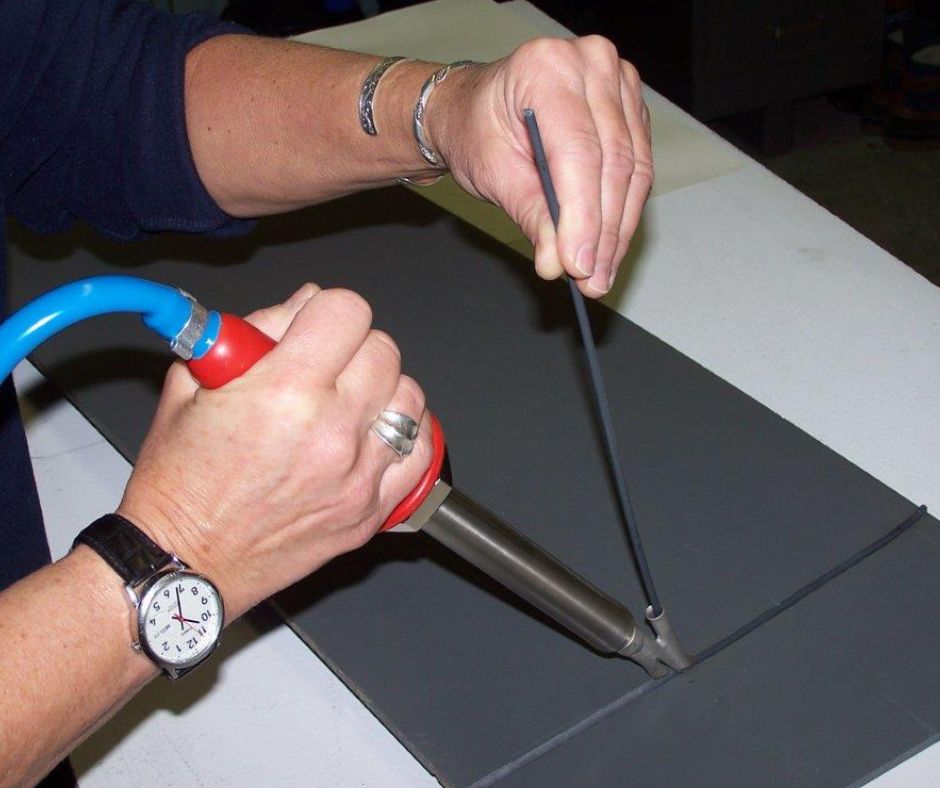

Essential Tools and Equipment
Plastic welding requires specific tools and equipment to ensure successful and safe operations. It is essential to have the right set of tools and adhere to safety precautions to minimize risks and achieve optimal results.
List of necessary tools and equipment for plastic welding
1. Plastic Welding Gun or Torch: This is the primary tool used for generating heat to melt the plastic. It typically includes temperature and airflow controls for precise adjustments.
2. Welding Nozzles: Different welding techniques may require specific types and sizes of nozzles. They direct the heated airflow onto the plastic surface.
3. Welding Rods or Filler Material: These are plastic rods or strips that are melted and applied to the joint to enhance strength and create a solid bond. Select the appropriate filler material compatible with the plastic being welded.
4. Cutting Tools: Utility knives, scissors, or cutters are necessary for preparing and shaping the plastic components before welding.
5. Clamps or Fixtures: These tools help hold the plastic parts in the desired position during welding to ensure accurate alignment and prevent movement.
6. Scrapers or Cleaning Tools: Scraper blades or brushes are used for removing debris, old welds, or contaminants from the plastic surfaces before welding.
7. Heat Sources and Controllers: Depending on the welding technique, additional heat sources such as hot plates or ultrasonic generators may be required. These devices provide controlled heat for specific welding methods.
8. Safety Equipment: Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial when working with plastic welding tools. This includes safety glasses or goggles, heat-resistant gloves, and protective clothing to shield against heat, sparks, and fumes.
Safety precautions to follow while working with plastic welding tools
1. Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in the working area to dissipate fumes and prevent the accumulation of potentially harmful gases. Work in a well-ventilated space or use local exhaust ventilation if necessary.
2. Eye and Face Protection: Wear safety glasses or goggles that are designed to protect against flying debris, hot plastic particles, and harmful UV radiation generated during plastic welding.
3. Hand and Body Protection: Use heat-resistant gloves to protect your hands from burns and injuries. Additionally, wear appropriate clothing made of flame-resistant materials to minimize the risk of burns from hot plastic or sparks.
4. Fire Safety: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and be aware of potential fire hazards. Plastic welding involves heat and flammable materials, so be prepared to respond quickly in case of emergencies.
5. Electrical Safety: If using electrically powered tools or equipment, ensure proper grounding and avoid working in wet conditions. Follow electrical safety guidelines to prevent electrical shock or other electrical hazards.
6. Training and Familiarity: Gain proper training and familiarize yourself with the specific tools and equipment you are using. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines before operating any plastic welding tool.
Preparing for Plastic Welding
Preparing the surfaces and plastic parts before welding is crucial to ensure successful bonding and achieve strong, durable joints. Proper surface preparation involves cleaning and prepping the plastic components appropriately.
Surface preparation techniques
1. Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be welded to remove any dirt, dust, grease, or contaminants. Use a mild detergent or a plastic-specific cleaning agent and a soft cloth or sponge to gently clean the surfaces. Ensure that the cleaning agent is compatible with the type of plastic being welded.
2. Abrasion: In some cases, especially when working with smooth or glossy plastic surfaces, it is essential to create a rough texture or micro-scratches to improve adhesion. This can be done using sandpaper, abrasive pads, or a wire brush. Gently sand or abrade the surfaces to provide a better bonding surface.
3. Surface Priming: Depending on the type of plastic and the specific welding technique, applying a primer may be necessary. Primers are designed to improve the adhesion between the plastic surfaces and the welding filler material. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions or seek expert advice to determine if a primer is needed and the appropriate type to use.
Proper cleaning and prepping of plastic parts
1. Disassembly If applicable, disassemble the plastic parts to ensure access to all the areas that require welding. This allows for better control and visibility during the welding process.
2. Alignment Proper alignment of the plastic parts is crucial for achieving accurate and strong welds. Ensure that the parts are aligned correctly before starting the welding process. The use of clamps or fixtures can help hold the parts in place during welding.
3. Trimming and Shaping Trim or shape the plastic parts as needed before welding. Remove any excess material or burrs that may interfere with the welding process or compromise the strength of the joint. Use appropriate cutting tools to achieve clean and precise edges.
4. Preheating In certain cases, preheating the plastic parts may be necessary to improve the welding process. Preheating softens the plastic and reduces the likelihood of stress or cracking during welding. Follow the recommended preheating temperature and duration specific to the type of plastic being welded.
5. Compatibility Check Ensure that the plastics being welded are compatible. Some plastics may have different melting points or chemical compositions that can affect the welding process. Verify compatibility and consult material data sheets or experts if necessary.
Plastic Welding Techniques
Hot Gas Welding
1. Explanation of hot gas welding process
Hot gas welding is a technique that uses a heat source, typically a hot air gun or torch, to melt the plastic surfaces to be joined. The molten plastic is then pressed together, creating a strong bond as it cools and solidifies. Hot gas welding is commonly used for joining large plastic sheets or components, such as in the construction of tanks, pipes, or automotive parts.
2. Step-by-step instructions for hot gas welding
- Prepare the plastic surfaces Clean and abrade the surfaces to be welded, ensuring they are free from dirt, contaminants, and oxidation.
- Set up the welding equipment Ensure the hot air gun or torch is in good working condition and set to the appropriate temperature and airflow settings. Use the recommended welding nozzle suitable for the plastic and joint configuration.
- Preheat the plastic Start by preheating the plastic surfaces with the hot air gun. Move the gun in a back-and-forth motion, evenly heating the surfaces until they become glossy or slightly molten.
- Merge the plastic Once the surfaces are adequately preheated, bring them together and press firmly. Maintain steady pressure to ensure a uniform bond along the entire joint. Adjust the heat and airflow as needed during the welding process.
- Welding rod/filler material If necessary, introduce a welding rod or filler material made from the same type of plastic as the components being joined. Melt the rod with the hot air gun and apply it along the joint to reinforce the bond and provide additional strength.
- Finishing touches Once the welding is complete, allow the joint to cool and solidify. Trim any excess or uneven plastic using appropriate cutting tools. Inspect the weld for quality, ensuring there are no gaps or weak areas.
Ultrasonic Welding
1. Explanation of ultrasonic welding process
Ultrasonic welding utilizes high-frequency vibrations to generate heat and weld the plastic parts. The parts to be joined are placed under pressure while ultrasonic vibrations create friction and heat at the interface, causing the plastic to melt and form a strong bond. Ultrasonic welding is commonly used for small plastic parts, such as electronics, medical devices, and automotive components.
2. Step-by-step instructions for ultrasonic welding
- Prepare the plastic parts Clean the surfaces to be welded, ensuring they are free from dirt, dust, and contaminants. Align the parts accurately and securely in the ultrasonic welding machine.
- Set up the ultrasonic welding machine Adjust the machine settings, including the amplitude, welding time, and pressure, based on the specific requirements of the plastic and joint configuration.
- Apply pressure Activate the ultrasonic welding machine to initiate the process. The machine will apply pressure to hold the plastic parts together.
- Generate heat The machine will generate high-frequency vibrations (ultrasonic waves) that create friction and heat at the contact surface between the plastic parts. The heat melts the plastic, bonding the surfaces together.
- Solidification and cooling After the ultrasonic vibrations cease, maintain pressure on the joint for a brief period to allow the plastic to solidify and form a strong bond. Once the bond has solidified, release the pressure.
- Finishing touches Trim any excess or uneven plastic using appropriate cutting tools. Inspect the weld for quality, ensuring there are no gaps or weak areas.
Hot Plate Welding
1. Explanation of hot plate welding process
Hot plate welding involves using heated plates to soften the plastic parts to be joined. The heated plates melt the plastic surfaces, and when the plates are removed, the molten plastic is pressed together to create a
bond. Hot plate welding is particularly useful for large and complex plastic parts, such as automotive bumpers or tanks.
2. Step-by-step instructions for hot plate welding
- Prepare the plastic parts Clean the surfaces to be welded, ensuring they are free from dirt, dust, and contaminants. Align the parts accurately and securely on the hot plate welding machine.
- Heat the plates Activate the hot plate welding machine and adjust the temperature settings according to the plastic being used. Allow the plates to reach the desired temperature.
- Place the plastic parts Position the plastic parts on the hot plates, ensuring they are in contact with the heated surfaces. Apply pressure if necessary to ensure good contact between the parts and the plates.
- Heating and melting Leave the plastic parts on the hot plates for a specific duration, allowing the heat to soften and melt the plastic surfaces. The time required will depend on the type and thickness of the plastic being welded.
- Joining the plastic Once the plastic surfaces have reached the desired melting point, remove the parts from the hot plates. Immediately press the molten plastic surfaces together, ensuring alignment and applying adequate pressure to create a strong bond.
- Cooling and solidification Maintain pressure on the joint for a sufficient duration to allow the plastic to cool and solidify. This ensures the bond becomes strong and durable.
- Finishing touches Trim any excess or uneven plastic using appropriate cutting tools. Inspect the weld for quality, ensuring there are no gaps or weak areas.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Potential challenges during plastic welding
1. Insufficient Bond Strength: The joint may not have the desired strength, resulting in a weak bond. This can occur due to inadequate surface preparation, improper temperature or pressure settings, or using incompatible welding materials.
2. Inconsistent Weld Quality: Inconsistencies in the weld appearance, such as uneven melting, gaps, or surface irregularities, can occur due to uneven heat distribution, poor alignment, or improper welding technique.
3. Material Compatibility Issues: Different types of plastics may have different melting points and chemical compositions, making it challenging to achieve a proper bond. It is essential to ensure compatibility between the plastics being welded.
4. Overheating or Burning: Excessive heat or prolonged exposure to heat can cause the plastic to overheat, burn, or develop discoloration. This can weaken the joint and compromise the overall weld quality.
Troubleshooting tips for common welding issues
1. Insufficient Bond Strength
– Review and improve surface preparation techniques, ensuring that surfaces are clean and properly abraded.
– Adjust the temperature and airflow settings to ensure adequate melting and fusion of the plastic.
– Use compatible welding rods or filler materials to reinforce the joint and enhance bond strength.
2. Inconsistent Weld Quality
– Ensure even heat distribution by maintaining consistent speed and distance during the welding process.
– Double-check the alignment of the plastic parts before and during welding.
– Consider adjusting the welding technique or equipment settings based on the specific requirements of the plastic being welded.
3. Material Compatibility Issues
– Verify the compatibility of the plastics being welded, considering their melting points and chemical compositions.
– Conduct small-scale test welds using samples of the plastic materials to ensure compatibility and evaluate bond strength before proceeding with larger-scale welding.
4. Overheating or Burning
– Adjust the temperature settings to a lower, more suitable range for the specific plastic being welded.
– Avoid prolonged exposure to heat by using quick and controlled welding motions.
– Consider using heat shields or heat-resistant tapes to protect adjacent areas from excessive heat.
Advanced Tips and Techniques
Overcoming complex welding scenarios
1. Joining Different Types of Plastics: When welding different types of plastics together, such as dissimilar materials or those with varying melting points, consider using specialty welding techniques like solvent welding or adhesive bonding. These methods rely on chemical reactions or bonding agents to create a strong joint between the different plastics.
2. Welding Thick or Large Plastic Parts: Welding thick or large plastic parts can pose challenges due to heat dissipation. In such cases, preheating the parts or using preheated fixtures can help maintain the required temperature during the welding process. Additionally, adjusting the welding technique, such as using multiple passes or applying filler material in layers, can ensure proper fusion and bonding.
3. Repairing Damaged or Cracked Plastic: Plastic welding can also be used for repairing damaged or cracked plastic parts. By carefully cleaning the damaged area, aligning the parts, and using appropriate welding techniques, it is possible to restore the integrity of the plastic component. Reinforcing the repair with additional filler material or reinforcement strips can further enhance its strength.
Advanced techniques to enhance plastic weld strength
1. Use Reinforcement Techniques: To enhance the strength of the plastic weld, consider using reinforcement techniques such as adding mesh, fabric, or metal inserts to the joint. These reinforcements provide additional structural support and improve the overall strength of the weld.
2. Multiple Pass Welding: For critical or high-stress applications, multiple pass welding can be employed. This technique involves making multiple welding passes over the joint, ensuring thorough fusion and a stronger bond. Allow each pass to cool before proceeding to the next to prevent overheating.
3. Vibration or Friction Stir Welding: Advanced welding techniques like vibration welding or friction stir welding can be employed for specific plastic applications. These methods generate heat through mechanical friction, resulting in strong, homogeneous bonds with minimal distortion or stress on the plastic parts.
4. Post-Weld Treatment: Consider post-weld treatments to further enhance the strength of the plastic weld. Techniques such as annealing, stress relieving, or post-weld heat treatment can help improve the mechanical properties and durability of the joint.
5. Quality Control and Testing: Implement quality control measures to ensure the integrity of the plastic welds. This may involve performing destructive or non-destructive testing methods, such as pull testing, visual inspection, or ultrasonic testing, to verify the strength and integrity of the welds.
Applications of Plastic Welding
Industries and sectors that rely on plastic welding
1. Automotive Industry: Plastic welding is widely used in the automotive sector for various applications such as bumper repairs, fuel tank manufacturing, interior component assembly, and HVAC system fabrication.
2. Construction and Building: Plastic welding finds applications in the construction industry for joining plastic pipes, fabricating roofing membranes, installing waterproof liners, and constructing tanks or containers.
3. Electronics and Electrical Industry: Plastic welding is utilized in the assembly of electronic components, creating housings, encapsulating circuitry, and sealing connectors.
4. Medical and Healthcare: Plastic welding is essential in the medical industry for manufacturing medical devices, such as syringes, IV components, and surgical instruments. It is also used for fabricating laboratory equipment and disposable medical products.
5. Packaging and Manufacturing: Plastic welding is crucial in the packaging industry for creating custom packaging solutions, sealing plastic bags, and producing plastic containers or bottles. It is also used in manufacturing processes for products such as toys, appliances, and consumer goods.
Examples of practical applications and projects
1. Repairing a Cracked Plastic Tank: Plastic welding can be used to repair a cracked plastic tank, such as a coolant reservoir or fuel tank, by cleaning the damaged area, aligning the cracked parts, and using the appropriate welding technique to create a strong and leak-proof bond.
2. Joining PVC Pipes for Plumbing: Plastic welding is commonly used for joining PVC pipes in plumbing systems. The process involves cleaning and preparing the pipe ends, heating them with a suitable welding tool, and fusing them together to form a reliable and durable joint.
3. Fabricating Plastic Signs or Displays: Plastic welding enables the fabrication of custom plastic signs or displays by joining plastic sheets or components together. This is commonly used in advertising, retail, and exhibition industries to create eye-catching and durable signage.
4. Assembling Automotive Interior Components: Plastic welding is employed in the automotive industry for assembling interior components such as dashboard panels, door trims, and console parts. This ensures a strong and seamless integration of plastic components in the vehicle interior.
5. Creating Waterproof Roofing Membranes: Plastic welding is used in the construction industry to create waterproof roofing membranes. Plastic sheets are welded together using hot air or hot wedge welding techniques to form a continuous and watertight barrier, ensuring protection against leaks and moisture.
FAQs
How to do plastic welding?
To do plastic welding, you need to clean and prepare the plastic surfaces, select the appropriate welding technique (such as hot gas welding, ultrasonic welding, or hot plate welding), heat the plastic to the melting point, join the parts together, and allow them to cool and solidify to form a strong bond.
What is the best plastic welding method?
The best plastic welding method depends on the specific application and the type of plastics being welded. Techniques like hot gas welding, ultrasonic welding, and hot plate welding are commonly used and each has its advantages and suitability for different scenarios.
What is an example of plastic welding?
An example of plastic welding is joining PVC pipes in plumbing systems. This involves using a welding tool to heat and fuse the ends of the pipes together, creating a strong and leak-proof connection.
What is welding plastic called?
Welding plastic is commonly referred to as plastic welding or thermoplastic welding.
What is the process of welding?
The process of welding involves joining two or more materials by melting them and allowing them to solidify, creating a strong bond. This is typically achieved by applying heat, pressure, or both to the materials being joined.
How easy is plastic welding?
The ease of plastic welding can vary depending on the technique and the skill level of the individual. Some techniques, such as hot gas welding, may require more practice and expertise to master, while others, like ultrasonic welding, can be relatively easier to learn.
Where is plastic welding used?
Plastic welding is used in various industries and sectors, including automotive, construction, electronics, medical, packaging, and manufacturing. It finds applications in tasks such as repairing plastic components, joining plastic pipes, fabricating plastic signs, and assembling plastic parts.
What machine is used for plastic welding?
Different machines and equipment are used for plastic welding, depending on the technique being employed. For example, hot gas welding often involves using a hot air gun or a welding torch, while ultrasonic welding utilizes an ultrasonic welding machine or a handheld ultrasonic welder. Hot plate welding utilizes a hot plate welding machine.
Is plastic welding safe?
When proper safety precautions are followed, plastic welding can be safe. It is important to wear protective equipment, work in a well-ventilated area, and adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific welding technique and equipment being used.
Is plastic welding hot work?
Plastic welding can involve the use of heat, and therefore, it can be considered a form of hot work. Precautions should be taken to ensure the safe handling of hot materials and to prevent accidents or injuries.
Conclusion
Plastic welding is a valuable skill that offers numerous benefits and applications across various industries. By mastering the techniques and understanding the fundamentals of plastic welding, individuals can join plastic components with strength, precision, and durability. Throughout this article, we have explored the importance of plastic welding and its benefits, such as cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and the ability to create strong bonds in a wide range of plastic materials. We have also delved into the different welding techniques, including hot gas welding, ultrasonic welding, and hot plate welding, along with step-by-step instructions for each.
Additionally, we discussed the essential tools and equipment required for plastic welding, as well as the safety precautions that should be followed to ensure a safe working environment. Proper surface preparation techniques and cleaning procedures were highlighted to achieve optimal welding results. Moreover, we addressed common challenges that may arise during plastic welding and provided troubleshooting tips to overcome them. Advanced tips and techniques were also shared to help individuals navigate complex welding scenarios and enhance the strength of plastic welds.
We explored the wide range of industries and sectors that heavily rely on plastic welding, including automotive, construction, electronics, medical, packaging, and manufacturing. Practical applications and projects were provided as examples to demonstrate the real-world significance of plastic welding in these industries.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders