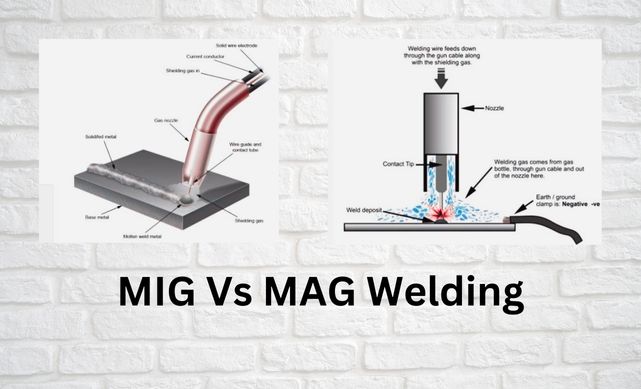
MIG Vs. MAG Welding
Introduction
Welding is a crucial process used in various industrial and manufacturing applications to join two or more metal parts. It involves heating the metal to its melting point and then fusing it together using a filler material. Among the different types of welding, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and MAG (Metal Active Gas) welding are two of the most commonly used techniques.
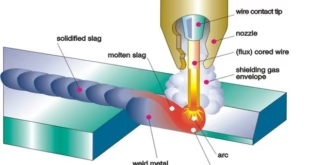
MIG welding uses a wire electrode that is continuously fed through a welding gun and an inert gas, such as argon or helium, to shield the weld from the surrounding air. MAG welding, on the other hand, uses an active gas, such as carbon dioxide, along with a wire electrode to create the welding arc and protect the weld from oxidation.
The popularity of MIG and MAG welding can be attributed to their ease of use, high efficiency, and versatility. They are widely used in various industries such as automotive, construction, and shipbuilding, among others.
In this outline, we will explore the differences between MIG and MAG welding, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and their applications. We will also provide tips and techniques for welding with both processes, and compare the two techniques to determine which is best for specific applications.
Overall, understanding the differences between MIG and MAG welding is crucial for selecting the right welding process for different applications. By doing so, manufacturers can ensure that their welding projects are completed efficiently, effectively, and to the highest possible standards.
MIG Welding
MIG welding is a popular welding technique that is widely used in various industries due to its high efficiency, ease of use, and versatility. In MIG welding, a wire electrode is continuously fed through a welding gun and an inert gas, such as argon or helium, is used to shield the weld from the surrounding air. This process creates a strong, clean weld that is free of defects and can be completed quickly.
Definition and Explanation of MIG Welding
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a welding process that uses a wire electrode to join two metal parts together. The wire electrode is fed through a welding gun, which creates an electric arc between the wire and the metal parts. The electric arc melts the wire and the metal parts, which then fuse together to form a solid joint.
The Equipment and Tools Needed for MIG Welding
To perform MIG welding, several pieces of equipment and tools are needed, including:
- Welding Machine: A welding machine is required to provide the electrical power needed to create the welding arc.
- Welding Gun: The welding gun is used to hold the wire electrode and create the arc between the wire and the metal parts.
- Wire Electrode: The wire electrode is the filler material used to fuse the metal parts together. It is available in different sizes and types to suit various welding applications.
- Inert Gas: An inert gas, such as argon or helium, is used to shield the weld from the surrounding air and prevent oxidation.
- Regulator: A regulator is needed to control the flow of gas from the tank to the welding gun.
- Protective Gear: Welders must wear protective gear, such as a welding helmet, gloves, and apron, to protect themselves from sparks and radiation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of MIG Welding
MIG welding has several advantages, including:
- High Efficiency: MIG welding is a fast and efficient welding process that can be completed quickly and easily.
- Easy to Use: MIG welding is a relatively easy welding process that can be learned quickly, making it an ideal choice for beginners.
- Versatility: MIG welding can be used to weld a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
- Clean Welds: MIG welding produces clean, high-quality welds that are free of defects and imperfections.
However, MIG welding also has some disadvantages, including:
- Limited Weld Thickness: MIG welding is not suitable for welding very thick metal parts, as it can produce shallow welds.
- Wind Sensitivity: MIG welding requires a stable environment, as wind and drafts can affect the welding arc and produce inconsistent welds.
Applications and Uses of MIG Welding
MIG welding is used in various industries and applications, including:
- Automotive Industry: MIG welding is widely used in the automotive industry to join metal parts together.
- Construction Industry: MIG welding is used to weld steel and aluminum structures in the construction industry.
- Manufacturing Industry: MIG welding is used in the manufacturing industry to join metal parts together, such as in the production of furniture, appliances, and machinery.
Techniques and Tips for MIG Welding
To achieve the best results with MIG welding, several techniques and tips should be followed, including:
- Proper Preparation: The metal parts to be welded should be cleaned and prepared properly to ensure a strong, clean weld.
- Welding Technique: The welding technique used should be smooth and consistent to produce a clean, uniform weld
- Correct Voltage and Wire Speed: The correct voltage and wire speed should be set on the welding machine to match the thickness and type of metal being welded. This helps to ensure a proper and consistent weld.
- Appropriate Shielding Gas: The appropriate shielding gas should be used based on the type of metal being welded. This helps to prevent oxidation and other impurities from forming in the weld, which can weaken it.
- Welding Angle and Direction: The angle and direction of the welding gun should be maintained consistently throughout the welding process to ensure even penetration and a consistent weld.
- Welding Speed: The welding speed should be consistent and controlled to prevent overheating of the metal and to produce a strong and clean weld.
- Cooling Time: The metal should be allowed to cool sufficiently between welds to prevent overheating and warping of the metal.
By following these techniques and tips, a welder can produce strong, clean, and consistent welds with MIG welding. It is also important to practice and hone your skills over time to become proficient in MIG welding.
MAG Welding
MAG welding is a popular welding technique that is widely used in various industries due to its high efficiency, ease of use, and versatility. In MAG welding, an active gas, such as carbon dioxide, is used along with a wire electrode to create the welding arc and protect the weld from oxidation. This process creates a strong, clean weld that is free of defects and can be completed quickly.
Definition and Explanation of MAG Welding
MAG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is a welding process that uses an active gas, such as carbon dioxide, along with a wire electrode to join two metal parts together. The wire electrode is fed through a welding gun, which creates an electric arc between the wire and the metal parts. The electric arc melts the wire and the metal parts, which then fuse together to form a solid joint.
The Equipment and Tools Needed for MAG Welding
To perform MAG welding, several pieces of equipment and tools are needed, including:
- Welding Machine: A welding machine is required to provide the electrical power needed to create the welding arc.
- Welding Gun: The welding gun is used to hold the wire electrode and create the arc between the wire and the metal parts.
- Wire Electrode: The wire electrode is the filler material used to fuse the metal parts together. It is available in different sizes and types to suit various welding applications.
- Active Gas: An active gas, such as carbon dioxide, is used to create the welding arc and protect the weld from oxidation.
- Regulator: A regulator is needed to control the flow of gas from the tank to the welding gun.
- Protective Gear: Welders must wear protective gear, such as a welding helmet,
Advantages of MAG welding:
- High welding speed: MAG welding is a high-speed welding process, which makes it an efficient method for large-scale production.
- Versatile: MAG welding can be used on a variety of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and mild steel.
- Minimal slag: MAG welding produces minimal slag, which makes it easier to clean and reduces the need for post-welding clean-up.
- Good quality welds: MAG welding produces high-quality welds that have good mechanical properties and are visually appealing.
Disadvantages of MAG welding:
- Limited to flat and horizontal positions: MAG welding is limited to flat and horizontal positions, which makes it difficult to use in vertical or overhead positions.
- Gas shielding required: MAG welding requires a gas shield, which can add to the overall cost of the process.
- Sensitive to wind: MAG welding is sensitive to wind and drafts, which can disrupt the gas shield and affect the quality of the weld.
Applications and uses of MAG welding:
- Automotive manufacturing: MAG welding is commonly used in the automotive industry for the production of frames, bodies, and other components.
- Shipbuilding: MAG welding is used in shipbuilding to join large sections of metal.
- Construction: MAG welding is used in construction for the fabrication of structural steel components.
- Industrial manufacturing: MAG welding is used in the production of machinery and equipment.
Techniques and tips for MAG welding:
- Clean the metal: It’s important to clean the metal before welding to ensure a strong, clean weld.
- Select the right wire: The wire used in MAG welding should be appropriate for the type of metal being welded.
- Use the correct gas: The gas used in MAG welding should be appropriate for the type of metal being welded.
- Maintain the correct distance: The distance between the welding gun and the workpiece should be maintained to ensure a consistent weld.
- Control the travel speed: The travel speed of the welding gun should be controlled to ensure a consistent weld.
- Avoid gaps: Gaps between the metal pieces being welded should be avoided, as they can lead to incomplete penetration and a weak weld.
Comparison of MIG and MAG welding
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and MAG (Metal Active Gas) welding are two commonly used welding techniques that are very similar in terms of their principles and application. However, they differ in terms of the type of shielding gas used during the welding process. MIG welding uses a shielding gas that is inert, such as argon or helium, which does not react with the metal being welded. This type of welding is commonly used for welding aluminum and other non-ferrous metals, as well as for welding thin metal sheets. MIG welding is also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW). On the other hand, MAG welding uses a shielding gas that is active, such as carbon dioxide, which reacts with the metal being welded. This type of welding is commonly used for welding carbon steel, stainless steel, and other ferrous metals. MAG welding is also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW). One of the key differences between MIG and MAG welding is the type of electrode used. In MIG welding, a consumable wire electrode is used, which is fed continuously into the welding gun. The welding arc is created between the wire electrode and the metal being welded, melting the wire and the base metal together to form a weld joint.
In MAG welding, a similar consumable wire electrode is used, but it is coated with a flux that releases an active gas during the welding process. This gas reacts with the metal being welded, creating a welding arc and melting the wire and the base metal together to form a weld joint. Another difference between MIG and MAG welding is the type of welding application they are best suited for. MIG welding is commonly used for welding thin metal sheets and non-ferrous metals, as it provides a precise and clean weld with minimal spatter. On the other hand, MAG welding is best suited for thicker metals, particularly ferrous metals, due to its ability to produce deeper and more penetrating welds. MIG welding is often used in the automotive and aerospace industries, as well as for hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts who work with metal. It is also commonly used in the welding of aluminum, copper, and other non-ferrous metals, as well as for welding thin sheets of steel. MAG welding, on the other hand, is often used in heavy-duty industrial applications such as shipbuilding, construction, and heavy machinery manufacturing. It is particularly useful for welding thicker steel plates and other ferrous metals, such as those used in the construction of buildings, bridges, and other large structures.
Overall, the choice between MIG and MAG welding depends on the specific needs of the welding project, such as the type and thickness of the metal being welded, the desired finish, and the available equipment and resources.
FAQs
What is better MIG or MAG welding?
MIG and MAG welding are both arc welding processes that use a wire electrode to join metal. The main difference between them is the type of gas used as a shielding gas. MIG welding uses pure argon or a mixture of argon and helium as a shielding gas, while MAG welding uses a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide.
Can you mag weld with a MIG welder?
It is possible to perform MAG welding using a MIG welder, but it requires a different type of wire and a different gas mixture.
What is MAG welding used for?
MAG welding is commonly used for welding carbon steels, stainless steels, and aluminum alloys in a variety of industries, including automotive, shipbuilding, and construction.
Is CO2 welding MIG or MAG?
CO2 welding is also known as MAG welding, as it uses a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide as the shielding gas.
What are the disadvantages of MAG welding?
The disadvantages of MAG welding include a higher risk of spatter, a less stable arc, and the need for more frequent cleaning of the nozzle and contact tip.
What is MAG welding called?
MAG welding is also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW).
Which welding is strongest?
The strength of a weld depends on various factors, including the materials being joined, the welding process used, and the skill of the welder. Generally, a properly executed weld will be strong enough for its intended use.
Which type of welding is best?
The best welding process depends on the specific application and materials being joined. MIG and MAG welding are both widely used and can produce high-quality welds when done correctly.
What are the 3 disadvantages of MIG welding?
Some disadvantages of MIG welding include a lower deposition rate, the need for a clean welding surface, and a higher risk of porosity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and MAG (Metal Active Gas) welding are effective and commonly used welding techniques in the industry. However, the main difference between the two is the type of gas used in the welding process. MIG welding uses an inert gas such as argon while MAG welding uses an active gas such as carbon dioxide.
MIG welding is preferred for welding non-ferrous metals, while MAG welding is used for welding ferrous metals. MIG welding is also preferred for welding thin materials, while MAG welding is used for welding thicker materials. Additionally, MAG welding can produce deeper penetration and faster welding speeds than MIG welding.
Ultimately, the choice between MIG and MAG welding depends on the specific welding requirements and the materials being welded. Both techniques have their own advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to choose the right welding method for the job in order to achieve the best possible results.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders