Thermit welding Process
Introduction
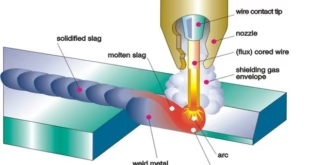
Thermit welding is a process in which a thermite mixture, composed of metal powder and a metallic oxide, is ignited and burns at a very high temperature to melt the metal and fuse two pieces of metal together. Thermit welding is different from traditional welding methods such as arc welding, gas welding, and resistance welding as it does not require an external heat source or an electric current. Thermit welding offers many advantages such as the ability to weld large or heavy pieces of metal, the ability to weld in remote or inaccessible locations, and the ability to weld metals with different melting points.
Chemical energy stored in a variety of forms can be used for welding purposes. First chemical energy is converted into heat energy, and then this heat energy is used as heat for welding purposes. There are classified into two types; oxyfuel welding processes and thermit welding processes. The term “thermit welding” is derived from “thermite,” which is a generic term for a reaction between metal oxides and reducing agents. The thermite mixture consists of metal oxides and metallic-reducing agents. The metal oxides have low heats of formation after oxidation converted to high heats of formation. This produced excess heat of formation of the reaction products is thus used to provide the required heat in welding formation.
Thermit welding is a type of welding that uses heat that is generated from exothermic chemical reactions to produce coalescence (merging two materials to form one mass). The aluminothermic process occurs between aluminum powder and metal oxide, where aluminothermic reactions are a chemical reaction that uses aluminum as the reducing agent at high temperature. As a result of this reaction molten metal is generated that is used as filler metal for joining the workpieces in the welding process. Hence, no external heat, current, or filler material is not required in thermit welding.
For example: If aluminum and metal oxide are reacted through external heat the aluminothermic reaction occurs will occur through the following equation:
Metal Oxide + Aluminum → Aluminum oxide + Metal + Heat
Following are common examples of thermit welds reactions with heat produced:
The ignition temperature of the thermit granules used for welding is about 1200°C (2200°F) so it is safe from fire hazards.
The combustion of iron and aluminum oxide produces heat up to 4500°F. As iron and aluminum oxide have different densities, they become separated automatically. The liquid iron fills the ceramic mold built around the welding parts while aluminum oxide slag floats up and is removed subsequently. Copper and Chromium metals have thermit mixtures that use different metal oxides instead of ferrous oxide.
The thermit process was developed by Hans Goldschmidt in the mid of 1890s. It is used in welding steel casting and forging. Thermite welding for developed basically for joining rail track joining, joining steel pipes, and steel wire work. Thermit welding is a chemical welding process that uses exothermic reactions to provide the required heat energy. For a thermit reaction, a mixture of aluminum powder and iron oxide in a ratio of 1:3 by weight produces heat energy with a temperature reading of 3000°C. To start or initiate the thermit mixture, preheating temperature requirement is 1300 °C.
Steps of Thermit Welding
Following are important steps for Thermit welding:
- It is compulsory to clean the metal parts to be welded. Also, prepare the edges of metals properly
- The wax pattern is also needed for the joint to be fused. Pour some hot wax on it to obtain the one.
- Then place the molding box around the joint and the sand is loaded all over the wax pattern very carefully. It provides the necessary pouring basin, riser, sprue, and gating system.
- The bottom opening is used to drain the molten wax. It helps to preheat the joint to be ready for welding
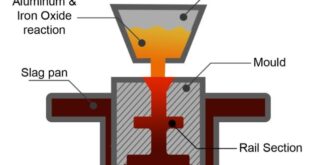
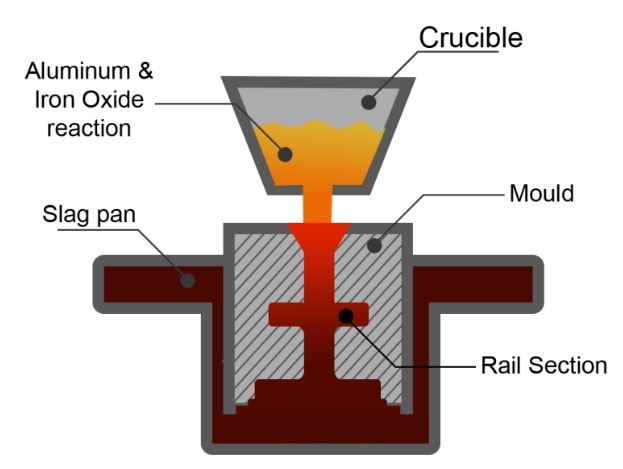
- It is time to mix the Thermit in a crucible (a vessel where a thermit chemical reaction takes place). This is made from refractory material to withstand the extreme heat and pressure which is produced during this aluminothermic reaction.
- The igniter i.e., barium oxide or magnesium is put on the mixture and lighted with red hot metal rods.
- This reaction is completed in a very short time, a highly heated molten iron flows into the cavity around the joint to be welded.
- The molten material joins both metals and solidifies into a smooth strong joint.
- The welded joint cools down slowly.
Thermit Welding Process
Thermit welding is a process that uses a thermite mixture, consisting of metal powder and a metal oxide, to create a high-temperature exothermic reaction. The heat generated by this reaction is used to melt the ends of two pieces of metal, which are then joined together. The process can be used to weld various types of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper.
The general outline of the process is as follows:
- Prepare the joint by cleaning and aligning the ends of the metal pieces to be welded.
- Place the thermite mixture into a crucible, and position the crucible between the two pieces of metal.
- Ignite the thermite mixture, which generates heat and melts the metal in the crucible.
- As the metal in the crucible melts, it is poured into the joint between the two pieces of metal, filling any gaps and fusing the two pieces together.
- Allow the metal to cool and solidify, completing the welding process.
It is a very precise process and requires skilled and trained personnel to execute it.
Applications of Thermit welding
- Thermit welding is commonly used in the railway industry for the repair and maintenance of rail tracks.
- Thermit welding is also used in the pipeline industry for the repair and maintenance of pipelines.
- Thermit welding is used in the construction of industrial structures such as factories and power plants.
- Thermit welding is also used for repairs and maintenance of equipment and machinery.
Safety and Quality Control in Thermite Welding
Thermite welding is a highly specialized form of welding that uses a thermite mixture, which is ignited to produce an extremely high temperature flame. Safety and quality control are critical when performing thermite welding. Safety measures include proper training and the use of personal protective equipment such as heat-resistant gloves, face shields, and flame-retardant clothing. The thermite mixture and the reaction area should be kept away from flammable materials and there should be a fire extinguisher on hand in case of an accident. Quality control measures include proper preparation of the thermite mixture, ensuring that the reaction area is clean and free of debris, and the use of a suitable ignition device. The weld should be inspected for proper alignment, penetration, and overall quality. Additionally, The welding process should be performed in a well-ventilated area, and all precautions should be taken to avoid inhaling the fumes produced by the thermite reaction.
FAQs
Which metal is commonly used in thermit welding?
Iron oxide and aluminum are commonly used in thermite welding.
Why is thermite welding important?
Thermite welding is important because it allows for high-temperature welding to be done without the need for an external power source or flame.
How heat is generated in thermit welding process?
Heat is generated in the thermite welding process through a chemical reaction between the iron oxide and aluminum, known as a thermite reaction.
Which gas is used in thermite welding?
No gas is used in thermite welding.
Can thermite burn underwater?
Thermite cannot burn underwater as it requires oxygen to sustain the chemical reaction.
What is another name of thermite process?
Another name for the thermite process is exothermic welding.
Can thermite burn through steel?
Thermite can burn through steel, but it is not typically used for this purpose.
Which catalyst is used in thermite reaction?
A metal oxide, such as ferric oxide, is used as a catalyst in the thermite reaction.
What is the main purpose of the thermite process?
The main purpose of the thermite process is to create a high-temperature heat source for welding and other industrial applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thermite welding is a highly efficient and reliable method for joining rail tracks. It utilizes a thermite mixture, which when ignited, produces extremely high temperatures that melt the ends of the rail tracks. The molten metal is then poured into a mold, where it cools and solidifies, creating a strong and durable joint. This method is faster and more cost-effective than traditional methods such as gas or arc welding, and it does not require the use of electricity or other specialized equipment. However, it does require specialized training and safety precautions must be taken to prevent injury or damage to equipment. Overall, thermite welding is a valuable tool for maintaining and upgrading rail infrastructure.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders