Unveiling the Undercut in Welding
Welding, a crucial industrial process, is not without its challenges. One such challenge that often goes unnoticed but can significantly compromise weld integrity is “undercut.” In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of undercut in welding, exploring its causes, identification methods, impact on joints, prevention strategies, and much more.
Introduction
Definition of Undercut in Welding
Undercut is a common welding defect characterized by a groove or depression along the weld toe or weld face. This defect can weaken the joint and lead to structural issues if not addressed promptly.
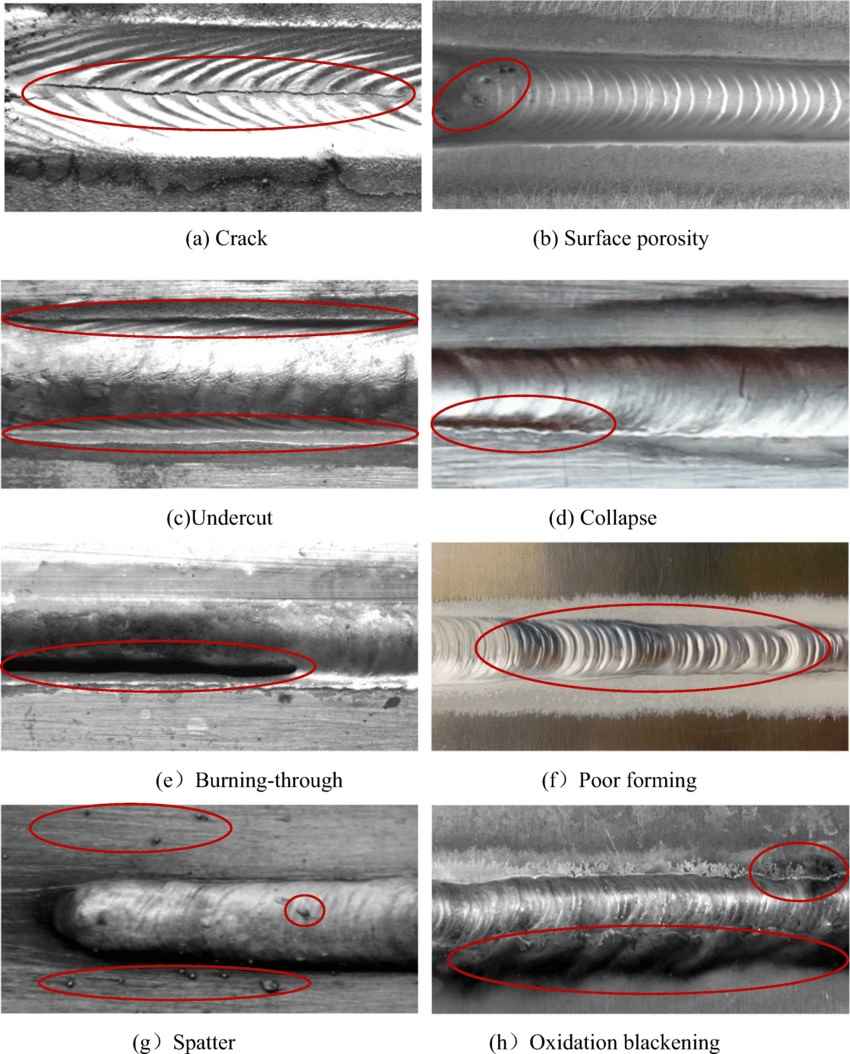
Importance of Addressing Undercut Issues
Understanding and addressing undercut is vital for maintaining the integrity of welded structures. Ignoring undercut can result in catastrophic failures, posing risks to both safety and the longevity of welded components.
Causes of Undercut
Welding Parameters
Inconsistent welding parameters, such as improper current, voltage, or travel speed, can contribute to undercut formation. Adjusting these parameters to match material specifications is crucial in preventing undercut.
Poor Welding Techniques
Improper techniques, like excessive weaving or improper torch angles, can lead to undercut. Welders must be trained in best practices to minimize the risk of undercut during welding.
Inadequate Equipment
Using substandard welding equipment can contribute to undercut. Quality welding machines, electrodes, and protective gases are essential for achieving strong and defect-free welds.
Identifying Undercut
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is the first line of defense against undercut. Welders and inspectors should be trained to recognize the signs of undercut, including visible grooves or depressions.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Methods
In addition to visual inspection, non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic testing or radiography can be employed to detect undercut that may not be visible to the naked eye.
Impact on Welded Joints
Structural Weakness
Undercut significantly compromises the structural integrity of welded joints, making them more susceptible to failure under stress or load.
Corrosion Susceptibility
The presence of undercut creates pockets where corrosion can initiate, leading to long-term damage to the welded structure. Preventing undercut is key to enhancing corrosion resistance.
Prevention and Best Practices
Adjusting Welding Parameters
Regularly calibrating welding machines and ensuring proper parameters based on material specifications are essential steps in preventing undercut.
Proper Welding Techniques
Training welders in proper techniques, including maintaining a consistent travel speed and avoiding excessive weaving, can go a long way in preventing undercut.
Quality Equipment Usage
Investing in high-quality welding equipment, electrodes, and protective gases ensures a more stable and controlled welding process, minimizing the risk of undercut.
Common Misconceptions about Undercut
Undercut vs. Weld Penetration
Clarifying the difference between undercut and weld penetration is essential to dispel common misconceptions and promote accurate understanding.
Addressing Myths About Prevention Methods
Debunking myths surrounding prevention methods helps welders adopt effective strategies without falling prey to misinformation.
Undercut as a Surface Defect
Contrary to popular belief, undercut is not just a surface defect. It can extend deep into the weld, compromising the overall strength of the joint.
Relation to Welding Material Thickness
Undercut can occur in welds of varying material thicknesses. It’s not exclusive to thin or thick materials, emphasizing the need for consistent prevention measures.
Real-world Examples
Case Studies on Undercut Remediation
Examining real-world case studies where undercut issues were successfully addressed provides valuable insights into effective remediation strategies.
Success Stories in Weld Quality Improvement
Highlighting success stories of industries that implemented robust undercut prevention measures and witnessed significant improvements in weld quality.
Advanced Welding Technologies
Automation in Welding Processes
Automated welding processes, with precise control over parameters, can significantly reduce the risk of undercut. Robotics play a crucial role in achieving high-quality welds consistently.
Robotics and Undercut Mitigation
Exploring how robotics and automation technologies are being utilized to mitigate undercut by ensuring precision and repeatability in welding processes.
The Role of Welding Inspections
Regular Inspections for Early Detection
Establishing regular inspection routines is critical for the early detection of undercut. Identifying and addressing undercut in its early stages can prevent more extensive damage.
Impact of Undercut on Welding Certification
The presence of undercut can impact welding certification. Understanding the criteria for certification and ensuring compliance is essential for welders and industries alike.
Overcoming Challenges in Undercut Removal
Post-Weld Treatment Options
Exploring post-weld treatment options, such as grinding or re-welding, to effectively remove undercut and restore the integrity of the welded joint.
Collaboration between Welders and Inspectors
Emphasizing the importance of collaboration between welders and inspectors in addressing undercut challenges. Effective communication is key to successful mitigation.
Undercut in Different Welding Types
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Examining how undercut manifests in GMAW processes and the specific considerations required for preventing and addressing it in this welding type.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Understanding the challenges and solutions related to undercut in SMAW, a widely used welding process in various industries.
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Highlighting specific considerations for preventing and addressing undercut in submerged arc welding, particularly in large-scale and automated applications.
Future Trends in Weld Quality Assurance
Innovations in Welding Technology
Exploring emerging technologies that are shaping the future of welding and how these innovations contribute to higher-quality welds with reduced undercut risks.
Industry Standards and Evolving Practices
The role of industry standards in shaping welding practices and how evolving standards contribute to improved weld quality and reduced undercut instances.
Case-specific Undercut Solutions
Tailoring Solutions to Unique Welding Projects
Recognizing that each welding project is unique and may require specific solutions for undercut prevention and remediation.
The Role of Welding Engineers in Mitigating Undercut
Highlighting the crucial role of welding engineers in analyzing, preventing, and addressing undercut issues in complex welding projects.
Importance of Continuous Learning
Professional Development for Welders
Encouraging welders to engage in continuous learning and professional development to stay updated on the latest techniques and technologies for preventing undercut.
Staying Updated on Welding Techniques and Technologies
The significance of staying informed about advancements in welding techniques and technologies to adapt and enhance undercut prevention strategies.
FAQs
Is undercut only a visual issue, or does it affect the strength of the weld?
Undercut extends beyond the surface and significantly weakens the structural integrity of the weld.
Can automated welding processes completely eliminate the risk of undercut?
While automation reduces the risk, proper calibration and oversight are still necessary to prevent undercut.
How often should welding inspections be conducted to detect undercut early?
Regular inspections, at least after every significant welding project, are essential for early undercut detection.
Does the thickness of the welding material affect the likelihood of undercut?
Undercut can occur in welds of varying material thicknesses, emphasizing the need for consistent prevention measures.
What role do welding engineers play in mitigating undercut in complex projects?
Welding engineers analyze, prevent, and address undercut issues in complex projects, ensuring the highest quality welds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and effectively addressing undercut in welding are crucial for ensuring the longevity and safety of welded structures. By identifying causes, implementing preventive measures, and staying abreast of industry advancements, welders can minimize the impact of undercut and contribute to a stronger, more resilient welding industry.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders



