What is Argon Welding?
Introduction
Explanation of welding
Welding is the process of joining two or more materials, typically metals, by melting and fusing them together. It is an important process used in various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and repair. Welding requires a heat source, filler material, and shielding gas to protect the weld area from contamination and oxidation.
Overview of Argon Welding
Argon welding, also known as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), is a type of welding process that uses an inert gas, typically argon, to shield the weld area from atmospheric gases. This process is commonly used to weld aluminum, stainless steel, and other non-ferrous metals. Argon welding is known for its high quality, precision, and versatility, making it a popular choice in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical.
What is Argon Welding?
Definition of Argon Welding
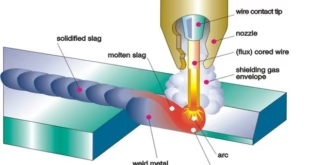
Argon welding is a type of welding process that uses an electric arc between a tungsten electrode and the workpiece to melt and fuse two or more metals together. During the process, a stream of argon gas is used to shield the weld area from atmospheric gases and prevent oxidation.
Importance of Argon Welding
Argon welding is important because it provides a high-quality, clean weld that is free from defects such as porosity, cracks, or contamination. This process is particularly useful for welding thin materials and for welding materials that are sensitive to oxidation, such as aluminum and stainless steel. Argon welding also allows for precise control over the welding process, making it a popular choice for intricate welding applications.
Types of Argon Welding
There are several types of argon welding, including manual GTAW, automatic GTAW, and pulsed GTAW. Manual GTAW involves using a handheld torch to manually control the welding process. Automatic GTAW involves using a machine to control the welding process, and pulsed GTAW involves pulsing the welding current to achieve better control over heat input and weld penetration.
How does Argon Welding work?
Explanation of the welding process
Argon welding works by creating an electric arc between a tungsten electrode and the workpiece. The tungsten electrode is held in a torch and is used to create the arc, while the workpiece is held in a clamp or fixture. The arc creates a high temperature, which melts the base metal and the filler material, if used, forming a weld pool.
Role of Argon gas in the process
During the welding process, a stream of argon gas is used to shield the weld area from atmospheric gases and prevent oxidation. Argon is an inert gas, meaning that it does not react with other elements or compounds. This makes it an ideal gas for shielding the weld area, as it will not cause any chemical reactions or contamination.
Equipment used in Argon Welding
The equipment used in argon welding includes a welding machine, a tungsten electrode, a welding torch, a power source, and a shielding gas supply. The welding machine provides the power source for the welding process, while the tungsten electrode and the welding torch are used to create the arc. The shielding gas supply provides a stream of argon gas to shield the weld area from atmospheric gases.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Argon Welding
Advantages
Argon welding has several advantages, including:
- High-quality welds: Argon welding produces high-quality welds that are free from defects such as porosity and cracks. This is due to the shielding gas used, which protects the weld area from atmospheric gases that can cause defects in the weld.
- Precise control: Argon welding allows for precise control over the welding process, making it ideal for intricate welding applications. This control over the process allows welders to create precise welds that meet specific requirements.
- Clean welds: Argon welding produces clean welds that are free from contamination and oxidation. This is due to the inert nature of the shielding gas, which does not react with the base metal or filler material.
- Suitable for a variety of metals: Argon welding is suitable for welding a variety of metals, including aluminum and stainless steel. This makes it a versatile process that can be used in various industries.
Disadvantages
Argon welding also has some disadvantages, including:
- High skill level required: Argon welding requires a high level of skill and training to perform correctly. This is due to the precision required in the welding process and the need for control over the heat input.
- Expensive equipment: Argon welding equipment can be expensive, especially for high-end machines that offer greater control and precision.
- Slow welding speed: Argon welding can be slower than other welding processes, such as MIG welding, due to the need for precise control and slower heat input.
- Limited penetration: Argon welding may not penetrate as deeply as other welding processes, such as stick welding or flux-cored welding, which can limit its use in some applications.
Applications of Argon Welding
Industries where Argon Welding is commonly used
Argon welding is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. It is also used in industries that require high-quality welds, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
Specific applications of Argon Welding
Specific applications of Argon welding include welding of aluminum and stainless steel components in aircraft and aerospace industries, welding of medical devices and implants, and welding of precision components in electronics and semiconductor industries.
Safety in Argon Welding
Importance of safety in welding
Safety is a critical aspect of Argon welding, as it involves high temperatures, high voltage, and hazardous gases. Welders must take the necessary safety precautions to protect themselves and others from potential hazards.
Safety measures to take during Argon Welding
Some safety measures to take during Argon welding include wearing proper protective equipment such as helmets, gloves, and clothing, using ventilation systems to remove hazardous gases, and properly grounding the welding equipment to prevent electrical shocks.
FAQs
What is argon welding used for?
Argon welding is commonly used for welding non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and titanium. It is also used for welding stainless steel and other high-quality materials that require precise control over the welding process.
What is argon welding called?
Argon welding is also known as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), and Heliarc welding.
Is argon and TIG welding the same?
Argon gas is commonly used as the shielding gas in TIG welding. However, TIG welding refers to the specific welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld, while argon gas is used as the shielding gas in this process.
Is argon good for welding?
Yes, argon gas is an excellent choice for welding because of its inert properties. It does not react with the base metal or filler material, producing clean welds free from oxidation and contamination.
What are 5 uses for argon?
Argon gas has several uses, including:
- Welding: Argon gas is commonly used as a shielding gas in TIG welding.
- Lighting: Argon gas is used in fluorescent light bulbs and other gas discharge lamps.
- Refrigeration: Argon gas is used in refrigeration systems to cool and preserve food and other perishable items.
- Semiconductor manufacturing: Argon gas is used in the manufacturing of semiconductors and other electronic components.
- Medical applications: Argon gas is used in medical applications, such as laser surgery and cryosurgery.
Which material is used for argon welding?
Argon welding is commonly used for non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and titanium. It is also used for welding stainless steel and other high-quality materials.
Which welding is the strongest?
Different welding techniques are suitable for different applications and materials. However, generally, welding techniques such as TIG welding and stick welding can produce strong welds.
Is argon gas flammable?
No, argon gas is not flammable. It is an inert gas and does not react with other elements or compounds.
What color is argon?
Argon gas is colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
What type of gas is argon?
Argon is a noble gas, also known as an inert gas. It is non-reactive and does not readily form chemical compounds with other elements.
What is called inert gas?
An inert gas, also known as a noble gas, is a group of chemical elements that are non-reactive and do not easily form chemical compounds with other elements. Some common inert gases include helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Argon welding is a versatile and precise welding process that produces high quality, clean welds suitable for a variety of industries. While it requires a high level of skill and expensive equipment, it offers several advantages such as precise control over the welding process and the ability to weld a variety of metals. By taking proper safety precautions, welders can perform Argon welding safely and effectively.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders