What is the Function of Flux in Welding?
Introduction
Flux is a material that plays a critical role in the welding process. It is used to improve the quality and consistency of a weld by cleaning the metal surfaces, protecting the weld from oxidation and other contaminants, and providing a consistent flow of molten metal. In this article, we will be discussing the functions of flux in welding, its benefits and usage, and how it affects the overall quality of the weld.
Welding flux is a material that is used in certain types of welding to protect the weld pool and surrounding base metal from atmospheric contamination, remove impurities from the base metal, and prevent the formation of oxides in the weld metal. The flux also helps to shape the weld pool and provides a smooth, uniform surface on the weld. There are two types of welding flux: active and inactive. Active welding fluxes contain ingredients that react with the base metal to form slag, which solidifies on the surface of the weld and protects the weld from oxidation and contamination. Inactive welding fluxes do not react with the base metal and are used primarily to protect the weld pool from oxidation and contamination.
What is Welding Flux?
Welding flux is combinations of various materials such as silicate and carbonates, it is used to form a protective layer in welding process that prevents contamination of gases in welding process.
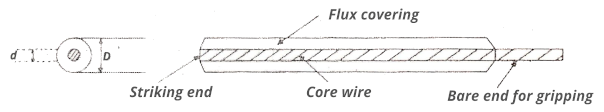
As the flux has less density as compared to metal to be welded, so flux melts and floats above the weld. The flux is always present in outer layer of welding electrodes. The core wire is in the middle and flux layer covers the core wire, the other end of core wire is kept that is used for gripping. Hence the welding flux helps in protecting the weld from contamination of gases during the welding process.
Types of flux coatings
There are different types of flux coatings based on welding power source, material to be welded, applications of the welding. Following are types of flux coatings for electrodes
- Cellulose type
- Rutile electrode type
- Acid type
- Acid rutile type
- Basic rutile type
- Oxidizing type
- Basic type
Flux Coating Material of Welding Electrode
The flux coating materials of welding electrodes are used based on the application. The details of few types of coating materials are as follow:
- Flux agents: Silica, Calcium oxide (CaO), Dolomite, Lime, Borax, and Fluorite.
- Slag formers: Titania, Titanate, Rutile, Asbestos, Silica flour, Alumina, Feldspar, Iron powder, Titania, Potassium titanate, Manganese dioxide.
- Arc stabilizers: Potassium silicate, Zirconium carbonate, Potassium oxalate, Potash, Feldspar, Lithium carbonate, Titania.
- Gas forming materials: Limestone, cellulose, Wood flour.
- Binding agents: Dextrin, Sodium silicate, Potassium silicate, Asbestos, Gum, Sugar.
- Deoxidizers and alloying materials: Ferrosilicon, Ferrotitanium, Ferrochromium, Ferromanganese, Ferromolybdenum, Electro-nickel, Electro-manganese, and metals in powdered form.
- Slipping agents: Glycerin, Kaolin clay, Talc, Bentonite clay, Mica, China clay.
Functions of Flux in Welding Process
The purpose of flux coating is shielding the molten metal from contamination with atmospheric gasses. The flux coating form a shielding gas and slag and protects the molten metal metal from contamination. Flux coating provides ease in striking assistance and arc stability. It also helps in controlling the shape of arc. It helps increase the penetration power. It can be helpful in using alloys in welding. It helps in avoiding cold cracking as it controls the hydrogen gas. It helps in removing slag easily. It helps in monitoring and controlling mechanical properties if welding.
Welding flux is a material that is used in certain types of welding, such as gas metal arc welding (GMAW) and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW). It serves several important functions, including:
- Acting as a protective barrier to shield the weld pool and surrounding base metal from atmospheric contamination
- Acting as a cleaning agent to remove oxides and other impurities from the surface of the base metal
- Acting as a deoxidizer to prevent the formation of oxides in the weld metal
- Acting as a slag-forming agent to protect the weld metal from oxidation and to provide a smooth, uniform surface on the weld
When used properly, welding flux can improve the overall quality of the weld by reducing porosity, improving penetration, and increasing the strength and ductility of the weld. However, if the flux is not properly cleaned off after the welding process, it can lead to poor weld quality and potential corrosion issues.
Applications of Flux Coating on Electrodes
Following are the applications of flux coating on electrodes:
- In welding process, the flux melts and creates a shielding layer around the arc. This layer prevents the weld from contamination of atmospheric gases.
- It also plays an important role when it deoxidizes and refines the welding metal from chemical reactions.
- The welding flux also plays important role in controlling the arc voltage and current intensity.
- It prevents hardening by slowing down cooling time etc.
- It Increases filler rod flow and creates a stronger bond and eliminates problems such as porosity.
- It allows for difficult metals to be welded both to each other, as well as a variety of other materials.
- It is also helpful in reducing the amount of weld spatter that produces during welding.
- The welding flux melts and creates shield which is also helpful in shielding molten weld puddle.
- The slag produced on the weld metal protects it from the atmosphere.
- It is also helpful in producing a smooth finishing on weld surface and also controls weld bead profile to form.
- Flux coating helps to get higher currents without getting overheat as flux coating insulate the electrode which is helpful for higher currents.
- Sometimes, iron power or ferro-alloys are added in flux material to increase the weld deposition rates.
- Vertical and overhead welding is also possible by controlling the viscosity of the slag (using different types of coating materials i.e., flux coating).
FAQs
What are the benefits of using flux in our weld?
Flux is a material that is used to improve the quality and consistency of a weld by cleaning the metal surfaces and protecting the weld from oxidation and other contaminants. Some benefits of using flux in welding include:
- Improving the quality of the weld by reducing porosity and spatter
- Protecting the weld from oxidation and other contaminants
- Improving the consistency of the weld by stabilizing the arc and providing a consistent flow of molten metal
In which method flux is used for welding?
Flux is typically used in arc welding methods, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW).
What is the purpose of flux on the electrode?
The purpose of flux on the electrode is to provide a protective layer around the electrode, which helps to stabilize the arc and protect the weld from oxidation and other contaminants.
What are the five functions of flux?
The five main functions of flux in welding are:
- Cleaning the metal surfaces
- Protecting the weld from oxidation and other contaminants
- Stabilizing the arc
- Providing a consistent flow of molten metal
- Improving the overall quality of the weld
Where should flux be applied?
Flux should be applied to the surfaces of the metal that will be welded, before the weld is made.
Is flux welding strong?
Flux welding is strong, as it provides a consistent flow of molten metal, which helps to improve the overall quality of the weld.
Does flux core need gas?
Flux-cored welding does not need gas, as the flux is already present in the electrode.
Should you always use flux? When should you use flux?
Flux is not always necessary for welding, but it can be beneficial for certain types of welding, such as welding dirty or rusty metal or when welding in outdoor conditions where wind or drafts may affect the weld. It is important to determine the welding process and conditions before deciding whether to use flux or not.
What is welding flux powder and its uses?
welding flux powder is a type of chemical called cleaning or purifying agent. This chemical is used to assist fusion of metals or welding. It has its major uses in metal joints or metallurgy. It is used to reduce the temperature on surface of metal. It protects the surface from contamination and erosion.
What is flux core welding used for?
The flux core welding is a welding process used for welding dirty, rusted, or contaminated metals. This welding process use a flux core shield that’s why it is best for all types of welding projects and all welding positions. The flux cored arc welding process is easy method and is not difficult to learn and perform.
What are safety measures for flux core welding?
Standard safety measures must always be taken while performing any kind of welding task. Always make sure to have a proper safety suit so that the potential fire risks are removed from welding place. Proper welding safety suit must include leather boots, no cuff sleeves, safety cap at the head so that your head don’t get injured in case of sparks and spatter. AWS have provided detailed guideline for safety standards that should be followed in any type of welding task. Always take right precautions according to the safety standards.
What is flux in gas welding?
In gas welding, flux is a mixture of chemicals or alloys . The flux in gas welding protects the molten weld metal from contamination with oxygen and nitrogen present in the atmosphere. The flux also helps in controlling arc stability, striking assistance and mechanical properties.
What happens when welding without flux?
Welding without flux is possible but the final product is not of high quality. Without flux the weld would be sputtery and messy as the flux is absent that smooths the flow of the molten metal during welding. Without shielding gas or flux the welding joint would be a brittle weak weld. And there can be holes in your welding these holes are called porosity.
Why is flux needed in welding?
There are many reasons for which the flux is necessary for welding. The flux helps in arc striking and stability. It protects the molten meatal after shielding it. The welding flux melts and creates shield which is also helpful in shielding molten weld puddle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, flux is an essential component of the welding process. It serves multiple functions, including cleaning the metal surfaces, protecting the weld from oxidation and other contaminants, stabilizing the arc, providing a consistent flow of molten metal, and improving the overall quality of the weld. Its usage is not always necessary, it depends on the welding process and conditions, but it can be beneficial for certain types of welding. Understanding the functions of flux and its proper usage is crucial for achieving high-quality welds and ensuring the safety of the welder. By understanding the role of flux in welding, welders can make more informed decisions about which welding techniques and materials to use for a specific project.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders