Tubular Cored Wire Welding
Introduction
The welding industry has witnessed significant advancements in technology, and one notable innovation that has gained prominence is Tubular Cored Wire Welding. This method represents a sophisticated approach to joining metals, offering distinct advantages over traditional welding techniques.
Definition
Tubular cored wire welding is a specialized welding process that utilizes a tubular electrode filled with various materials, such as flux or metal powders, to facilitate the welding operation. This method falls under the broader category of arc welding and comes in different variations, each tailored to specific applications and welding requirements.
Importance in the Welding Industry
The importance of tubular cored wire welding in the welding industry cannot be overstated. This method has emerged as a go-to solution for fabricators and welders due to its unique set of advantages. From increased deposition rates to enhanced welding efficiency, tubular cored wire welding offers a versatile and efficient approach to joining metals, making it a key player in the contemporary welding landscape.
Brief History and Evolution
The roots of tubular cored wire welding can be traced back to the mid-20th century when welding professionals sought alternatives to traditional welding processes. Over the years, the method has evolved through extensive research and development, leading to the refinement of techniques, materials, and equipment. Understanding the historical context of tubular cored wire welding provides valuable insights into its evolution and the factors that have contributed to its current prominence in the welding industry.
Types of Tubular Cored Wires
Tubular cored wires are a diverse family of welding consumables, each designed to cater to specific welding applications. Two prominent subtypes within this category are Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) and Metal-Cored Arc Welding (MCAW).
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Self-shielded FCAW
Self-shielded flux-cored arc welding involves a tubular electrode filled with flux compounds that generate a protective atmosphere when exposed to the heat of the arc. This eliminates the need for external shielding gases, making it a convenient and versatile option, particularly in outdoor welding environments. Self-shielded FCAW is often preferred for its portability and ease of use.
Gas-shielded FCAW
Gas-shielded flux-cored arc welding employs an external shielding gas to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contaminants. This method enhances the overall quality of the weld and allows for greater control over the welding process. Gas-shielded FCAW is commonly used in applications where precision and weld aesthetics are paramount, such as in fabrication shops and manufacturing plants.
Metal-Cored Arc Welding (MCAW)
Composition and Characteristics
Metal-cored arc welding utilizes a tubular electrode filled with a core of metallic powders. This unique composition combines the benefits of both solid wire and flux-cored wire welding, offering improved weld quality, higher deposition rates, and increased travel speeds. The metal core provides stability to the arc and contributes to the mechanical properties of the weld.
Advantages over Solid Wires
Metal-cored arc welding presents distinct advantages over traditional solid wire welding. The increased deposition rates and improved penetration of metal-cored wires make them highly efficient, reducing overall welding time. Additionally, the composition of metal-cored wires enhances the mechanical properties of the weld, making it a preferred choice in applications where strength and durability are critical.
Advantages of Tubular Cored Wire Welding
Tubular cored wire welding has gained widespread acceptance in the welding industry due to its numerous advantages, making it a preferred choice for welders and fabricators across various applications.
Increased Deposition Rates
One of the standout advantages of tubular cored wire welding is the significant increase in deposition rates compared to traditional welding methods. The composition of the tubular wire allows for a higher volume of filler material to be deposited in a shorter time, resulting in faster welding processes. This increased efficiency is particularly beneficial in large-scale welding projects where productivity is a key consideration.
Enhanced Welding Efficiency
Tubular cored wire welding offers enhanced welding efficiency by optimizing the heat input and arc stability. The unique composition of the tubular wire, whether filled with flux or metal powders, contributes to a stable arc and better control over the welding parameters. This improved efficiency translates to reduced downtime, lower energy consumption, and ultimately, cost savings for welding operations.
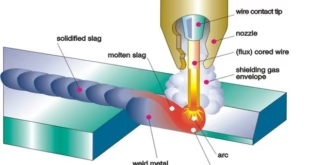
Improved Penetration and Fusion
The design and characteristics of tubular cored wires contribute to improved penetration and fusion in the welding process. This is especially advantageous when welding thicker materials or when dealing with challenging joint configurations. The ability of tubular cored wires to provide deeper weld penetration ensures better joint integrity and weld quality, meeting the stringent requirements of various welding applications.
Reduction in Welding Fume Emissions
In comparison to certain other welding methods, tubular cored wire welding often results in reduced welding fume emissions. This is particularly true in the case of self-shielded flux-cored arc welding, where the flux compounds within the wire generate a protective atmosphere, minimizing the release of harmful fumes into the surrounding environment. This reduction in fume emissions contributes to a safer and healthier workplace for welding professionals.
Versatility in Various Welding Applications
Tubular cored wire welding stands out for its versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of welding applications. Whether in structural welding, pipeline construction, heavy equipment fabrication, shipbuilding, or the automotive industry, the adaptability of tubular cored wires allows welders to address diverse challenges effectively. This versatility makes tubular cored wire welding a go-to choice for industries with varied welding needs.
Applications of Tubular Cored Wire Welding
Tubular cored wire welding has found widespread application across various industries, owing to its versatility, efficiency, and ability to meet the specific demands of different welding scenarios. Here, we explore key applications where tubular cored wire welding has proven to be particularly advantageous.
Structural Welding
Tubular cored wire welding plays a crucial role in structural welding, where the fabrication of beams, columns, and other load-bearing elements demands a combination of strength and efficiency. The increased deposition rates and improved penetration of tubular cored wires make them well-suited for the rapid and robust joining of structural components. This application is essential in the construction of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
Pipeline Welding
In the construction and maintenance of pipelines, where weld quality and integrity are paramount, tubular cored wire welding shines. The method’s ability to provide deep penetration and high deposition rates is particularly advantageous in the welding of long-distance pipelines. Whether in the oil and gas industry or other pipeline applications, tubular cored wire welding ensures reliable and durable welds.
Heavy Equipment Fabrication
The fabrication of heavy equipment, such as bulldozers, excavators, and industrial machinery, demands welding processes that can handle thick materials and provide efficient, high-quality welds. Tubular cored wire welding, with its enhanced efficiency and penetration capabilities, is well-suited for heavy equipment fabrication. This application contributes to the production of durable and reliable machinery used in various industries.
Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding requires welding methods that can withstand the harsh conditions of marine environments. Tubular cored wire welding, with its ability to provide deep penetration and high-quality welds, is widely employed in shipbuilding. The versatility of this welding method allows shipbuilders to address different materials and joint configurations, ensuring the structural integrity of vessels in the challenging conditions they may encounter at sea.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, where precision and efficiency are crucial, tubular cored wire welding finds applications in the fabrication of vehicle components. From chassis assembly to bodywork, the increased deposition rates and improved weld quality contribute to the manufacturing of durable and lightweight automotive structures. Tubular cored wire welding is particularly valuable in the production of high-strength and crash-resistant vehicle components.
Welding Process and Equipment
Efficient and successful tubular cored wire welding requires careful attention to the welding process itself and the selection of appropriate equipment. Here, we delve into the key aspects of the welding process and the equipment involved.
Setup and Preparation
Before initiating tubular cored wire welding, a thorough setup and preparation process is essential. This includes:
- Material Preparation: Ensuring that the base metals are clean and free from contaminants is crucial for achieving high-quality welds. Proper cleaning, beveling, and fit-up of the joint contribute to the overall success of the welding process.
- Electrode Selection: Choosing the appropriate tubular cored wire based on the specific welding application is critical. Factors such as material type, joint configuration, and desired weld properties influence the selection of the tubular cored wire.
- Joint Design: Determining the appropriate joint design for the welding application is essential. Factors such as joint type (butt joint, fillet joint, etc.) and the thickness of the materials being joined impact the welding process and parameters.
- Shielding Gas Selection (if applicable): In gas-shielded flux-cored arc welding, selecting the right shielding gas is important. The choice of gas depends on factors such as material type, desired weld characteristics, and environmental conditions.
Welding Parameters and Techniques
Achieving optimal weld quality and efficiency relies on precise control of welding parameters and employing appropriate techniques:
- Voltage and Amperage Settings: Adjusting voltage and amperage based on the specific requirements of the tubular cored wire and the welding application is crucial. This ensures proper arc stability, penetration, and deposition rates.
- Travel Speed: Controlling the travel speed of the welding torch is essential for maintaining the desired bead profile and avoiding issues such as insufficient penetration or excessive heat input.
- Welding Techniques: Employing appropriate welding techniques, such as weaving or stringer beads, depends on the joint configuration and the desired outcome. Skilled operators use techniques that optimize the deposition of filler material and ensure uniform penetration.
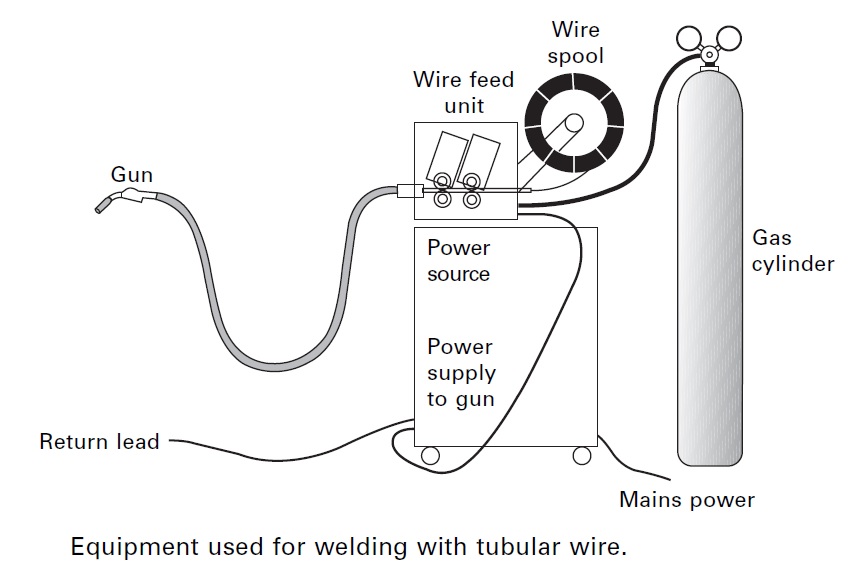
Welding Machines Suitable for Tubular Cored Wire
The welding machine plays a pivotal role in tubular cored wire welding. Considerations for selecting suitable welding machines include:
- Power Source: Choosing the right power source—whether it’s a conventional welding machine or an advanced inverter—depends on the specific requirements of the welding application.
- Wire Feeder: An efficient wire feeder is crucial for delivering the tubular cored wire to the welding arc consistently. Features such as adjustable feed speed contribute to precise control over the welding process.
- Polarity Settings: Tubular cored wire welding may require different polarity settings depending on the type of wire being used. Understanding and adjusting the polarity settings on the welding machine is essential for optimal performance.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount in any welding operation. Specific safety considerations for tubular cored wire welding include:
- Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential, especially in indoor welding environments, to control and disperse welding fumes generated during the process.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Welders should use appropriate PPE, including welding helmets, gloves, flame-resistant clothing, and respiratory protection if required.
- Welding Fume Extraction: Employing effective welding fume extraction systems, particularly in enclosed spaces, helps minimize exposure to harmful fumes.
- Training: Ensuring that operators are well-trained in the specific techniques and safety protocols associated with tubular cored wire welding is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring overall workplace safety.
Challenges and Solutions
While tubular cored wire welding offers numerous advantages, certain challenges may arise during its implementation. Addressing these challenges requires a combination of proper handling, advanced control measures, and a commitment to environmental and safety considerations. In this section, we explore common challenges associated with tubular cored wire welding and propose effective solutions.
Handling and Storage of Tubular Cored Wires
Challenge: Improper handling and storage of tubular cored wires can lead to issues such as moisture absorption, degradation of flux properties, and overall diminished welding performance.
Solution:
- Dry Storage: Store tubular cored wires in a dry environment to prevent moisture absorption. Moisture can negatively impact the flux composition, leading to porosity and other welding defects.
- Proper Handling Procedures: Handle tubular cored wires with care to avoid damage to the delicate flux or metal powder core. Employ equipment like wire liners and contact tips suitable for the specific type of tubular wire being used.
- Adherence to Manufacturer Recommendations: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding storage conditions, shelf life, and handling procedures to maximize the lifespan and effectiveness of tubular cored wires.
Control of Welding Parameters
Challenge: Inconsistent control of welding parameters may result in variations in weld quality, including issues with penetration, fusion, and overall integrity.
Solution:
- Advanced Welding Machines: Invest in modern welding machines equipped with advanced controls for voltage, amperage, and wire feed speed. This allows for precise adjustment of welding parameters to meet the requirements of different tubular cored wires and welding applications.
- Regular Calibration: Regularly calibrate welding equipment to ensure accurate parameter settings. This helps maintain consistency in weld quality and reduces the likelihood of defects.
- Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training to welding operators on the importance of maintaining optimal welding parameters. Skilled operators contribute significantly to achieving consistent and high-quality welds.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
Challenge: Tubular cored wire welding can generate welding fumes and pose environmental and safety concerns if not properly managed.
Solution:
- Effective Ventilation Systems: Implement efficient ventilation systems to control and remove welding fumes from the work environment. This is crucial for maintaining air quality and ensuring the health and safety of welding personnel.
- Welding Fume Extractors: Use welding fume extraction systems to capture and filter out harmful particulates. This is especially important in indoor welding spaces where fumes can accumulate.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Mandate the use of appropriate PPE, including respiratory protection, to minimize direct exposure to welding fumes.
Operator Training and Skill Development
Challenge: Inadequate operator training and skill development can lead to suboptimal welding performance and increased likelihood of defects.
Solution:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Implement comprehensive training programs for welding operators, covering both theoretical knowledge and practical skills related to tubular cored wire welding.
- Hands-on Workshops: Provide hands-on workshops and practical exercises to allow operators to apply their knowledge in real-world welding scenarios.
- Continuous Learning: Encourage ongoing learning and skill development to keep operators abreast of advancements in tubular cored wire welding technology and techniques.
Comparative Analysis with Other Welding Methods
Tubular cored wire welding competes with several established welding methods in the industry. Each method has its unique characteristics and applications. In this section, we conduct a comparative analysis of tubular cored wire welding with solid wire welding, stick welding, and gas metal arc welding (GMAW), outlining the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Solid Wire Welding
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Solid wire welding, particularly in processes like gas metal arc welding (GMAW), is known for its simplicity and ease of use.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Solid wires are often more economical than tubular cored wires, making them a cost-effective choice for certain applications.
- Cleaner Welds: Solid wire welding tends to produce cleaner welds with fewer spatters, especially when used with proper shielding gases.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Deposition Rates: Solid wire welding generally has lower deposition rates compared to tubular cored wire welding, impacting overall productivity.
- Limited Penetration: Achieving deep penetration in thick materials can be challenging with solid wire welding.
- Less Suitable for Outdoor Applications: In outdoor welding environments, solid wire welding may face challenges related to wind interference and shielding gas dispersion.
Stick Welding
Advantages:
- Portability: Stick welding, or shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), is highly portable and suitable for field applications.
- Versatility: Stick welding can be used on a variety of materials and in various positions.
- No External Shielding Gas Required: Stick welding doesn’t require an external shielding gas, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Deposition Rates: Stick welding typically has lower deposition rates compared to tubular cored wire welding.
- Limited Precision: Achieving precision in welds can be more challenging with stick welding.
- Slag Removal: The process generates slag that needs to be removed, adding to post-weld cleanup time.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Advantages:
- High Deposition Rates: GMAW, or metal inert gas (MIG) welding, can achieve high deposition rates, contributing to increased productivity.
- Versatility: GMAW is versatile and can be used on a variety of materials.
- Reduced Post-Weld Cleanup: GMAW often results in cleaner welds with minimal spatter, reducing post-weld cleanup efforts.
Disadvantages:
- External Shielding Gas Required: GMAW relies on an external shielding gas, making it less suitable for outdoor applications where wind can disperse the gas.
- Equipment Sensitivity: GMAW equipment can be sensitive to changes in wire feed speed, voltage, and gas flow, requiring careful setup and adjustment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tubular Cored Wire Welding
Advantages:
- High Deposition Rates: Tubular cored wire welding offers high deposition rates, leading to increased welding efficiency and productivity.
- Improved Penetration: The method provides improved penetration, making it suitable for welding thicker materials.
- Versatility: Tubular cored wire welding is versatile and applicable to a wide range of materials and welding scenarios.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Tubular cored wires can be more expensive than solid wires, impacting the overall cost of welding operations.
- Complexity: The process may require more advanced equipment and operator training compared to simpler methods like solid wire welding.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of tubular cored wire welding continues to evolve with advancements in technology, research, and industry demands. Several trends and innovations are shaping the future of this welding method.
Research and Development in Tubular Cored Wire Technology
Material Innovations: Ongoing research focuses on developing new and improved materials for the core of tubular cored wires. This includes enhanced flux formulations and metal powders to further optimize weld quality and performance.
Advanced Alloys: The exploration of advanced alloys within tubular cored wires is a key area of research. This could lead to the development of specialized wires tailored for specific applications, offering superior strength, corrosion resistance, and other desirable properties.
Microstructural Control: Researchers are delving into methods to refine the microstructure of welds produced by tubular cored wire welding. This includes optimizing grain structure and minimizing defects to enhance the mechanical properties of welded joints.
Integration of Robotics and Automation
Automated Welding Systems: The integration of robotics and automation in tubular cored wire welding is expected to increase. Automated welding systems can enhance precision, consistency, and efficiency, especially in high-volume manufacturing settings.
AI and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies are likely to be incorporated into welding automation. These technologies can optimize welding parameters in real-time, adapting to variations in materials and joint configurations.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): The use of collaborative robots, or cobots, in tubular cored wire welding may become more prevalent. Cobots work alongside human operators, providing assistance and improving overall productivity while maintaining safety.
Sustainable Practices in Tubular Cored Wire Manufacturing
Environmentally Friendly Flux Formulations: Research is underway to develop flux formulations with reduced environmental impact. This includes exploring eco-friendly alternatives and minimizing the use of substances that contribute to air pollutants during welding.
Recyclability: Manufacturers are exploring ways to enhance the recyclability of tubular cored wires. This involves designing wires with materials that are easier to recycle, reducing the overall environmental footprint of the welding process.
Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes: Sustainable practices extend to the manufacturing of tubular cored wires. Efforts are being made to implement energy-efficient processes and reduce the carbon footprint associated with the production of welding consumables.
Potential New Applications
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Tubular cored wire welding may find new applications in additive manufacturing processes, including 3D printing of metal components. This could open up possibilities for fabricating complex structures with improved material properties.
High-Temperature Applications: Advances in tubular cored wire technology may enable its use in high-temperature applications, such as aerospace and nuclear industries, where the ability to withstand extreme conditions is crucial.
Micro-Welding: As tubular cored wire welding technology progresses, it may be adapted for micro-welding applications, allowing for precise and intricate welds in fields like electronics and medical device manufacturing.
Case Studies
The following case studies highlight successful implementations of tubular cored wire welding in various industries, drawing lessons learned and emphasizing best practices. Additionally, real-world performance and cost comparisons provide valuable insights into the efficacy of this welding method.
Successful Implementations in Various Industries
Pipeline Construction:
- Industry: Oil and Gas
- Application: Tubular cored wire welding has been successfully implemented in the construction of pipelines. The high deposition rates and deep penetration capabilities have accelerated the welding process, contributing to the timely completion of pipeline projects.
Shipbuilding:
- Industry: Maritime
- Application: Tubular cored wire welding is widely utilized in shipbuilding, where the versatility of the process allows for efficient welding of various materials and joint configurations. The improved penetration and reduced post-weld cleanup contribute to the fabrication of durable and high-quality ship structures.
Automotive Component Manufacturing:
- Industry: Automotive
- Application: In the automotive industry, tubular cored wire welding has been employed in the manufacturing of critical components. The high deposition rates and improved penetration facilitate the production of strong and lightweight structures, contributing to the overall performance and safety of vehicles.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Operator Training:
- Lesson Learned: Comprehensive operator training is essential for successful tubular cored wire welding. Skilled operators contribute to better control of welding parameters and ensure the proper handling of tubular wires.
- Best Practice: Implement ongoing training programs that cover both theoretical knowledge and hands-on practice. This ensures that operators stay proficient in the latest techniques and equipment.
Material Selection:
- Lesson Learned: The choice of tubular cored wire significantly impacts the success of welding operations. Selecting the appropriate wire based on material compatibility and application requirements is crucial.
- Best Practice: Establish clear guidelines for material selection, considering factors such as joint configuration, material thickness, and desired weld properties. Regularly review and update material specifications based on advancements in tubular cored wire technology.
Quality Control and Inspection:
- Lesson Learned: Rigorous quality control measures and inspection protocols are necessary to ensure weld quality and integrity.
- Best Practice: Implement non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection, to assess the quality of tubular cored wire welds. Regularly review and enhance quality control procedures based on lessons learned from previous projects.
Real-world Performance and Cost Comparisons
Performance Metrics:
- Comparison Focus: Tubular cored wire welding vs. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
- Findings: In a structural welding application, tubular cored wire welding demonstrated higher deposition rates and improved penetration compared to GMAW. This resulted in faster welding speeds and increased productivity.
Cost Analysis:
- Comparison Focus: Tubular cored wire welding vs. Solid Wire Welding
- Findings: While tubular cored wires may have a higher upfront cost than solid wires, the increased deposition rates and efficiency often lead to lower overall welding costs. This is particularly evident in high-volume production scenarios, where the benefits of speed and productivity outweigh the material cost difference.
Environmental Impact:
- Comparison Focus: Tubular cored wire welding vs. Stick Welding
- Findings: Tubular cored wire welding, especially in gas-shielded variants, tends to produce fewer welding fumes compared to stick welding. This environmental advantage contributes to a safer and healthier workplace.
FAQs
Is tubular cored wire welding suitable for all materials?
Tubular cored wires are versatile and can be used for various materials, but it’s essential to choose the right type based on the specific material and application.
How does tubular cored wire welding contribute to cost savings?
The increased deposition rates and efficiency of tubular cored wire welding result in less material consumption and reduced labor costs.
Are there any safety considerations unique to tubular cored wire welding?
While the general safety measures apply, users should be cautious about the flux components and follow recommended handling procedures.
Can tubular cored wire welding be automated?
Yes, tubular cored wire welding is compatible with automated systems, providing efficiency and precision in large-scale projects.
What industries benefit the most from tubular cored wire welding?
Industries such as automotive, construction, and shipbuilding find significant advantages in terms of efficiency and weld quality with tubular cored wire welding.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tubular cored wire welding stands as a dynamic and promising welding method, poised to play a pivotal role in the future of the welding industry. By embracing innovation, promoting education, and fostering collaboration, the welding community can further unlock the full potential of tubular cored wire welding and contribute to a more efficient, sustainable, and versatile welding landscape.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders