What is Cold Welding
Introduction
Definition of cold welding:
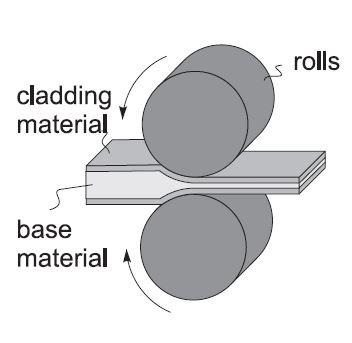
Cold welding is a solid-state welding process in which two metals are joined together at room temperature under high pressure, without the need for heat or external energy.
Brief history and discovery of cold welding
Cold welding was first discovered in the 1940s by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), who found that certain metals could bond together when placed in intimate contact under high pressure. It was initially thought to be a phenomenon that occurred only in a vacuum, but later research showed that it could occur in air as well.
The Science of Cold Welding
Explanation of the process of cold welding
Cold welding occurs when two clean, flat metal surfaces are brought into contact under high pressure. The pressure causes the atoms at the interface of the metals to diffuse and intermix, creating a metallurgical bond. This bond is typically stronger than the original materials themselves.
Factors that contribute to cold welding
The success of cold welding depends on several factors, including the surface roughness, cleanliness, and ductility of the metals being joined. Surfaces that are too smooth or too rough can make it difficult for the metals to bond properly. Similarly, any contaminants on the surfaces, such as oil or dirt, can interfere with the bonding process.
Comparison to traditional welding methods
Cold welding differs from traditional welding methods, which rely on the application of heat to melt the materials being joined. This can create issues such as distortion, warping, and residual stresses in the final product. In contrast, cold welding can create a joint without these problems, making it an attractive option in certain applications.
Advantages of cold welding
- No heat affected zone: Since cold welding doesn’t require any heat, there is no heat affected zone (HAZ) around the joint. This means that the properties of the metals being joined are not affected by the welding process.
- No filler material required: Cold welding doesn’t require any filler material, so there is no need to worry about the quality of the filler material or its compatibility with the metals being joined.
- High-quality joints: Cold welding can produce joints that are as strong as the original metals. The joint is created by bonding the metals at the atomic level, resulting in a seamless and uniform bond.
- Cost-effective: Since cold welding doesn’t require any heat or filler material, it can be a cost-effective alternative to other welding methods.
Disadvantages of cold welding
- Limited to certain metals: Cold welding is most effective with metals that have similar crystal structures and surface finishes. It may not work well with dissimilar metals or metals with different surface finishes.
- Requires high pressure: Cold welding requires high pressure to be applied to the metals being joined, which can make the process difficult and time-consuming.
- Requires precise preparation: The metals being joined must be prepared precisely, with clean and smooth surfaces, in order to achieve a successful cold weld. Any imperfections or contaminants on the surfaces can interfere with the bonding process.
- Limited joint size: Cold welding is typically limited to joining small to medium-sized components, and may not be suitable for larger or more complex components.
Applications of Cold Welding
Industries that use cold welding
Cold welding is used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, microelectronics, and medical devices. It is often used to join small or delicate components that would be damaged by traditional welding methods.
Advantages of cold welding over traditional welding methods
The advantages of cold welding include its ability to join dissimilar metals, its lack of heat-affected zone (HAZ), and its ability to create strong and durable joints without introducing residual stresses.
Specific examples of cold welding applications
Some specific examples of cold welding applications include wire bonding in microelectronics, the sealing of spacecraft components, and the joining of small medical implants.
Safety Consideration in Cold Welding
While cold welding is generally considered to be a safe welding process, it is still important to take proper safety precautions to avoid any potential hazards. Here are some safety measures that should be taken during cold welding:
- Wear protective equipment: As with any welding process, it is important to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, eye protection, and respiratory protection.
- Follow manufacturer instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the cold welding equipment, including proper setup and operation procedures.
- Avoid touching the equipment: Avoid touching the welding equipment during operation, as the high pressure used in cold welding can be dangerous if not handled properly.
- Use proper ventilation: Ensure that the area in which you are performing the cold welding process is well-ventilated to avoid any buildup of fumes or gases.
- Keep the work area clean: Keep the work area clean and free of clutter to avoid any tripping hazards or interference with the welding process.
- Train and supervise personnel: It is important to properly train and supervise any personnel who will be performing cold welding to ensure that they understand the proper safety procedures and can perform the process safely
Challenges and Limitations of Cold Welding
Difficulties in achieving consistent and reliable cold welds
One of the biggest challenges in cold welding is achieving consistent and reliable results. The process is highly dependent on the cleanliness and flatness of the surfaces being joined, as well as the pressure and duration of the bonding process.
Limitations on the types of materials that can be cold welded
Cold welding is generally limited to metals that are ductile and have a high degree of contact compatibility. Brittle materials or those with low ductility, such as ceramics, are difficult to bond using this method.
Potential for contamination during the welding process
Any contamination of the surfaces being joined can interfere with the bonding process, making it important to carefully clean and prepare the surfaces beforehand.
Future Developments and Research
Current research on improving cold welding techniques and applications
Research is ongoing in the field of cold welding, with a focus on improving the consistency and reliability of the process. There is also interest in expanding the range of materials that can be cold welded and developing new applications for the process.
Potential for cold welding to be used in new industries and applications
As the technology and techniques for cold welding continue to improve, there is potential for it to be used in new industries and applications where traditional welding methods are not feasible.
FAQs
What is cold welding process?
Cold welding is a solid-state welding process that joins two clean, flat metal surfaces at room temperature under high pressure without the need for heat or external energy. The process relies on the inter-diffusion of atoms at the interface of the two metals to create a metallurgical bond.
Why is it called cold welding?
Cold welding is called so because it occurs at room temperature without the need for heat, unlike traditional welding methods that require high temperatures to melt and fuse the materials being joined.
What causes cold welding?
Cold welding occurs when two clean, flat metal surfaces are brought into contact under high pressure. The pressure causes the atoms at the interface of the metals to diffuse and intermix, creating a metallurgical bond. This bond is typically stronger than the original materials themselves.
What is the difference between TIG and cold welding?
TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), uses a tungsten electrode to produce an arc that melts the metal being joined, while cold welding does not require heat and works by applying pressure to the metals being joined. TIG welding can be used to join a wider range of metals than cold welding.
What material is used for cold welding?
Cold welding can be used to join a wide range of metals, including aluminum, copper, gold, silver, nickel, and titanium.
What is another name for cold welding?
Another name for cold welding is “pressure welding.”
What are the advantages of cold welding?
The advantages of cold welding include the ability to join dissimilar metals, lack of heat-affected zone (HAZ), and the creation of strong and durable joints without introducing residual stresses.
What is hot vs cold weld?
Hot weld is another term for traditional welding methods that use heat to melt and fuse the materials being joined, while cold weld refers to the process of joining two clean, flat metal surfaces at room temperature under high pressure.
What is the best cold weld?
The “best” cold weld depends on the specific application and the metals being joined. Different types of cold welding techniques may be more suitable for certain metals or industries.
Is cold welding stronger?
The bond created by cold welding can be stronger than the original materials being joined, making it a viable option for certain applications.
Is TIG welding AC or DC?
TIG welding can be performed using either AC or DC current, depending on the type of metal being joined.
Is cold welding stronger than welding?
Cold welding can create a strong and durable joint without introducing residual stresses, making it a viable option in certain applications. However, the strength of the joint depends on several factors, including the metals being joined, the surface preparation, and the pressure applied during the bonding process.
Which welding is strongest?
The strength of a weld depends on several factors, including the type of welding technique used, the metals being joined, and the skill of the welder. Some of the strongest welding techniques include TIG welding, MIG welding, and Stick welding.
Which type of welding is best?
The “best” type of welding depends on the specific application and the materials being joined. Different welding techniques may be more suitable for certain metals or industries.
Does cold welding need argon?
Cold welding does not require the use of any gas, including argon, as it does not involve the application of heat.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cold welding is a solid-state welding process that joins two metals together at room temperature under high pressure. It offers several advantages over traditional welding methods, including the ability to join dissimilar metals and create strong, durable joints without introducing residual stresses. However, the process is highly dependent on the cleanliness and flatness of the surfaces being joined, making it difficult to achieve consistent and reliable results. As research continues to improve the technology and techniques for cold welding, there is potential for it to be used in new industries and applications, making it an exciting area for future developments.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders