White Metal Welding
Introduction
White metal welding is a specialized welding technique used to join metals with white metal alloys. It is a process where two or more metal parts are fused together using heat, pressure, and the melting of a white metal alloy. The result is a strong, durable, and corrosion-resistant joint that can withstand high stress and extreme temperatures.
White metal welding is used extensively in various industries such as marine, construction, automotive, and aerospace industries, among others. It is particularly useful in situations where high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion are critical requirements. This is because white metal alloys are known to possess excellent properties like high melting point, good fluidity, low shrinkage, and good strength. The white metal alloys used in welding are usually composed of tin, lead, and antimony, with the proportions varying depending on the intended application. These alloys are often mixed with fluxes and covering powders to improve the flow, wetting, and shielding properties during the welding process. There are several techniques of white metal welding, including oxyacetylene welding, electric arc welding, gas shielded arc welding, and resistance welding. Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique largely depends on the type of metal being welded, the joint design, and the required strength and quality of the weld.
White metal welding requires careful preparation before the welding process begins. This includes surface preparation, cleaning, and degreasing to ensure that the metal surfaces are clean and free of contaminants that could weaken the weld. The joint design is also an important consideration, as it can affect the quality and strength of the final weld. White metal welding is an important and highly specialized technique that is widely used in various industries. Its many benefits, including strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, make it an ideal solution for many welding applications. In the following sections of this outline, we will explore the materials, techniques, advantages, and applications of white metal welding in greater detail.

Materials Used in White Metal Welding
White metal alloys, fluxes, and covering powders are all materials that are commonly used in white metal welding.
White metal alloys
White metal alloys are metal alloys that have a low melting point and are used as filler metals in white metal welding. These alloys typically consist of tin, lead, and antimony, but other metals such as copper, zinc, and silver may also be included. The composition of the alloy will depend on the specific application and the properties required of the resulting joint.
Fluxes
Fluxes are materials that are used to remove oxides from the surface of the metal and promote the flow of the filler metal. In white metal welding, fluxes are typically made of borax, ammonium chloride, or other chemicals. The flux is applied to the surface of the metal before the filler metal is added, and it helps to ensure a strong and clean joint.
Covering powders
Covering powders are materials that are used to protect the molten metal from oxidation during the welding process. These powders are typically made of a mixture of graphite, boron compounds, and other materials. The covering powder is applied to the surface of the molten metal, and it forms a protective layer that prevents oxidation and other contaminants from entering the weld.
Techniques of White Metal Welding
There are several types of welding techniques used in industry. Here are some details about four common welding techniques:
1- Oxyacetylene Welding
Oxyacetylene welding, also known as gas welding or oxy-fuel welding, is a welding technique that uses a flame produced by mixing oxygen and acetylene gases. The heat of the flame melts the metal surfaces to be joined, and a filler rod is added to the joint to create a strong bond. This technique is often used for welding thin materials such as sheet metal and pipes, and it is also used for cutting and brazing.
2- Electric Arc Welding
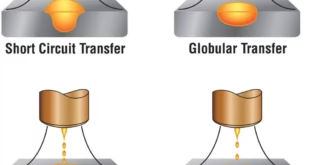
Electric arc welding is a welding technique that uses an electric arc to melt the metal surfaces to be joined. The arc is created by passing an electric current between an electrode and the metal surface. The heat of the arc melts the metal, and a filler rod is added to the joint to create a strong bond. There are several types of electric arc welding, including Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), and Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW).
3- Gas Shielded Arc Welding
Gas Shielded Arc Welding is a type of electric arc welding that uses a shielding gas to protect the weld from contamination. The shielding gas can be a variety of gases, including argon, carbon dioxide, or a mixture of gases. Gas Shielded Arc Welding is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
4- Resistance Welding
Resistance welding is a welding technique that uses an electric current to heat the metal surfaces to be joined. The metal surfaces are held together under pressure, and the heat generated by the electric current melts the metal, creating a strong bond. Resistance welding is commonly used in industries such as automotive, appliance, and electronics manufacturing.
Pre-Welding Preparations
Pre-welding preparation is a crucial step in the welding process. It ensures that the joint is clean, properly aligned, and free of contaminants that can compromise the quality of the weld. Here are some details about the three main aspects of pre-welding preparation: surface preparation, cleaning and degreasing, and joint design.
- Surface preparation: Surface preparation involves preparing the metal surfaces to be joined by removing any coatings, rust, or other contaminants that can interfere with the welding process. The metal surfaces should be clean, dry, and free of any debris or surface irregularities. This can be accomplished by using tools such as wire brushes, grinders, or sandblasting equipment.
- Cleaning and degreasing: Cleaning and degreasing is an essential part of surface preparation. The metal surfaces to be joined should be free of any oils, grease, or other contaminants that can affect the quality of the weld. Cleaning can be done using solvents, detergents, or other cleaning agents that are appropriate for the specific metal and the type of contaminants present.
- Joint design: Joint design is an important consideration in pre-welding preparation. The type of joint and the dimensions of the joint should be designed to provide adequate strength and to accommodate the type of welding process to be used. Joint design should also take into account factors such as the thickness and type of metal being joined, the expected stresses on the joint, and any specific requirements for the application.
White Metal Welding Process
White metal welding is a specialized welding process that is used to join metals that have a low melting point, such as lead, tin, or zinc. Here are some details about the white metal welding process, including equipment setup, preheating, welding process, and post-welding treatment:
Set up of equipment
The equipment needed for white metal welding includes a welding torch, a gas supply, a filler rod, and a flux. The torch is used to produce a flame, and the gas supply provides the fuel for the flame. The filler rod is used to add material to the joint, and the flux is used to protect the weld from oxidation.
Preheating
Preheating is an important part of the white metal welding process. The metal to be welded should be heated to a specific temperature to ensure proper fusion and to prevent cracking. The preheating temperature will vary depending on the specific metal being welded and the thickness of the material.
Welding process
Once the metal has been preheated, the welding process can begin. The welding torch is used to produce a flame that melts the metal surfaces to be joined. The filler rod is then added to the joint to create a strong bond. The flux is used to protect the weld from oxidation and to promote proper fusion.
Post-welding treatment
After the welding process is complete, the weld should be allowed to cool slowly to prevent cracking. Once the weld has cooled, it should be cleaned and inspected for any defects. If necessary, the weld can be machined or polished to achieve the desired finish.
Advantages of White Metal Welding
Here are some advantages of white metal welding:
- White metal welding is known for its high strength and durability. The resulting welds have the ability to withstand significant amounts of stress and pressure, making them ideal for use in applications where reliability is critical.
- White metal welding produces welds with excellent quality and precision. The process ensures that the weld is free of defects such as porosity, inclusions, and cracks, which can weaken the weld and cause it to fail.
- White metal welding can produce welds that are highly resistant to high temperatures. This makes them ideal for use in high-temperature environments such as furnaces, boilers, and power plants.
- White metal welding can be used to weld a wide range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals. This makes it a versatile welding process that can be used in a variety of industries and applications.
- White metal welding produces minimal distortion in the workpiece, which means that the finished product retains its shape and dimensions. This is particularly important in applications where accuracy and precision are critical.
- White metal welding requires minimal maintenance, making it a cost-effective option in the long run. The resulting welds are highly durable and resistant to wear and tear, which means that they require little maintenance over their lifespan.
- White metal welding is a relatively fast welding process, which means that it can be used to increase productivity and efficiency in manufacturing processes. This is particularly important in industries where production speed is critical to meeting demand.
Applications of White Metal Welding
White metal welding is a specialized welding technique used primarily in the repair and maintenance of machinery and equipment in the marine and power generation industries. The process involves melting a special alloy, called white metal, onto the surface of a damaged or worn part to restore its original shape and dimensions. Here are some common applications of white metal welding:
- Bearing and journal repairs: White metal welding can be used to repair damaged or worn bearings and journals in engines, pumps, turbines, and other machinery. The process involves building up the worn area with white metal and then machining it to the correct size and shape.
- Propeller repairs: Propellers on ships and boats can be damaged by impacts or wear over time. White metal welding can be used to rebuild damaged propeller blades and restore them to their original shape and dimensions.
- Valve and pump repairs: Valves and pumps in industrial settings can experience wear and corrosion over time. White metal welding can be used to repair worn or corroded valve and pump parts, extending the life of the equipment and avoiding costly replacements.
- Turbine repairs: Turbines in power generation plants can experience erosion and corrosion over time. White metal welding can be used to repair damaged turbine blades and other components, extending the life of the equipment and improving efficiency.
- Gearbox repairs: Gearboxes in machinery can experience wear and damage over time. White metal welding can be used to repair damaged gear teeth and other gearbox components, improving the performance and longevity of the equipment.
Safety Precautions
White metal welding involves working with high temperatures and molten metals, which can pose significant safety hazards if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some of the safety precautions that should be observed when performing white metal welding:
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Workers should wear appropriate PPE to protect themselves from the hazards associated with white metal welding. This may include heat-resistant gloves, face shields, safety glasses, aprons, and respirators.
- Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential to prevent the buildup of hazardous fumes and gases. The work area should be well-ventilated, and workers should wear respirators if necessary.
- Fire safety: White metal welding can generate sparks and heat, which can lead to fires if proper precautions are not taken. Fire extinguishers should be readily available, and workers should be trained in their use.
- Electrical safety: White metal welding equipment requires electricity to operate, so it is important to ensure that all electrical connections are properly grounded and that workers are trained in electrical safety.
- Machine guarding: Moving parts of the welding equipment should be properly guarded to prevent accidental contact with workers.
- Work area safety: The work area should be clean and free of clutter to prevent slips, trips, and falls. Workers should be trained in safe work practices, such as proper lifting techniques.
- Training and certification: Workers should be trained in the proper use of white metal welding equipment and techniques before performing any work. They should also be certified in white metal welding to ensure that they have the necessary knowledge and skills to perform the work safely.
FAQs
What is the best way to weld white metal?
White metal is a term that can refer to various low-melting-point alloys, such as pewter and babbitt metal. The best way to weld white metal depends on the specific alloy you’re working with. In general, white metals are often too soft and brittle for welding, so they are typically joined using techniques such as soldering or brazing.
What is a white welding rod used for?
A white welding rod is not a common type of welding rod, and the term may refer to various materials depending on the context. Without more information, it’s difficult to provide a specific answer.
Can white steel be welded?
White steel is a term that can refer to various types of high-carbon steel, such as Shirogami steel used in Japanese kitchen knives. Yes, white steel can be welded, but it requires careful attention to the welding technique and temperature control to avoid damaging the steel’s properties.
What are considered white metals?
White metals are a broad category of alloys that have low melting points and are often used in applications such as casting and bearings. Examples of white metals include pewter, babbitt metal, white brass, and some types of solder.
What temperature do you solder white metal?
The temperature required to solder white metal depends on the specific alloy you’re working with, as well as the type of solder and flux you’re using. In general, white metals have low melting points, so soldering can be done at relatively low temperatures, typically between 150°C to 300°C (300°F to 570°F).
How do you bond white metal?
White metal can be bonded using various techniques such as welding, soldering, brazing, and adhesive bonding. The specific method depends on the type of white metal and the application.
Can white steel rust?
White steel is a term that is not commonly used in the steel industry. However, if you are referring to stainless steel, then it generally has a higher resistance to rust and corrosion compared to other types of steel. However, stainless steel can still rust under certain conditions, such as exposure to saltwater or acidic environments.
What is white steel called?
White steel is not a common term in the steel industry. It’s possible that you may be referring to a specific type of steel, but without additional information, it’s difficult to provide an accurate answer.
Can white metal be glued?
Yes, white metal can be glued using various types of adhesives such as cyanoacrylate, epoxy, or polyurethane adhesives. The specific adhesive will depend on the type of white metal and the application.
What is white steel made of?
As mentioned earlier, white steel is not a common term in the steel industry. However, if you are referring to high-speed steel (HSS), which is sometimes called “white steel” due to its high carbon content and bright color, it is typically made of alloying elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, chromium, and vanadium.
Why do welders wear white?
Welders wear white to reflect heat and protect themselves from harmful UV rays and other hazards associated with welding. The white color also helps to make it easier to see the welding process and any defects in the weld.
What is the white stuff after welding?
The white stuff that can sometimes be seen after welding is called weld slag or spatter. It is a byproduct of the welding process and consists of melted metal and flux that solidifies on the surface of the weld. Weld slag should be removed after welding to ensure a clean and strong weld.
Conclusion
In conclusion, white metal welding can be an effective method for repairing or joining white metal parts. However, it is a specialized technique that requires specific knowledge, skill, and experience to perform correctly. The success of white metal welding depends on several factors, including the choice of filler metal, the preparation of the metal surfaces, and the application of heat. When performed correctly, white metal welding can produce a strong, reliable joint that can withstand the stresses and strains of use. However, it is important to note that white metal welding may not be suitable for all applications, and alternative methods may need to be considered for certain materials or situations. Overall, white metal welding is a valuable tool for those working with white metals, but it should only be performed by trained professionals with the necessary knowledge and expertise.
 Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders
Welding of Welders All about Welding and Welders